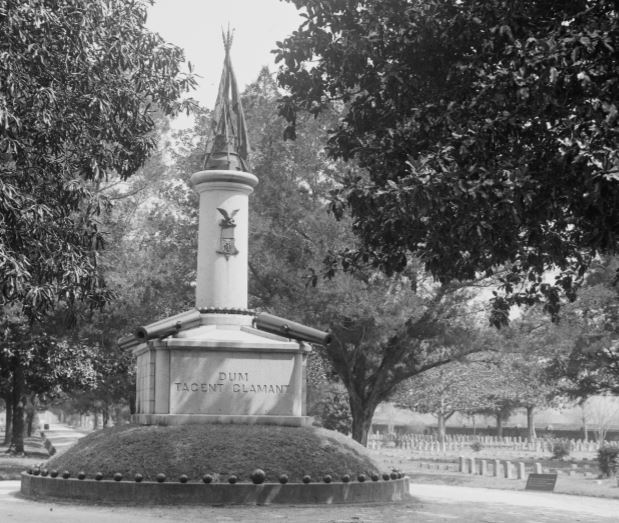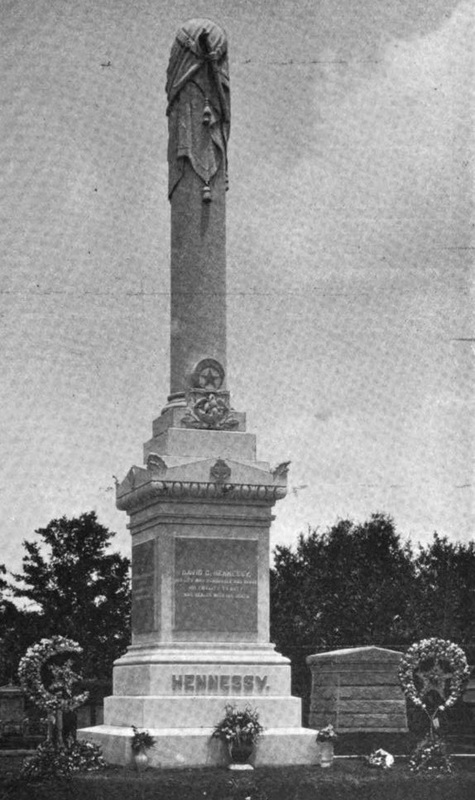|
How New Orleans weathered one of the greatest plagues in history. It’s nearly impossible to imagine a worldwide emergency like that which took place in 1918. Modern-day fiction and sci-fi writers have materialized similar fears – there is no shortage of post-pandemic fiction. For example, the HBO series The Leftovers posits a world in which two percent of the world’s population has vanished, the Max Brooks novel World War Z injects zombies into a frighteningly realistic image of how civilization would handle pandemic catastrophe. The list goes on. But we so often forget that something like this did happen. In 1918, a strain of pandemic influenza swept the globe three times, infecting millions and killing five percent of the world’s population. Medical science today cannot pin down exactly where it began. One prominent theory states that H1N1 influenza began with swine farms in Haskell County, Kansas in late January 1918.[1] Like other incidents of mutated influenza virus “jumping” from livestock to humans, it could have fizzled out in the local population. Yet nationwide mobilization in response to the United States’ entry into World War I meant that military camps were ubiquitous and population movement intensified. Influenza was transported to Camp Funston, Kansas, where it spread to other camps, other towns. The first wave of influenza traveled from the United States to Brest, France, in April 1918. Within the next month, it spread to Spain. Spain, neutral during World War I, was less likely to censor press reports of the disease. Hence, although the U.S., Britain, and France saw just as many cases of influenza, such incidents were not reported. The uneven press coverage created the appearance of the disease originating in Spain, giving it the incorrect moniker “Spanish Influenza.[2]” Influenza was documented in China and India by May 1918. The spring wave, however, was comparatively mild. The second wave of Fall 1918 would be devastating. As the summer of 1918 wore on and Allied victories in Europe continued, state and federal medical officials assumed disaster had been averted.
Attempts to quarantine the sick and curb the spread of influenza were often thwarted by the pressures of total war. In one especially salient instance, insistence from upper-crust social circles in Philadelphia caused medical leaders to allow a War Bonds parade to take place, despite the mounting evidence of an influenza epidemic. New cases of the illness soared in the days after this large public gathering. In metropolitan areas, the flu jumped from military to civilian populations, and then spread.
One hundred years ago this month, influenza arrived in New Orleans.
5 Comments
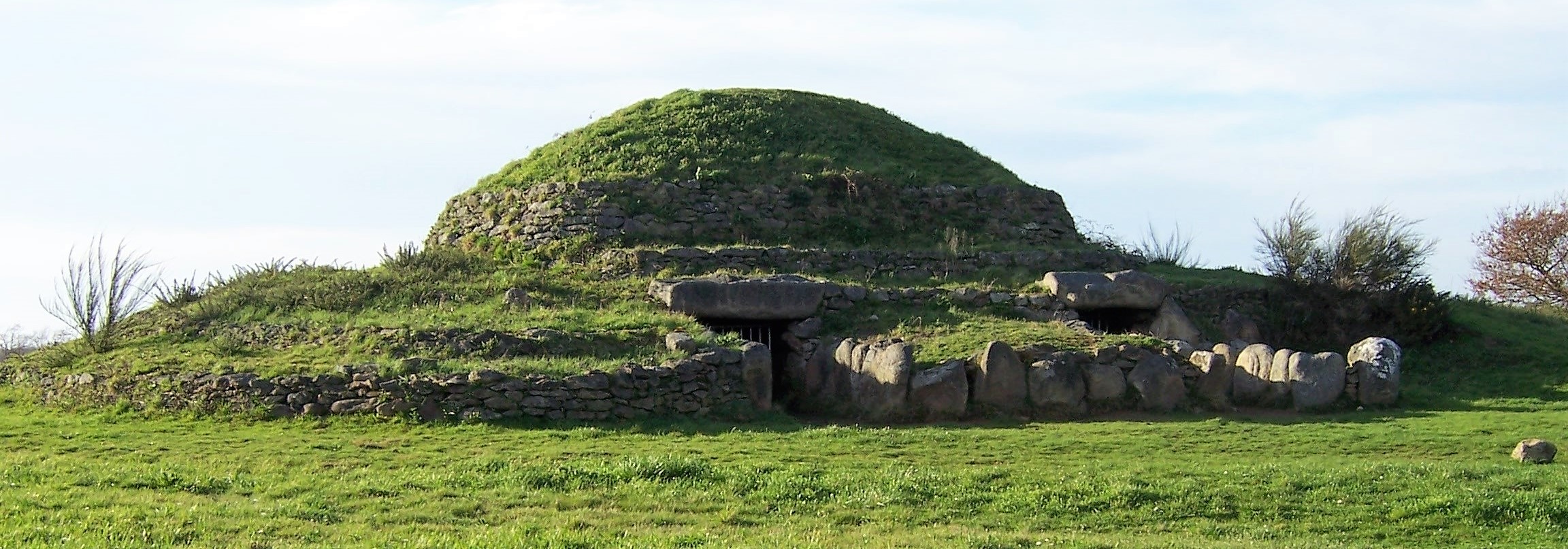
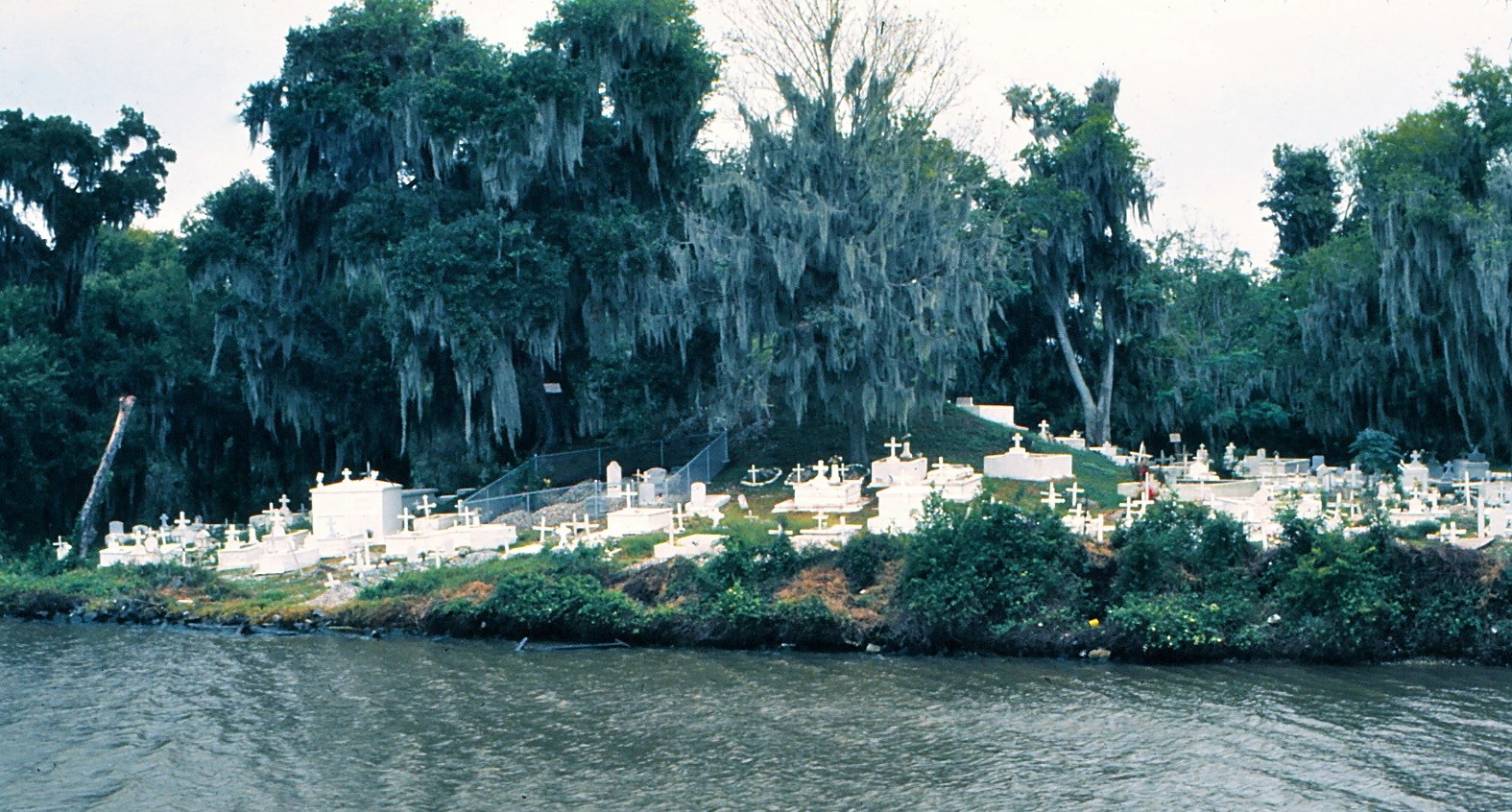
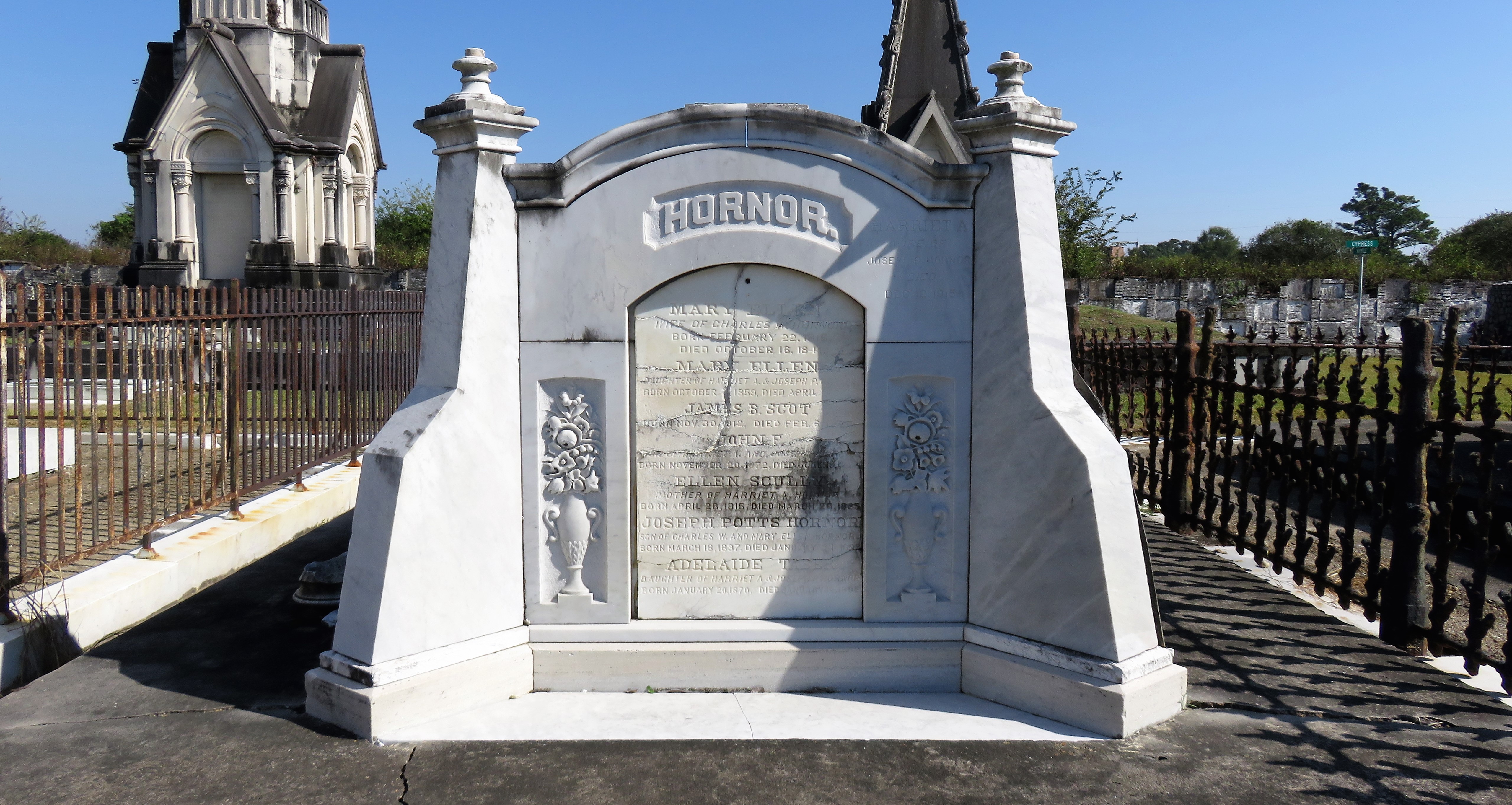
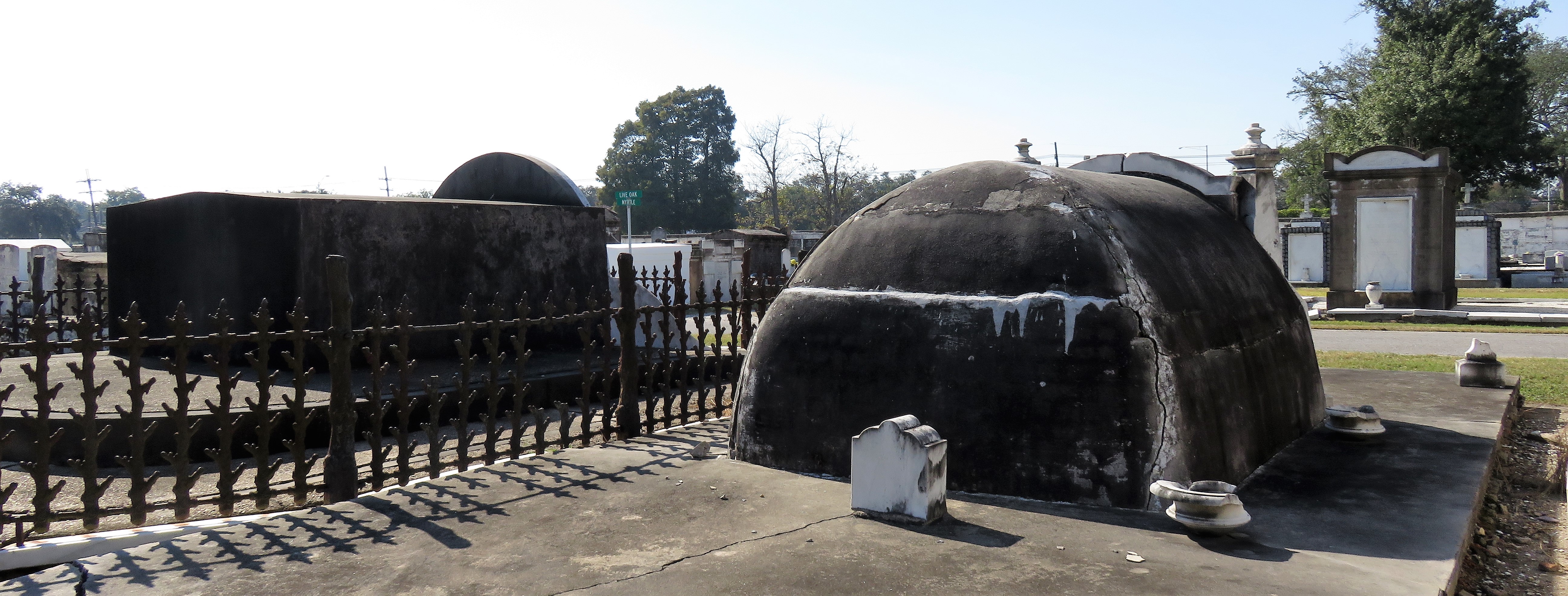
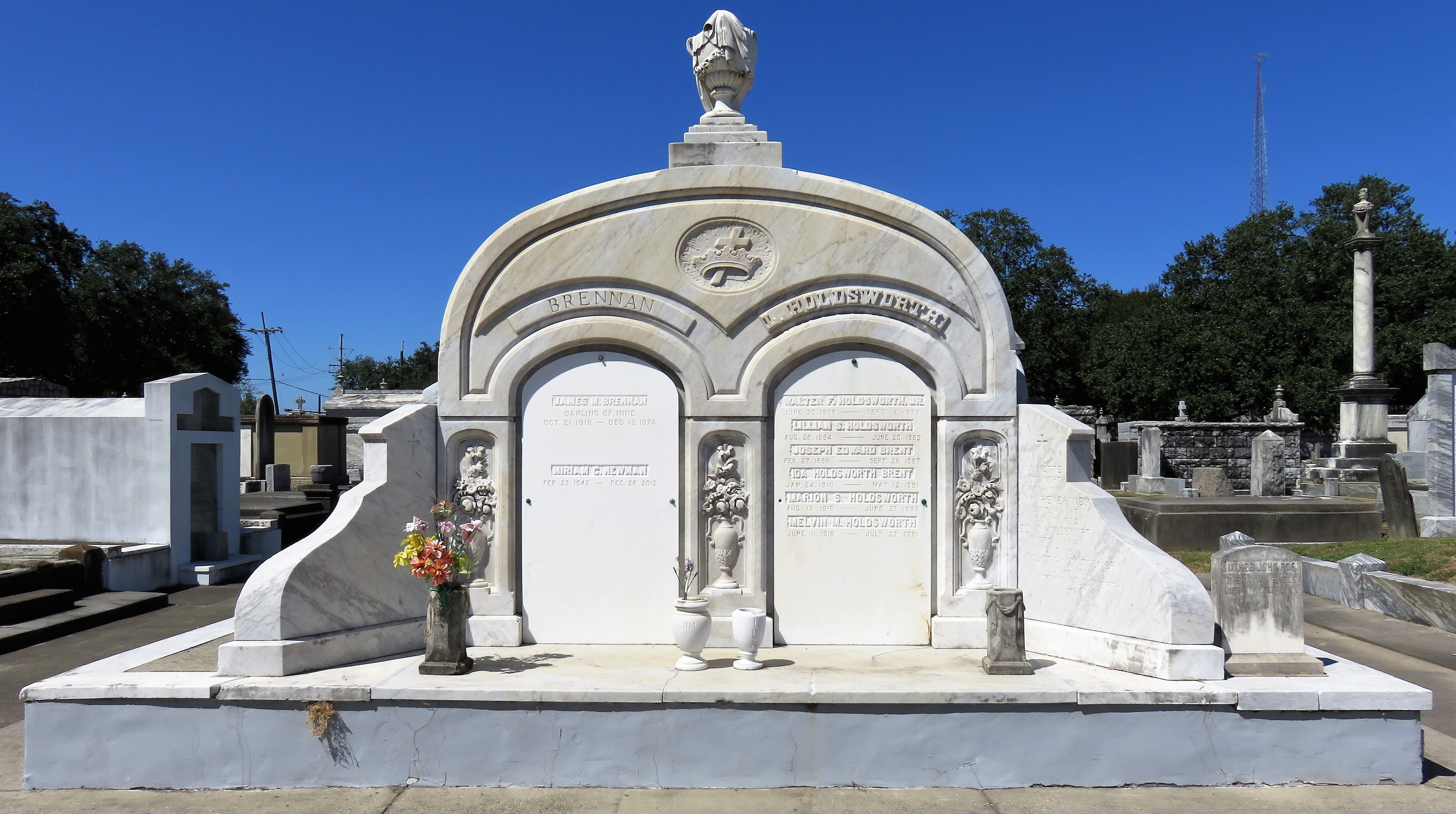
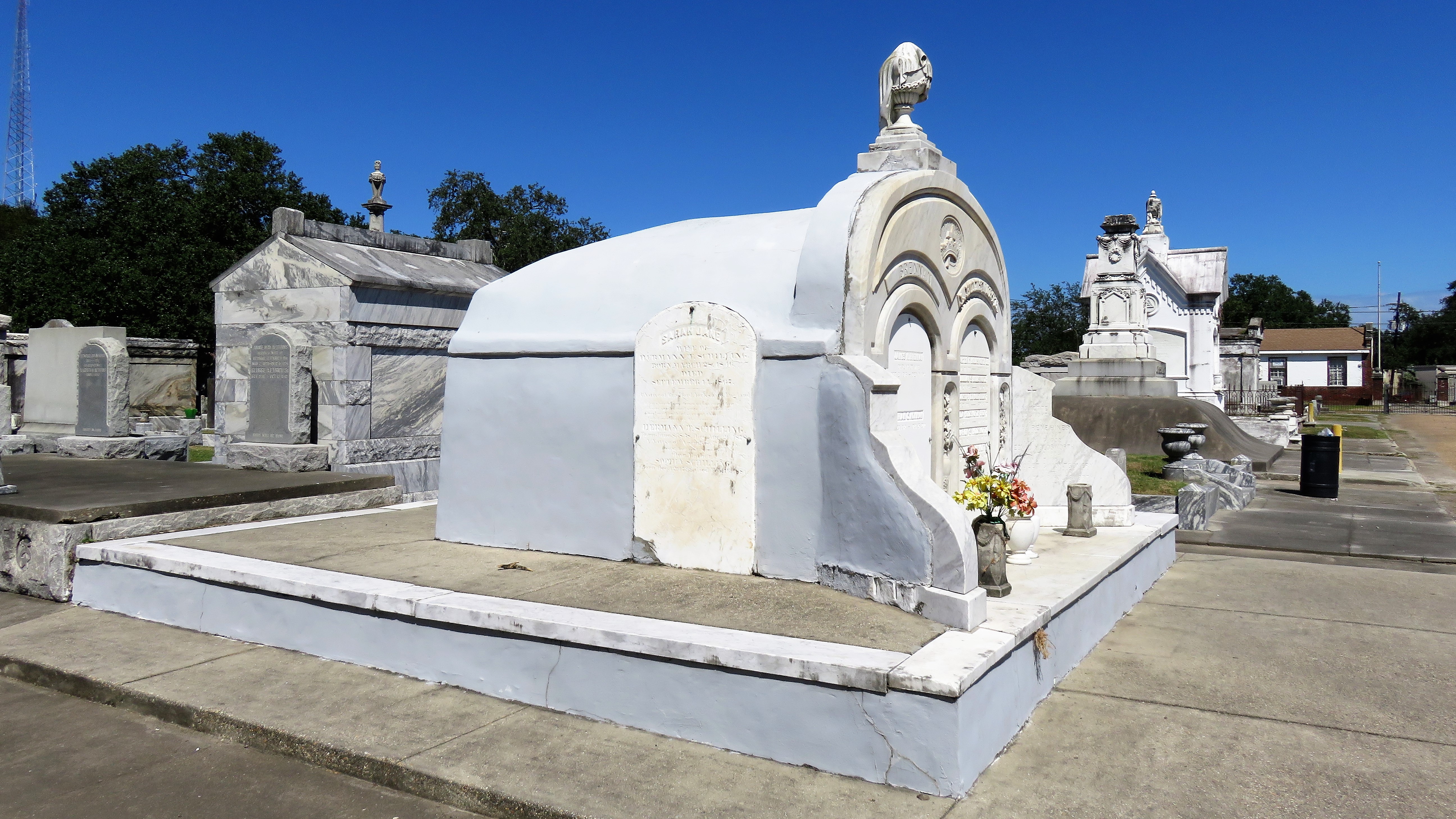
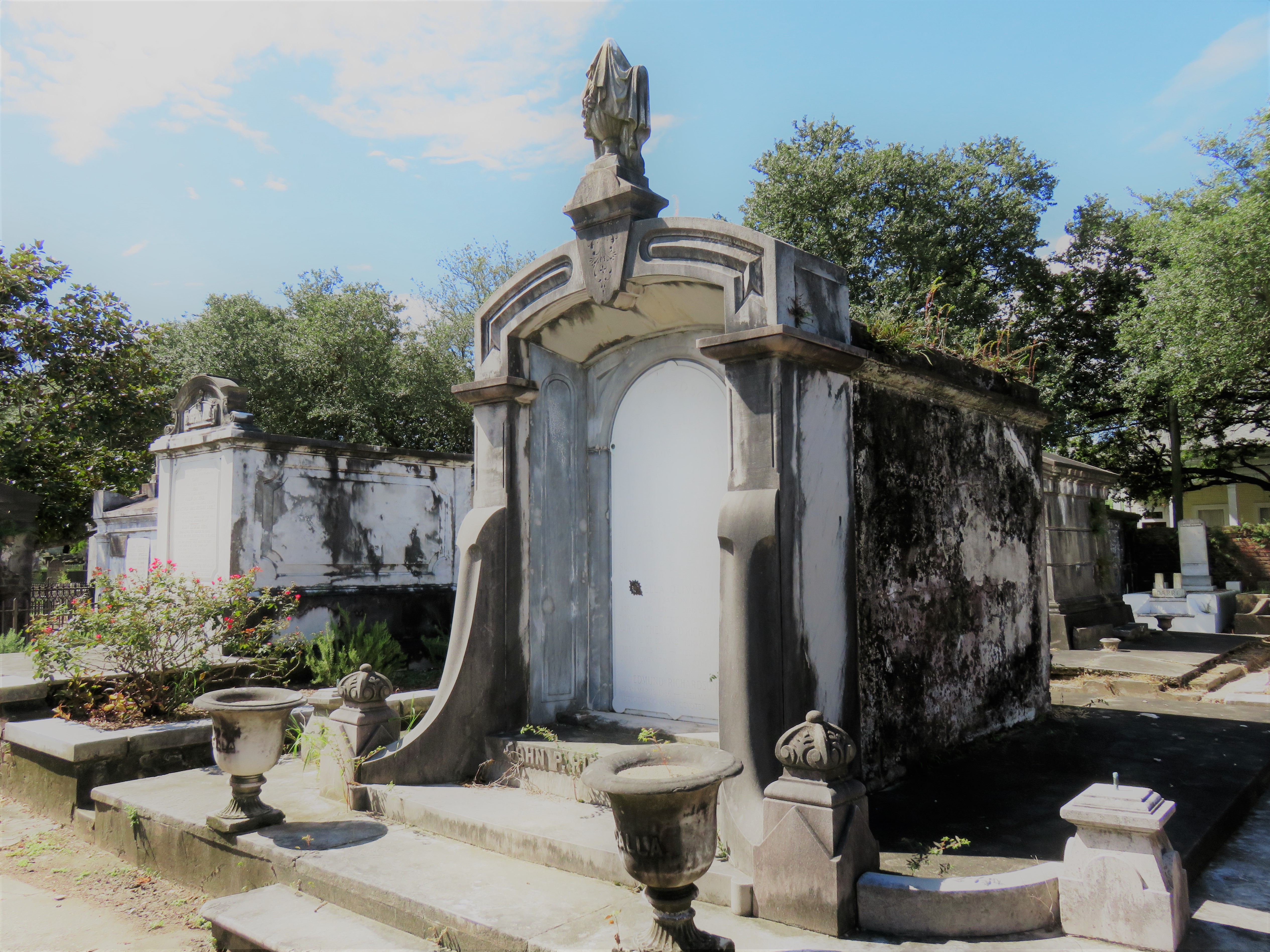
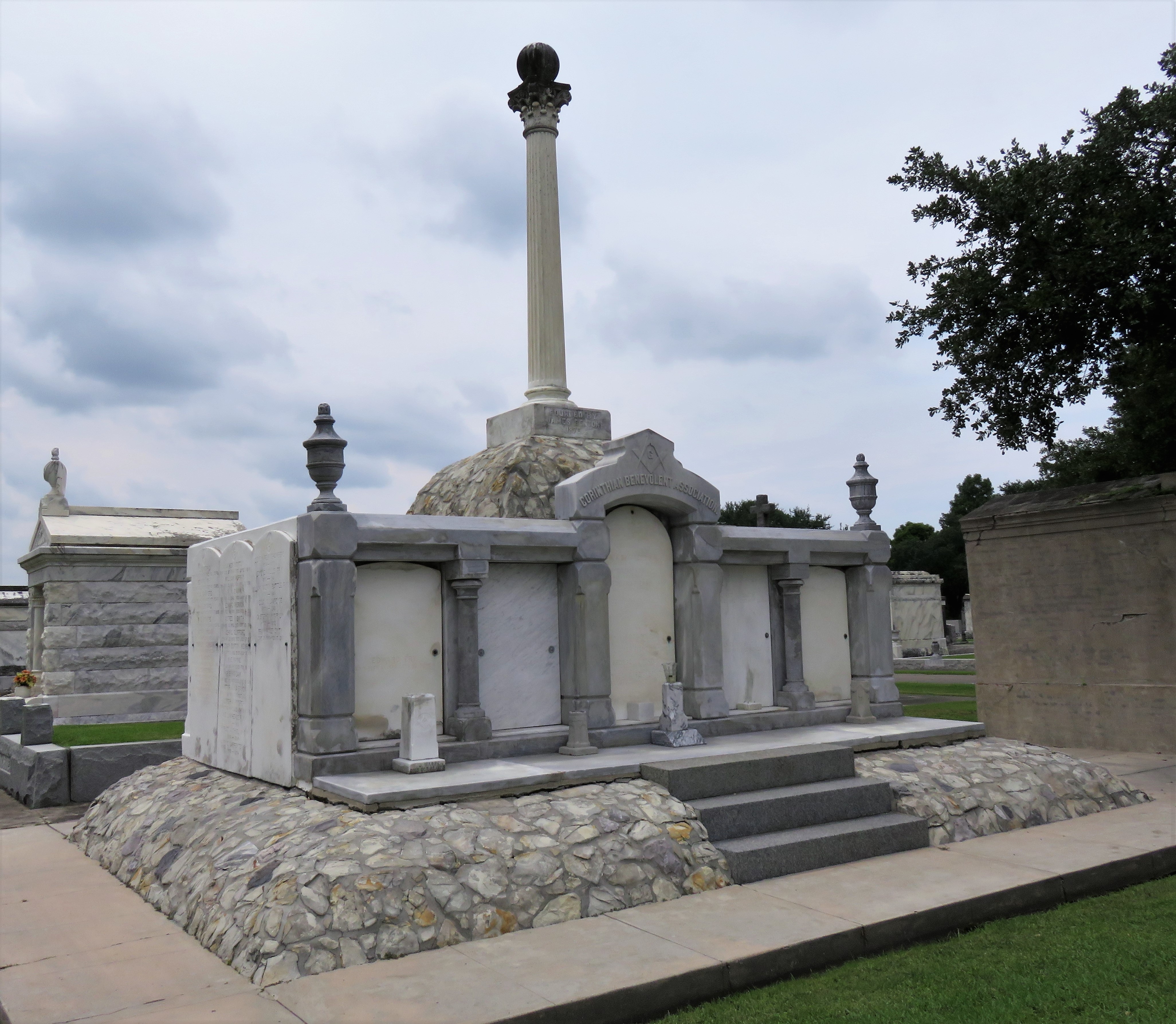
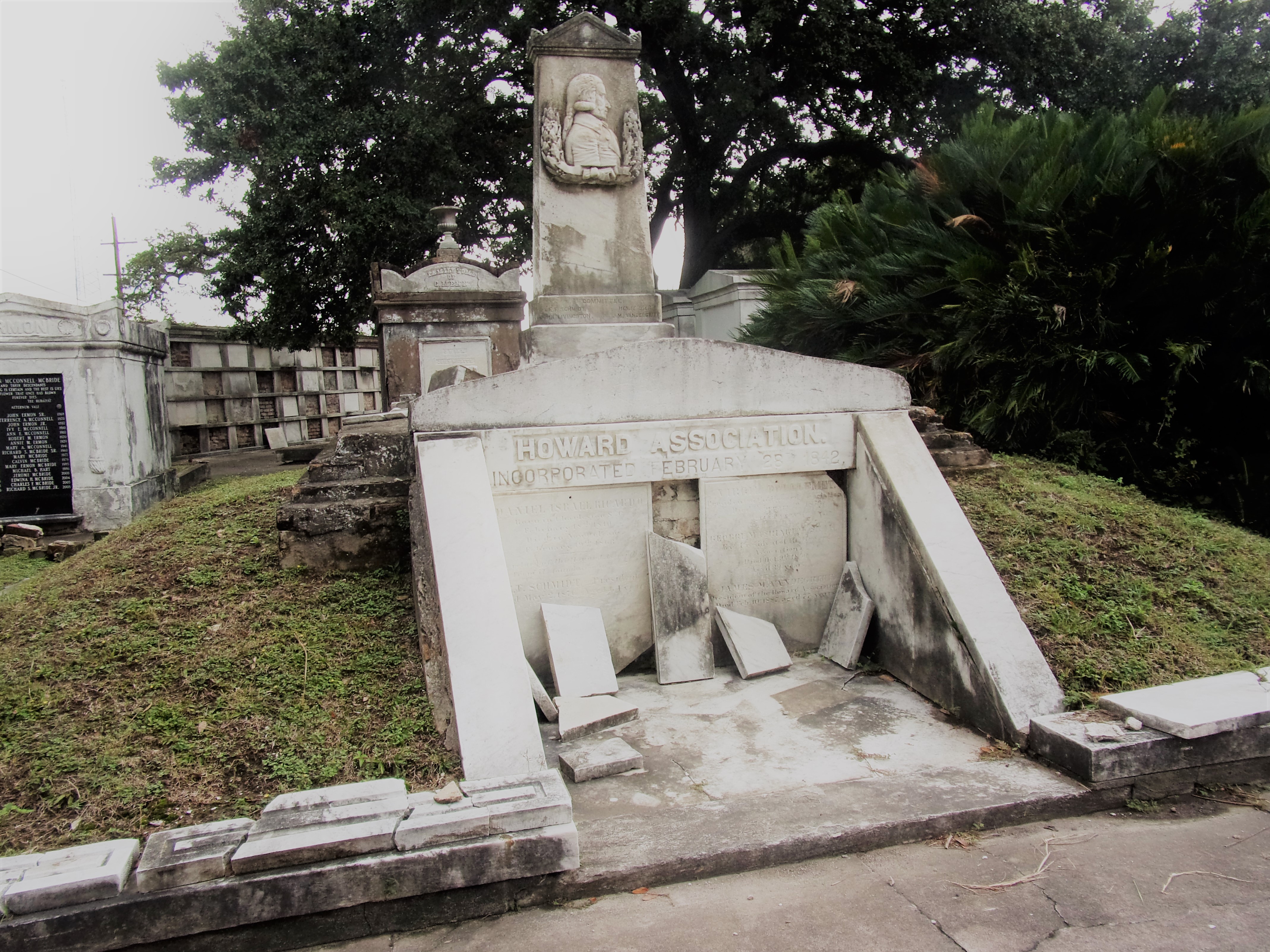
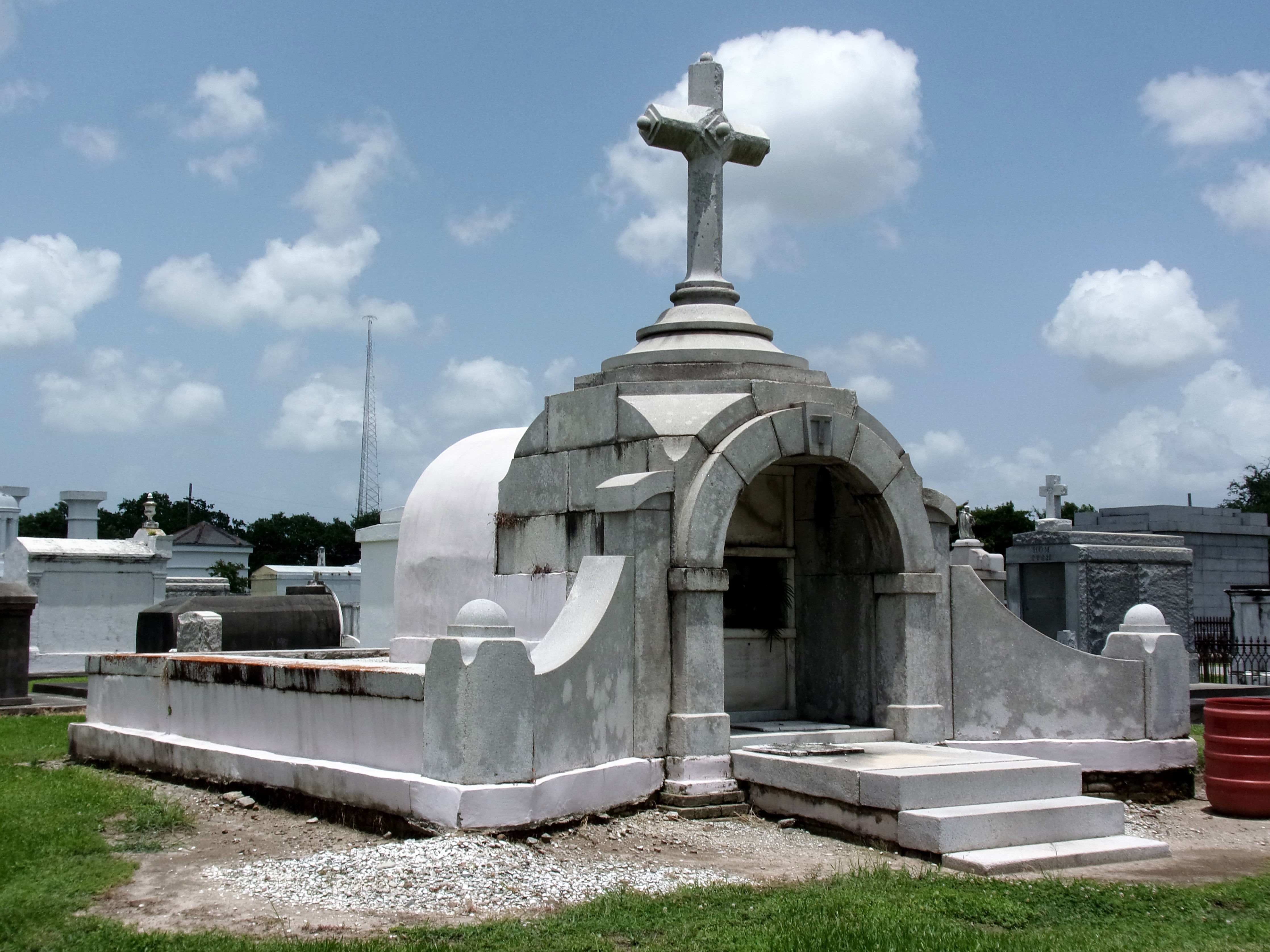
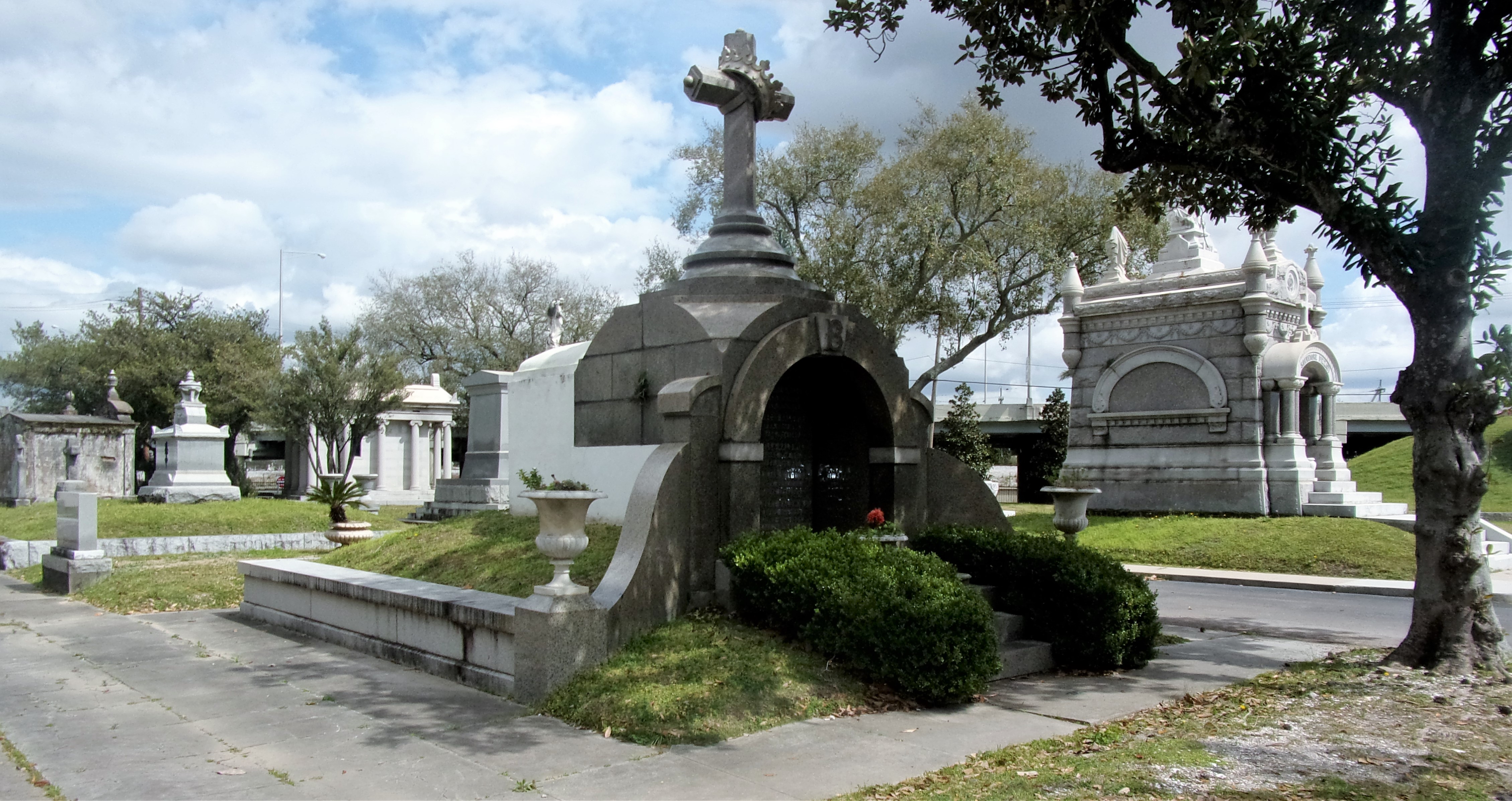
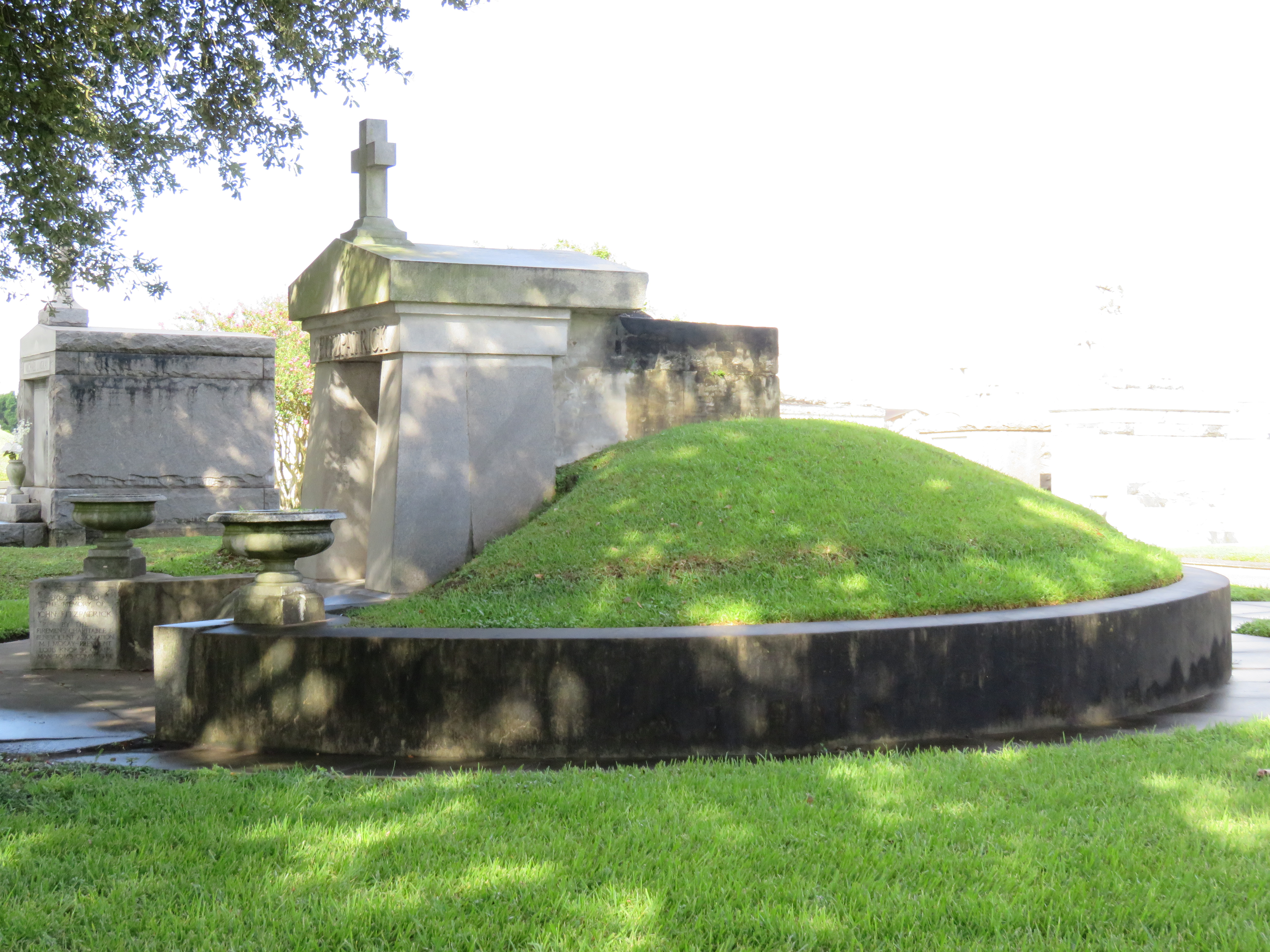
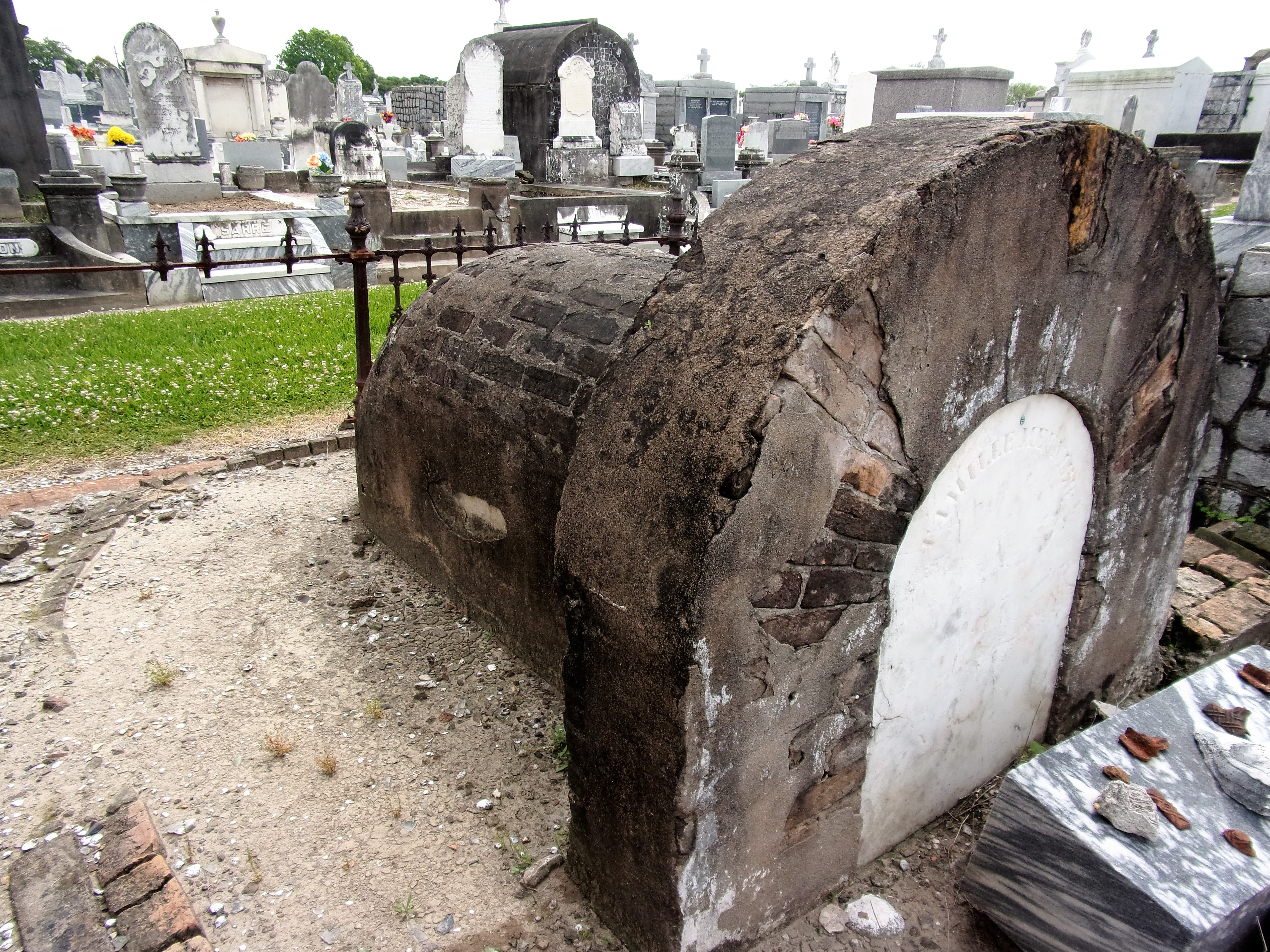
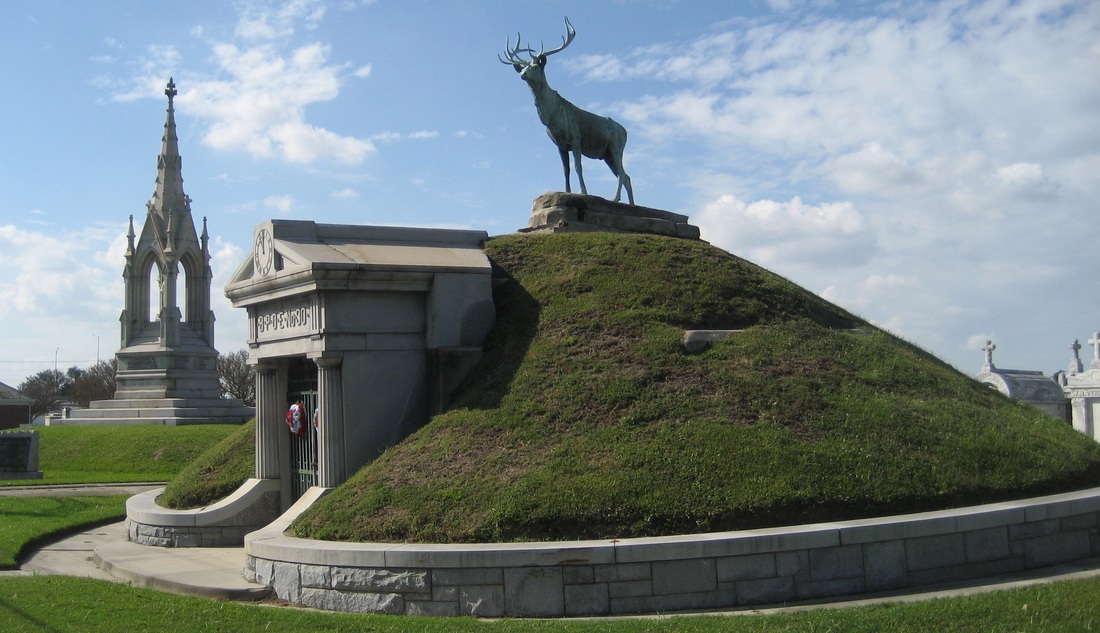
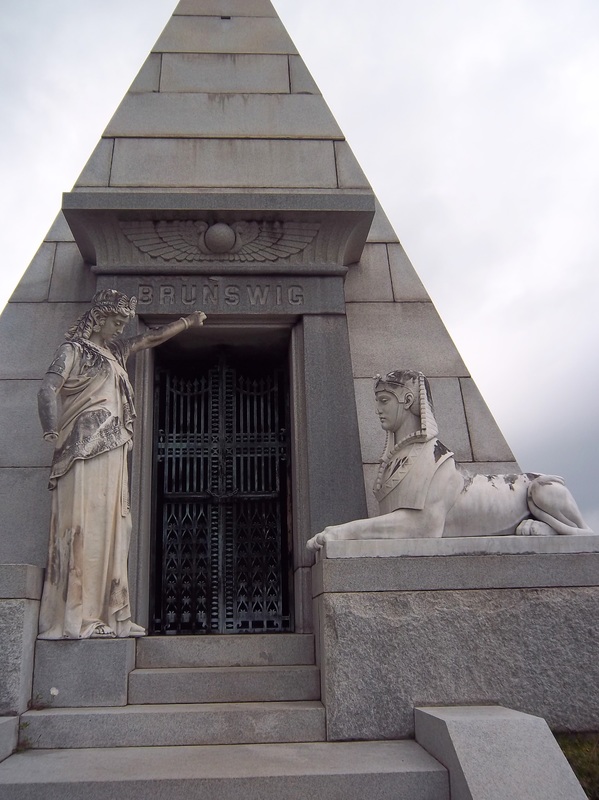
To call any cemetery landscape “eclectic” is usually an understatement. Within cemetery landscapes are the architectural whims of uncountable individuals, families, and craftsmen. And so it goes that in New Orleans cemeteries we pass a Gothic chapel and find a Celtic cross. Our landscapes are amalgams of recollection – Classical Greek, Roman, and Egyptian are at home with the Italianate, the Moorish Revival, and the Art Nouveau. This rich tradition has inspired architects to look backward for inspiration, but there is no farther backward one can reach than the tumulus. Known also as a barrow, the tumulus is a burial structure that rises from the ground as a hill or mound. Often, the tumulus bears a means of access from the side or top of the hill. Its origins span across the ancient world, both Old and New, representing a common type of burial shared between the ancient Norse, Etruscans, Chinese, Native Americans, and many, many more.[1] This type of burial also has its home in New Orleans cemeteries. The Elks Lodge tumulus in Greenwood Cemetery, and the Armies of Tennessee and Northern Virginia in Metairie Cemetery are often used as examples for the tumulus in modern cemeteries. Yet they are not alone in their unique appearance. The tumulus once graced many more New Orleans cemetery landscapes than it does today. In this blog post, we explore the origins, proliferation, and eventual disappearance of the tumulus in New Orleans cemeteries. Mounds, Barrows, and Antiquarians In Europe, mound, barrow, or tumulus burial was practiced by pre-Roman and Roman cultures. Tumuli can be found in nearly every European country – today as protected archaeological sites and heritage attractions.[2] The practice of mound burial was abandoned after the rise of Christianity and the development of churchyards in Europe. Until the cemetery landscape was reinvented by the rural cemetery movement in the early 19th century, the tumulus was a thing of ancient history. A number of factors contributed to the reintroduction of the tumulus to cemetery landscapes in Europe and the New World. With the establishment of cemeteries like Pere Lachaise in Paris, the understanding of cemetery landscapes shifted into one of green space and architectural eclecticism. From this cultural development sprang the Greek Revival architecture that proliferated New Orleans thanks in part to J.N.B. de Pouilly. But the gaze of nineteenth century Europeans and Americans did not exclusively look back to Greece. It turned to Egypt and the Middle East. It incorporated Gothic spires into new designs. And it looked even farther back to the mysterious mounds found in the European countryside. By the 1870s, the antiquaries of Europe excavated numerous tumuli in England, Italy, France, and Norway. Such discoveries were commonly featured in New Orleans newspapers.[3] An awareness of the burial mounds of great ancient cultures joined Greek temples and Gothic cathedrals in the consciousness of New Orleaneans. Furthermore, the people of the American South were familiar with mound burial in their own backyards. The presence of seemingly abandoned mounds in the southern and mid-western United States had captured the interest of Europeans since Hernando de Soto reported their existence in 1541. After colonization and into the nineteenth century, some of these mounds in Louisiana were repurposed by Americans for use as their own cemeteries. This was the case in Monroe’s Filhiol-Watkins Cemetery. Fleming Plantation Cemetery is also located on a Native American mound. By the mid-nineteenth century, mound burial was firmly rooted in the imagination of New Orleaneans. From these inspirations, the tumulus made its debut in cemetery landscapes. The Tumulus in New Orleans Like the city itself, New Orleans cemeteries are the product of many layers of community and identity. Each cemetery is a reflection of the people who made it their own. Cemeteries that were built and utilized by Irish, German, or American New Orleaneans developed with a different aesthetic than those shaped by French speakers. Each community drew upon their own culture and style to create their cemetery. The tumulus entered the popular consciousness in part via a new interest in archaeology and ancient architecture.[4] Though tumuli in New Orleans often had Greek Revival motifs, they were utilized by Americans elsewhere in the United States. Great northern cemeteries like Mount Auburn featured tumuli as part of their cultivated agrarian landscapes, as did closer cemeteries in Charleston and Savannah.[5] Thus, it is no surprise that tumuli in New Orleans appeared first in American and not Francophone cemeteries – decades before the Elks, the Army of Tennessee, or the Army of Northern Virginia. Tumuli are found primarily in the Canal Street cemeteries, including Cypress Grove, Masonic, Odd Fellows Rest, and Greenwood. They are also found in American-oriented cemeteries like Lafayette Cemeteries No. 1 and 2. There are dozens of tumuli to be found in our cemeteries, yet the untrained eye will not find one. Hidden Tumuli, or How the Lawnmower Changed Everything Most tumuli in New Orleans cemeteries no longer look like tumuli. Stripped of their grassy hill features, they appear instead simply as unusual tombs with rounded bodies. The Hornor and Holdsworth tumuli in Cypress Grove and Masonic Cemeteries (respectively) are good examples. Both constructed with a marble primary façade featuring relief carvings of cut flowers, they were likely carved by the same craftsperson, although neither structure is signed. Both tumuli have conspicuously rounded structures that seem to contrast with the grandiose style of their primary face. Yet when imagined as they originally appeared, as green hills from which their marble faces projected, their aesthetic comes together. There are many former tumuli in New Orleans cemeteries that have been stripped of their signature mounds. The John P. Richardson tomb, located in Lafayette Cemetery No. 1, was described in 1885 as “enclosed in a tall oval mound of turf, with marble doors set in a stone frame.”[6] The tumulus memorialized Richardson’s young daughters – Ella and Marguerite Callaway or “Calla,” ages six months and four years old. This original appearance could certainly not be deduced from examining the Richardson tomb today: its sweeping marble doors and arched primary face are attached to what appears to simply be a brick-and-mortar tomb. Dozens of former tumuli can be found in New Orleans cemeteries; most are identified by the slightly unusual appearance of the tomb body when compared to its front. Nineteenth century tumuli were designed to appear monumental in both mass and detail, with their entrances featuring sweeping side elements or rounded tops. The massive hill that comprised the tumulus body framed these features. Other examples of former tumuli include: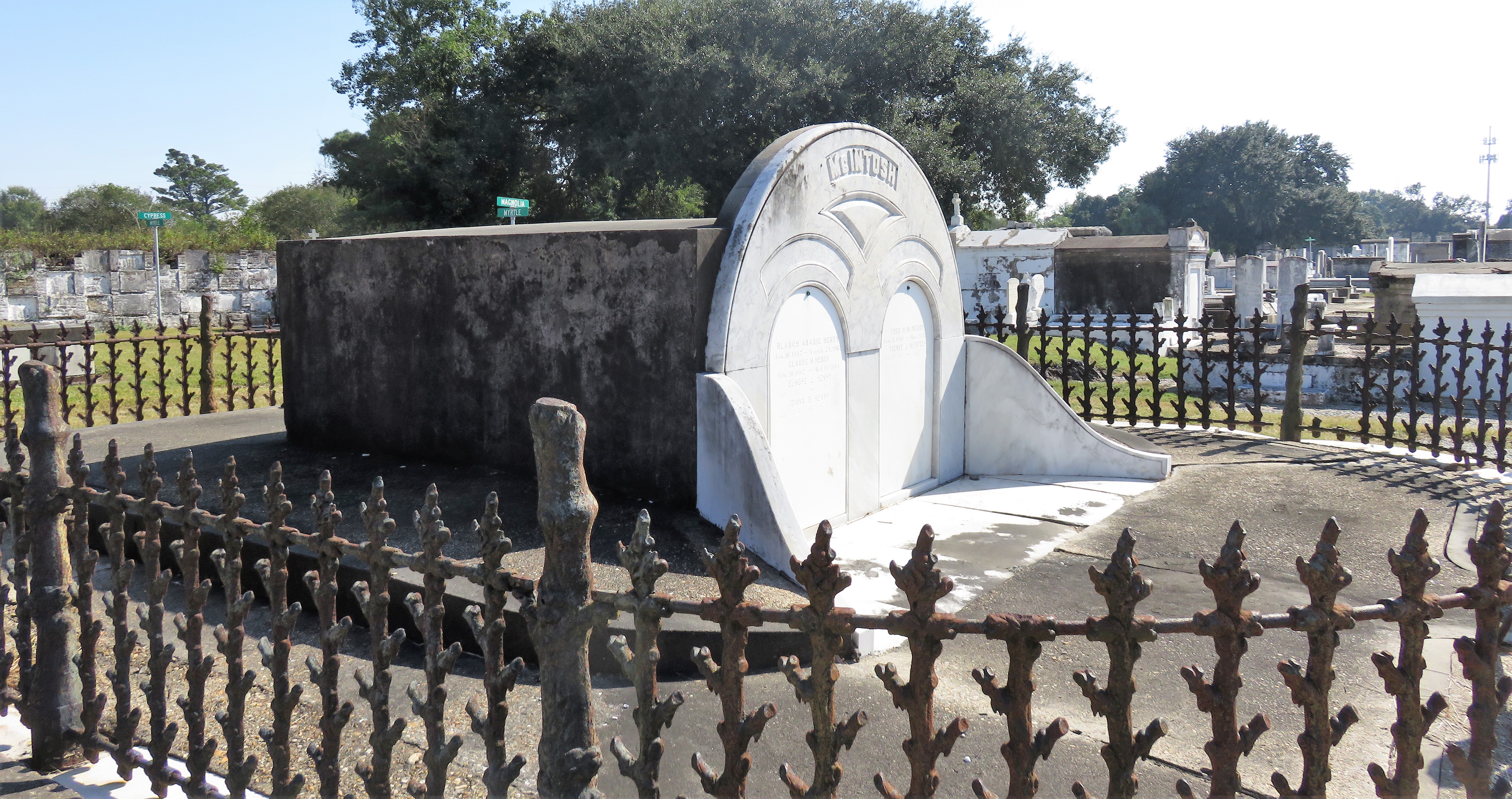  McIntosh tumulus, Cypress Grove Cemetery. In November 1873, the Nixon (now McIntosh) tomb was described as: "in the form of a mound overgrown with grass, with a large marble front. Along the top of the slab creeps an ivy, which will eventually cover the whole mound. The frontispiece was garnished on each side by a vase of white flowers." (New Orleans Republican) The disappearance of historic tumuli can be explained in the same way many other landscape features have been altered. As cemetery design, economics, and management changed, the tumulus was viewed as far too costly to maintain. Before the 1920s, cemeteries featured cultivated grounds with aisles paved in crushed shells – and they were manicured using manual, spiral-bladed lawn-cutters. Between 1920 and 1945, new lawnmowing equipment was patented with small gas-powered motors, cutting down on the labor required for landscape maintenance. This innovation was later supplemented by the availability of ready-mix concrete with which to pave once shell-strewn aisles. Finally, in the 1940s, industrialization of the monument and funerary industries led to most cemeteries eliminating the position of sexton (caretaker) from their ranks.
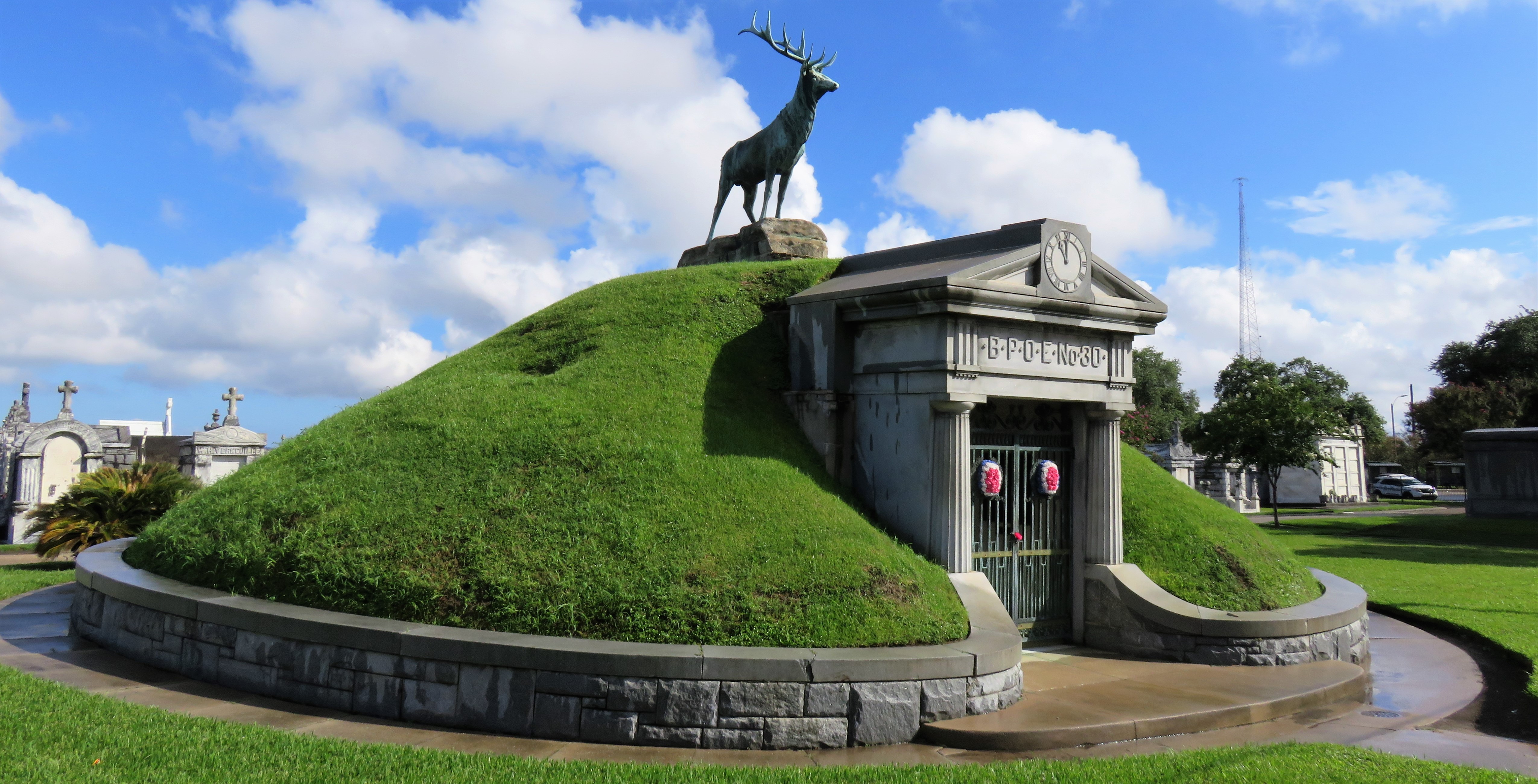
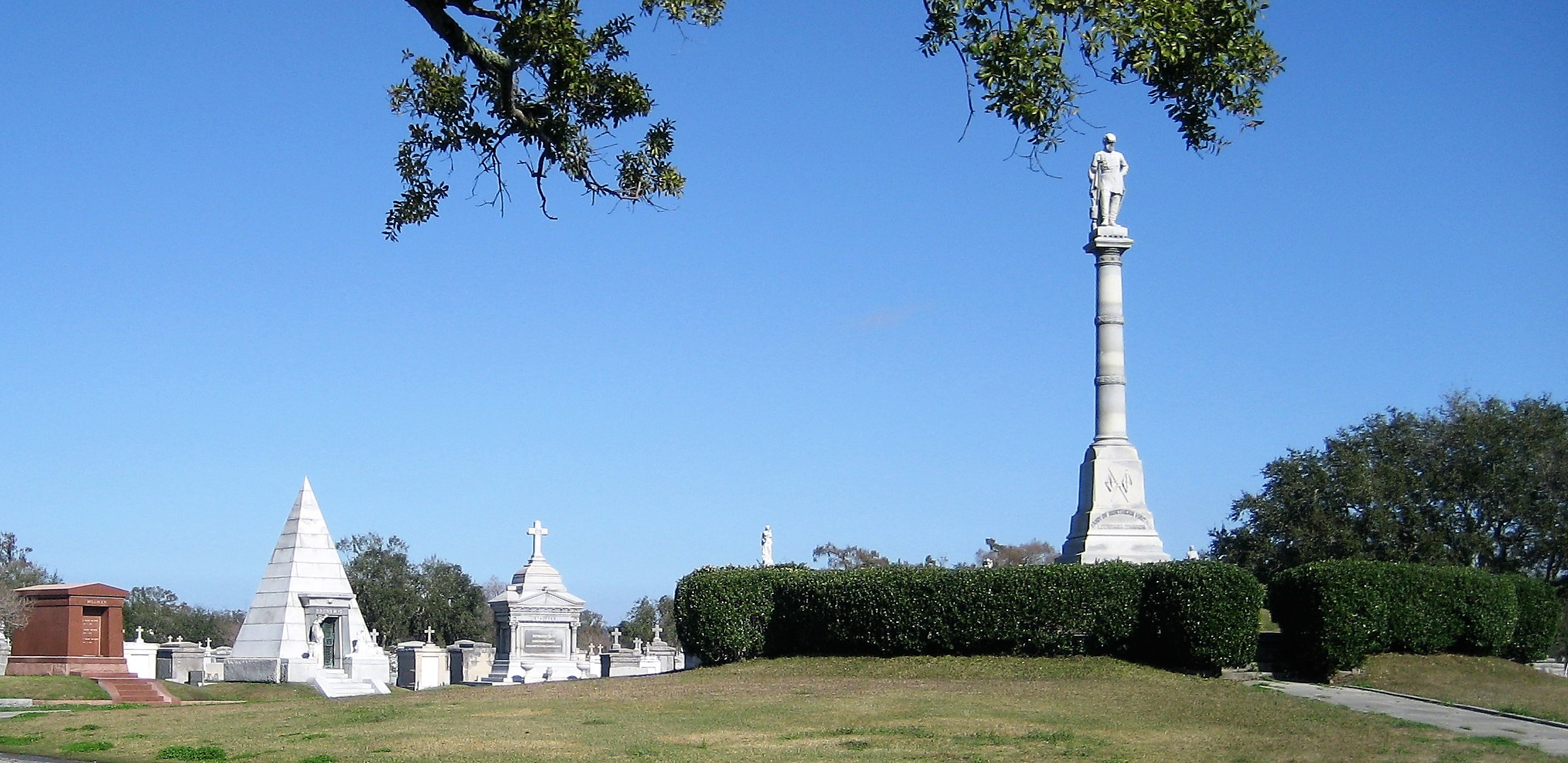
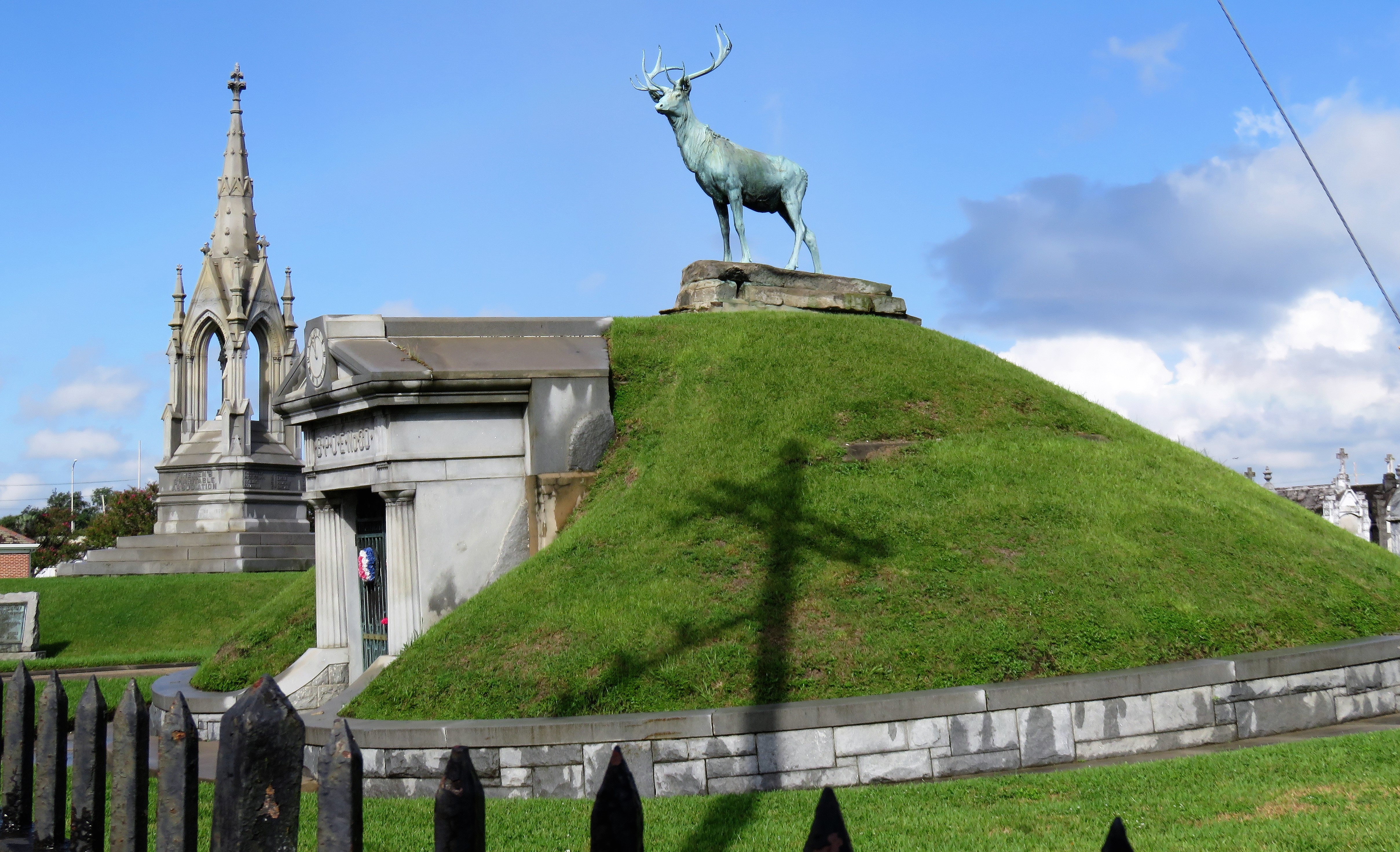
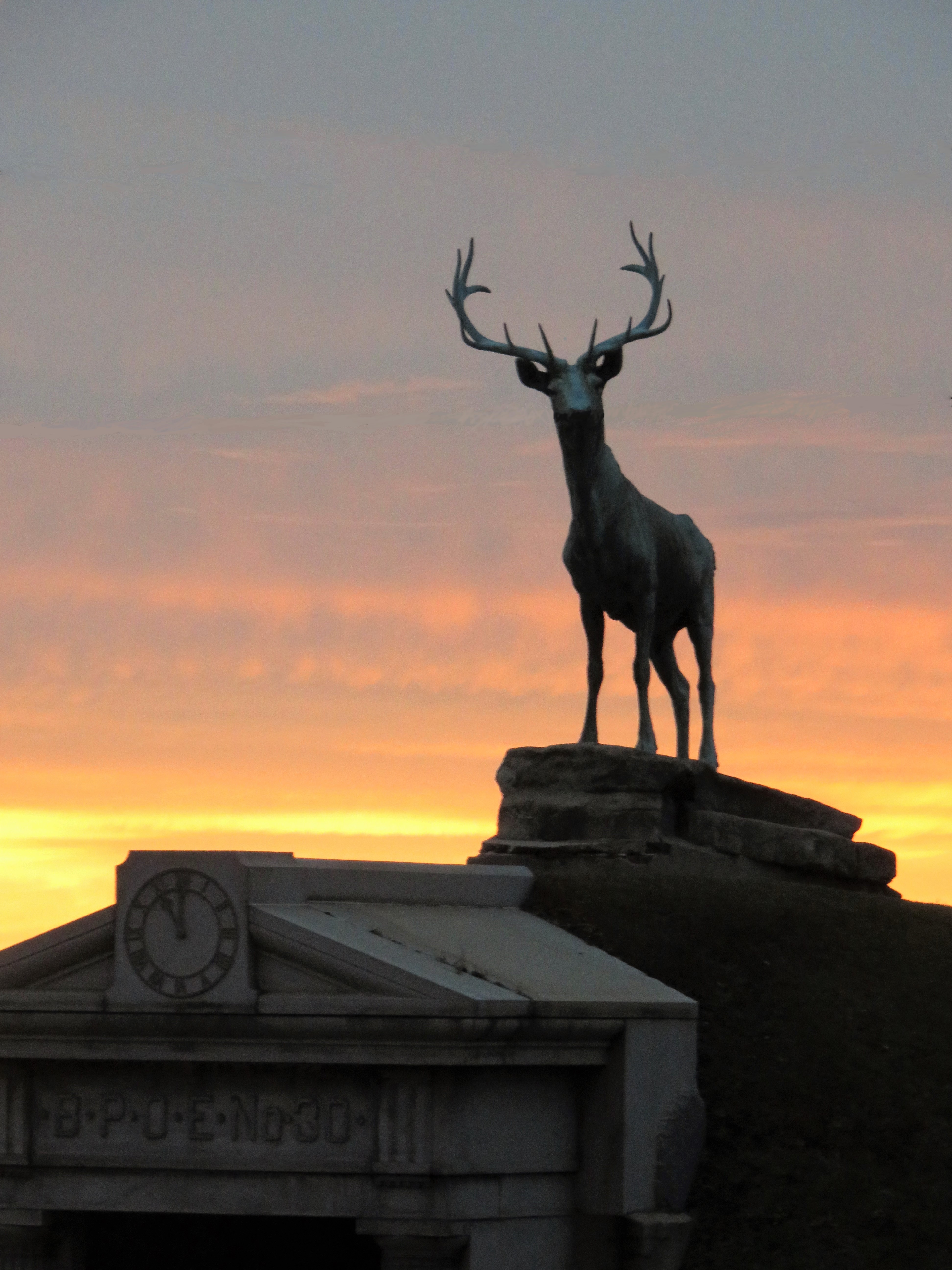
Each tumulus memorializes the fallen Confederate soldiers and deceased veterans associated with each division. After the Civil War, veterans of both Confederate and Union armies formed such benevolent associations for the support of their members. In the case of the Armies of Northern Virginia and Tennessee, perhaps the tumulus design was a nod to the military and fraternal connotations many ancient tumuli bear. Each tumulus features a remarkable sculpture at its hillside apex. The Army of Northern Virginia tumulus supports a 38-foot column atop which a sculpture of General Thomas Jonathan “Stonewall” Jackson stands. The Army of Tennessee features an equestrian bronze, sculpted by Alexander Doyle, depicting General Albert Sidney Johnston atop his horse, Fire Eater. Both tumuli are notable features of Metairie Cemetery, included in most histories of the cemetery.[7] The third notable tumulus in New Orleans is viewed daily by many city commuters. The tomb of the Benevolent Protective Order of Elks, Lodge 30, features a bronze elk standing atop its grassy summit. The tumulus is located in Greenwood Cemetery at the intersection of Canal Street and City Park Avenue, where the elk looks out above the traffic. The Elks lodge tumulus was first conceived of in 1911 by the local Elks, who held a great circus in downtown New Orleans to raise funds for the cause. In subsequent years, the Elks would commission monument man Albert Weiblen to construct the tomb at the cost of $10,000 (approximately $250,000 in 2016 currency). The structure was assembled of Alabama granite, shaped with a classical pediment, the center of which features a clock forever frozen at the eleventh hour, a reference to the “Eleventh Hour Toast” held by Elks when gathered together. Local legend has suggested that Albert Weiblen warned the Elks that the lot on which they wished the tumulus be constructed was not suitable for a structure of that size. It is true that, historically, City Park Avenue was once part of a navigation canal, an infill had only partially stabilized the soft earth. The story goes that the Elks decried Weiblen’s warning and enjoined he move ahead with construction. While primary sources for this story are nonexistent, the Elks Lodge tumulus does have a noticeable tilt toward Canal Street. Lessons in Preservation While the tumulus holds its place of honor in cemetery landscapes with the Elks and the Armies of Tennessee and Northern Virginia, it has faded from the everyday view of most cemeteries. Such a loss is difficult to quantify. Historic New Orleans cemeteries are dynamic places where features are constantly altered, modified, destroyed, or restored. Yet as we approach the task of preserving these cemeteries as functional landscapes, the tumulus offer some distinct lessons. Stripped-down tumuli confuse the historic appearance of cemeteries like Cypress Grove and Lafayette Cemetery No. 1. Had these structures been preserved, their green mounds would carry on the tradition of the cemetery as garden space; and they would properly communicate the historic landscape for both grieving family and heritage tourist alike. Stripped-down tumuli are an example of one cardinal rule of cemetery preservation: that once improper treatment has taken place, it’s nearly impossible to reverse. Each blow to responsible and considerate preservation is most likely permanent. Thus, while restoration is important, maintenance, documentation, and planned preservation are much more crucial. When the cemetery landscape is understood and preserved, large-scale restorations are less necessary. Finally, stripped-down tumuli teach us to deeply consider each structure as part of a whole, to read the structure for what isn’t there as much as for what is. Through this consideration, cemetery stewards can preserve these resources of history and heritage in a responsible manner that benefits generations to come. [1] Dan Hicks, et. al. Envisioning Landscape: Situations and Standpoints in Archaeology and Heritage (Routledge, 2016), 167.
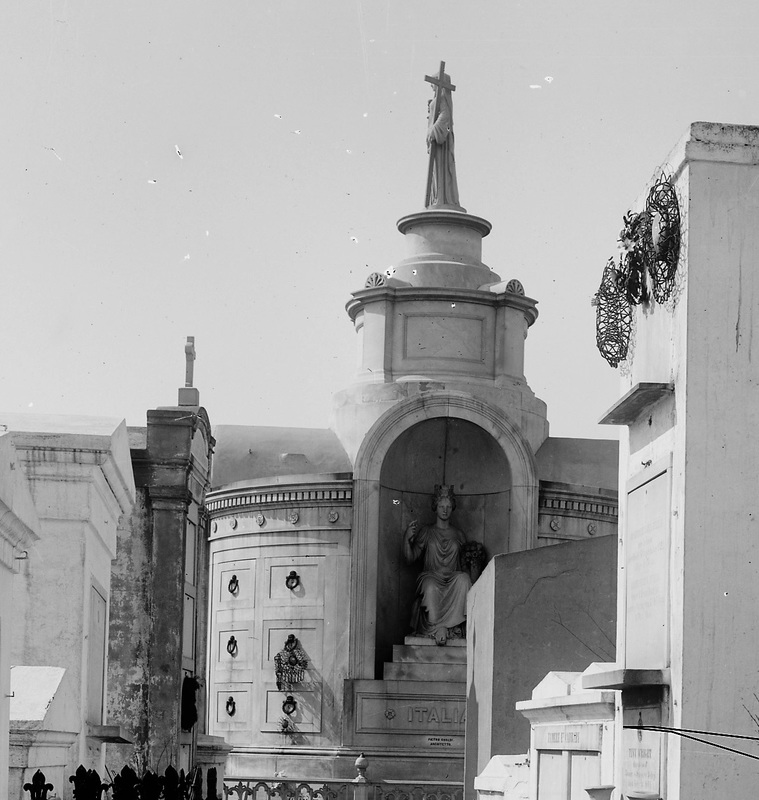
[2] James C. Southall, The Recent Origin of Man (Philadelphia: J.B. Lippincott & Co., 1875), 87-97. [3] “Jackson Mounds,” Daily Crescent, January 16, 1851; “Norwegian tumulus,” New Orleans Bulletin, April 8, 1874, 2; “Norwegian Tumulus,” Opelousas Journal, August 4, 1876, 1. [4] George F. Beyer, “The Mounds of Louisiana,” in Publications of the Louisiana Historical Society (New Orleans: 1895), 12-30. (Link) [5] Gibbes tumulus, Magnolia Cemetery, Charleston, SC, and HABS documentation (Library of Congress). [6] “All Saints Day,” Daily Picayune, November 2, 1885, p. 2. [7] Henri Gandolfo, Metairie Cemetery, An Historical Memoir: Tales of its statesmen, soldiers, and great families (New Orleans: Stewart Enterprises, 1981). Adapted from Emily Ford, “The Stonecutters and Tomb Builders of Lafayette Cemetery No. 1, New Orleans, Louisiana,” Master’s Thesis, Clemson University, 2012. Full text can be found for free here. Beyond sweeping landscapes and imposing architecture – within the “stories in stone” that are so beloved in New Orleans cemeteries, are the stones themselves. Much like the long-dead people they memorialize, these slabs of honed and carved limestone, marble, and granite journeyed great distances to become part of an irreplaceable cemetery landscape. Whose hands drew that stone from its quarry? Why is the marble found in Greenwood Cemetery drastically different from what we find in St. Louis Cemetery No. 2? Today we share the stories of quarries, infrastructures, and materials that make up New Orleans cemetery stonework. Louisiana Lacks Workable Native Stone The geology of southern Louisiana is similar to that of other states along the Gulf of Mexico. Comprised of mostly sedimentary rock, clay, limestone, and sandstone, Louisiana has few stone resources that would be desirable for cemetery monuments.[1] Furthermore, the stone that is quarried in Louisiana has historically been of poor quality for building. For example, during the 1850s construction of the Washington Monument in Washington, D.C., requests were made that each state donate a block of native stone to be placed in the interior of the monument. Louisiana sent a block of sandstone that, within the decade, was so crumbling and decayed that it was replaced with a block of Pennsylvania marble.[2] Thus, from the eighteenth century onward, the stone used in New Orleans cemeteries was imported from elsewhere. Various types of slate, marble, and granite were made available as trade routes and quarries opened. By the mid-nineteenth century, New Orleans merchants and dealers offered stone from a number of different places. As time went on, the availability and sources of stone widened.
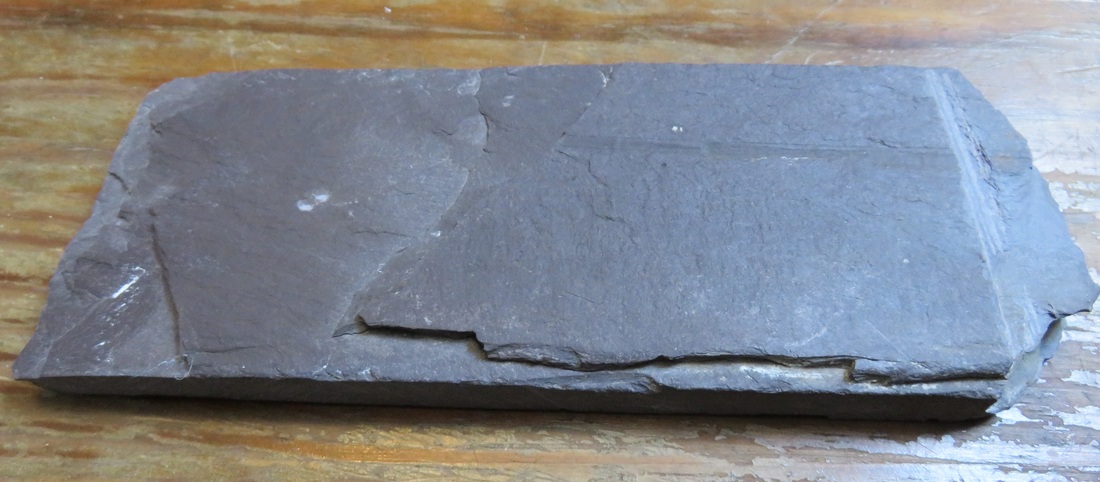
Arkansas slate was quarried from areas near the towns of Hot Springs, Little Rock, Benton, Malvern, or Mena. This small vein of quality slate, approximately 100 miles long, could produce stone of red, gray, green, or black appearance. Despite the availability of slate from Arkansas, Pennsylvania slate continued to be quarried and shipped to New Orleans. Historic Louisiana newspapers frequently mention the quality and availability of slate from the Bangor quarry in Northampton County. Given the same name as a slate quarry in Wales, the “Old Bangor” quarry had an office in New Orleans by the 1870s. Old Bangor slate is “very dark gray, and to the unaided eye has a fine texture and fine cleavage surface, almost without any luster. The sawn edge shows pyrite.” The Williamstown, Franklin, and Pen Arygl quarries of Pennsylvania also had retail agents in New Orleans, who advertised their slate to be of the same quality as that of Wales.[6]
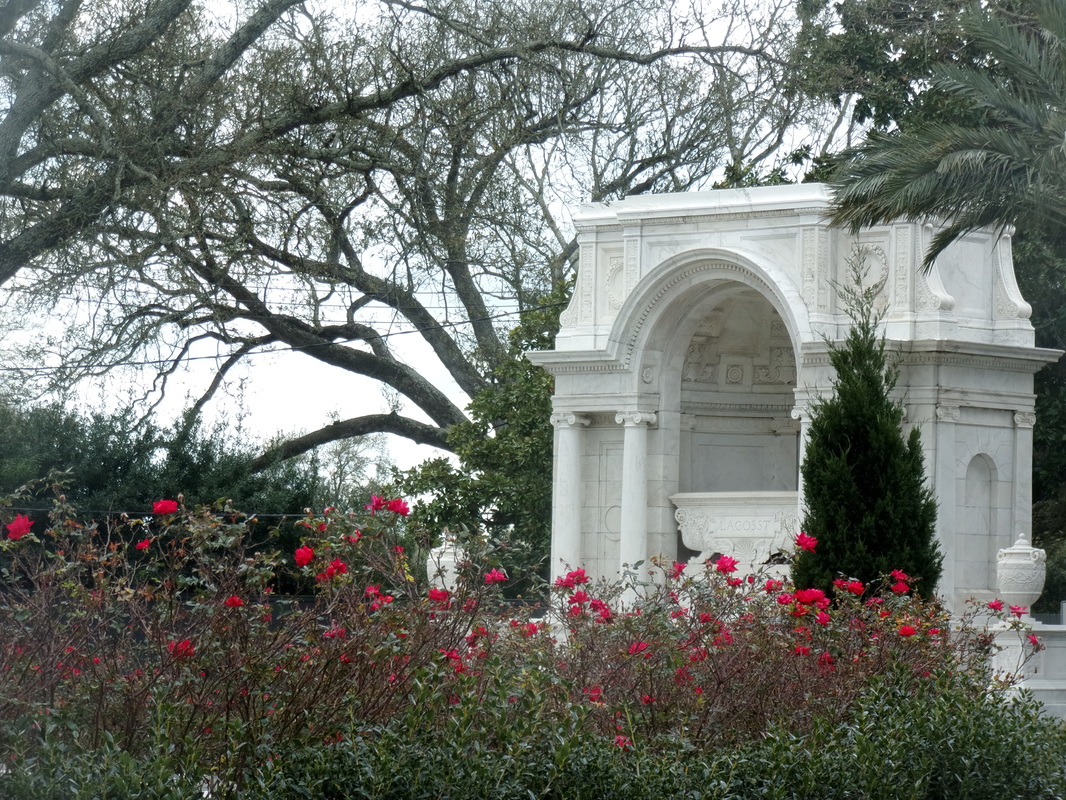
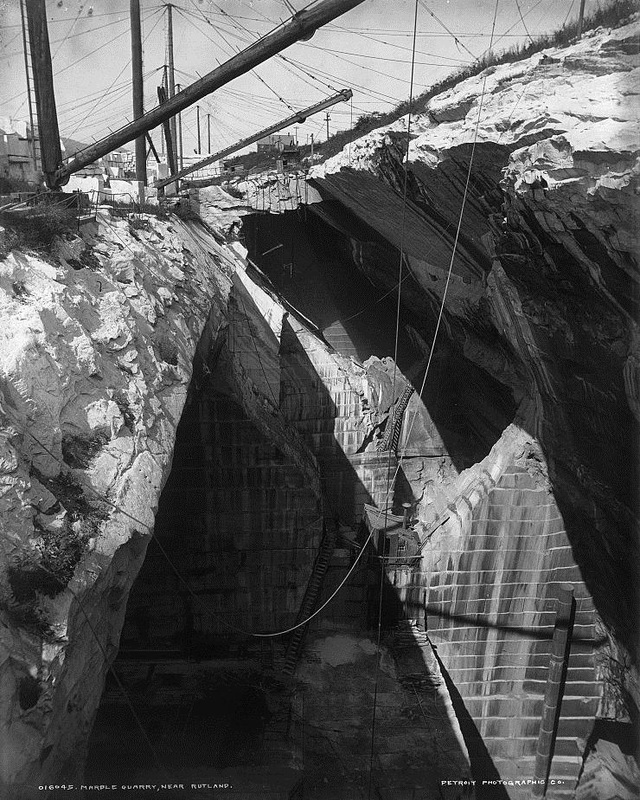
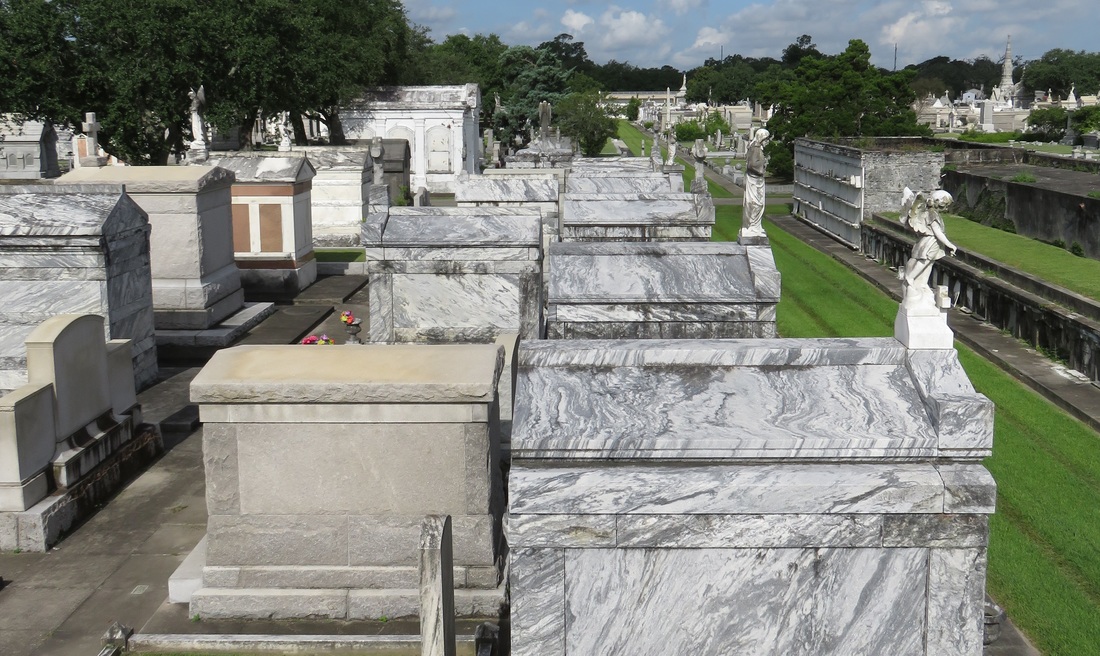
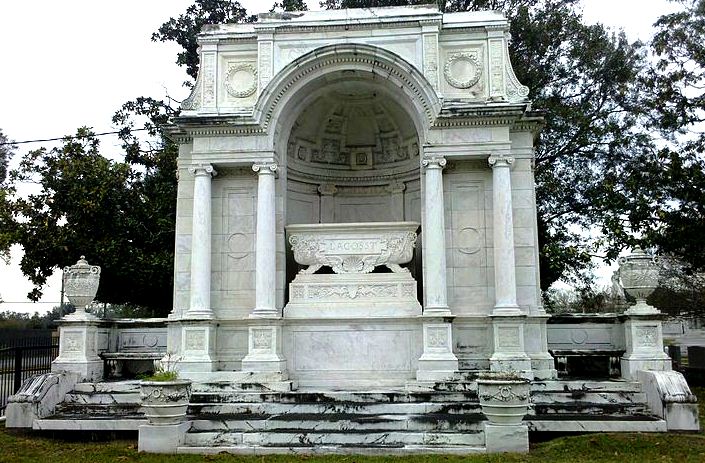
They form by the compression of these sediments, along with all the calcium-rich seashells within. They diverge when these sediments either compress and become sedimentary rock or, alternatively, are subject to higher pressures and become metamorphic. Limestone is sedimentary, marble is metamorphic. Limestone is most prevalent in the oldest remaining New Orleans cemeteries, namely St. Louis Cemetery No. 1 and 2, although precious isolated examples are found in other cemeteries. In this context, limestone was used for closure tablets. Limestone closure tablets are usually dark gray (likely quarried in Arkansas or Tennessee) and can be identified by the tiny fossilized shells included in the stone’s matrix. Around the mid-nineteenth century, whiter limestones were used in the same context as marble and are harder to identify. Some rough-faced stones that appear to be marble can be identified as limestone by spotting the shell inclusions within. These rare examples of white limestone were often quarried in Tennessee. Imported Marble: An Italian Commodity New Orleans was a primary hub for the import and export marble from both Europe and the United States. Used for closure tablets, shelves, memorial sculpture, apex sculptures, tomb cladding, and other decorative elements, marble was the medium in which cemetery stonecutters primarily worked throughout the nineteenth century. Based on documentary evidence, the quarries of Italy were the primary source of marble into the 1850s. Italian marble was either directly imported from Italy or arrived via northeastern ports like Boston or New York.[7] Florville Foy, who advertised aggressively throughout his career, frequently promoted his most recent shipment from Carrara or Genoa, cut into one, two, and three inch slabs. Paul Hippolyte Monsseaux similarly advertised his Italian marble stock.[8] New Orleans stonecutters dealt in and imported Italian marble through the nineteenth century. In the 1870s, stonecutter John Hagan (active 1854 – 1890s) stocked Italian marble “for sale at a small advance on New York prices.” George Stroud (active 1866 – 1899) cut his own Italian marble at Monsseaux’s steam cutting plant. James Reynolds (active 1866 – 1880) not only sold his Italian marble in New Orleans but also in Vicksburg, Mississippi.[9] Italian marble, often vernacularly referred to as “Carrara marble” regardless of its quarry of origin, is a stone of high-grade, consistent quality, and a variety of colors including cream, pure white, and blue. As one Alabama quarry owner conceded in 1909, “Italian marble has long been a standard, not only because the stone is undeniably high grade, but also because the blocks are so uniform in quality that all the slabs or pieces from a block can be used together.”[10] The cost of importing marble in New Orleans varied over the course of the nineteenth and twentieth century; at times, it actually cost less to import than marble from Vermont or Tennessee. Protective tariffs helped to stabilize the marble industry during the 1880s and 1890s, but the presence of the famed marble remained a factor among monumental craftsmen into the present. For example, in 1914, before Albert Weiblen purchased his own marble quarry in Georgia, he received a shipment of Italian marble so substantial it took two large derricks to lift the fifteen-ton blocks from the steamship in which it arrived.[11] Domestic Marble: Vermont, Alabama, Georgia, and Others The slow development of infrastructure and quarry technology prevented American quarries from competing with Italian marble in New Orleans until the 1850s. In 1845, one of the first marble quarries opened in Talladega County, Alabama. Five years later, another opened nearby, operated by J.M.N.B. Nix. Using a publicity tactic that would become common among quarry operators in the United States, the New Orleans Daily Picayune announced that “Alabama produces marble equal in fineness – that is, purity or clearness and susceptibility of polish – to any in the world, not excepting the most beautiful Italian, Vermont, or Egyptian.” It was Nix’s quarry that sent Alabama’s contribution to the Washington Monument.[12] Talladega marble can appear white, blue, or cream, and often displays black, green, or grey veins, although it is consistently characterized by the fineness of its grain. Its unpredictability in quality and appearance, however, made it costly to extract.[13] Alabama marble remained a presence among New Orleans cemetery craftsmen well into the twentieth century. One of the most recognizable and imposing monuments within Metairie Cemetery, the ornate sarcophagus of Eugene Lacosst, was crafted by Albert Weiblen from pure white Alabama marble.[14] As always, infrastructure dictated which materials were available in New Orleans at a given time period. In 1851, The Vermont Valley Railroad Company connected towns like Rutland to the greater markets in the East and South.[15] Only two years later, sources in New Orleans commented on the great productivity of the Rutland quarries, remarking that their product had gained “a reputation abroad as well as at home.”[16] Rutland and other Vermont marbles can be white, blue, or black. These quarries also produced pure-white sculpture-grade marble.[17] By 1900, Vermont produced more marble than any other American state, and the Rutland quarry was the highest-yielding quarry. Blocks of Vermont marble were sold for between $1.00 and $3.00 per cubic foot in New Orleans, where agents received shipments and distributed order throughout the South and West.[18] Like Alabama marble, marble quarried in Vermont remained in the stockpiles of New Orleans craftsmen into the mid- and late twentieth century. Vermont not only exported its marble to New Orleans, but its marble cutters as well. One account reflected that the stone cutting yards of New Orleans primarily employed skilled sculptors and polishers from the states of Vermont and Georgia.[19] By 1916, Georgia was second only to Vermont in its production of quarried marble. Although marble quarrying had existed in Georgia long before, it appears to only have gained prevalence in the New Orleans market after the Civil War. By 1888, the Georgia Marble Company in Pickens County claimed to be the largest marble quarry in the world.[20] Georgia marble is typically coarse-grained and appears in blue-gray, black, white, and Creole, which has dramatic sweeping shades of dark gray, black, and white.[21] Ubiquitous Georgia Creole Marble Between 1890 and the 1930s, Georgia Creole marble exploded in the New Orleans cemetery market and made an enormous mark on the landscape. This explosion was the result of expert marketing, improved infrastructure, and enormous supply. Modern monument men during this period utilized Georgia Creole marble in nearly every aspect of their work, from tomb cladding to headstones to vases and urns. The streamlined process of tomb building, now executed in a more “cookie cutter” style than previous generations, allowed many more tombs to be built in a short period of time, and Georgia Creole marble was the medium of choice.
Additionally, as marble is a metamorphosed type of limestone, it is naturally alkaline in quality. Thus, exposure to rain, which is naturally slightly acidic, or any other acidic substance (for example, hydrochloric acid mistakenly intended to clean the stone) will cause marble to granulate and “sugar” over time. An extreme example of marble deterioration can be found in St. Joseph’s Cemetery No. 1. The failure that likely occurred with this stone was related to moisture entrapment within the tomb itself. This, paired with the tight, compressive position of the tablet within the opening, caused the closure tablet to bow and “bubble” outward.
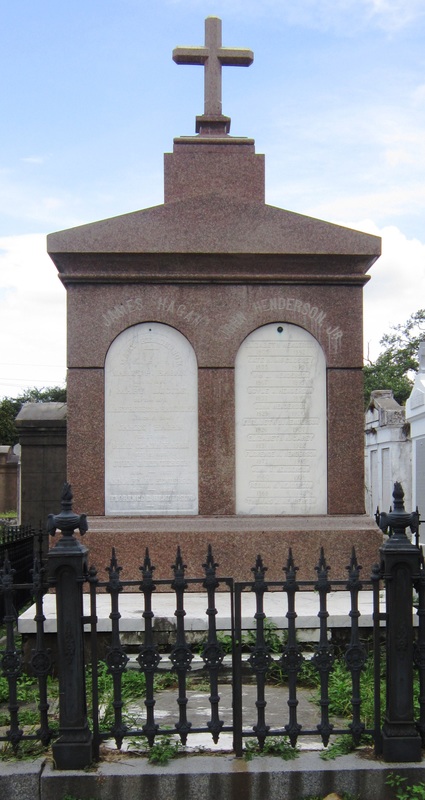
One of the most noticeable granite tombs in Lafayette Cemetery No. 1 is that of stonecutter and sexton James Hagan. This remarkable tomb was built of red-colored Scotch granite in 1872. Around the same time, Hagan also constructed the monument of Governor Henry Allen, which was also located in Lafayette Cemetery No. 1 until it was moved to the Old State Capitol in Baton Rouge in the 1880s. This monument, too, was carved from Scotch granite.[24]
[1] Louisiana Geological Survey, Geology and Agriculture: A Report on the Geology of Louisiana (Baton Rouge: 1902), 133-134.
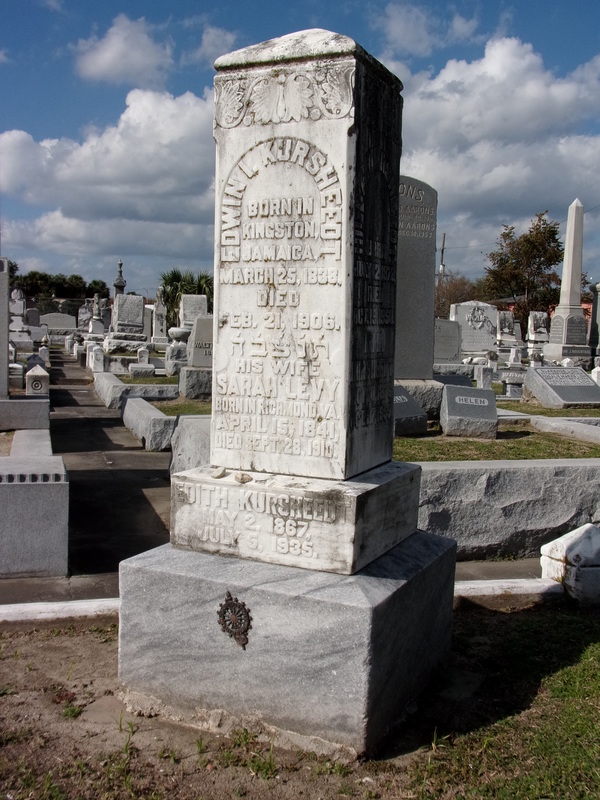
[2] National Park Service, Department of the Interior, Northeast Region, Architectural Preservation Division, The Washington Monument: A Technical History and Catalog of the Commemorative Stones (Washington, DC: National Park Service, 2005), 28. “Washington National Monument,” The Pittsfield Sun (Pittsfield, Massachusetts), August 22, 1850, page 1. The stone is referred to as “freestone,” meaning a soft, friable sedimentary stone. [3] Graham R. Thompson and Jonathan Turk, Introduction to Physical Geology (Rochester, NY: Saunders College Publishers, 1998), 133-137. Slate headstones are found commonly in the Northeast dating to the colonial period. Slate headstones are also present in cemeteries as far south as Charleston, South Carolina and Savannah, Georgia. However, no slate headstones are visible in the cemetery landscapes of New Orleans. [4] Mary Louise Christovich, Roulhac Toledano, and Betsy Swanson, New Orleans Architecture, Vol. I: The American Sector (Gretna, LA: Pelican Publishing, 1998), 57. [5] Daily Picayune, September 27, 1850, 2; Daily Picayune, May 2, 1853, 1; Daily Picayune, February 28, 1869, 11. [6] “Alexander Hill, Welsh and American Slates, Slabs, etc.” Morning Star and Catholic Messenger, July 4, 1875, 6. These slates priced from $6.50 to $10 per square; “Slates! Slates! Slates!” Ouachita Telegraph (Monroe, LA), July 22, 1872, 2. [7] “Brig Casket arrives from New York with sundry marble slabs,” Louisiana Advertiser, April 29, 1820, 3. “Barelli & Company, commission merchants, selling blocks of Italian marble,” Daily Picayune, March 21, 1845, 3. [8] Daily Picayune, November 10, 1848, 7; Daily Picayune, February 17, 1848, 3; Cohen’s New Orleans and Lafayette Directory for 1851 (New Orleans: Cohen’s Directory Company, 1851), page AT. [9] Edwards’ Annual Director to the Inhabitants, Institutions….etc., etc., in the City of New Orleans for 1871 (New Orleans: Southern Publishing Company, 1870), 275; Daily Picayune, May 18, 1871, 3. [10] Committee on Ways and Means, United States Congress, “Marble: The Alabama Marble Company, Gantts Quarry, Ala., Urges Retention of Duty on Marble,” in Tariff Hearings Before the Committee on Ways and Means of the House of Representatives, Sixtieth Congress, 1908-1909, Vol. VIII (Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office, 1909), 7886-7888. [11] “Ship Brings Cargo of Italian Marble,” Times-Picayune, July 27, 1914, 8. [12] “Alabama Marble,” Daily Picayune, October 1, 1845, page 2; Daily Picayune, May 18, 1871, 3. [13] Committee on Ways and Means, United States Congress, “Marble: The Alabama Marble Company, Gantts Quarry, Ala., Urges Retention of Duty on Marble,” in Tariff Hearings Before the Committee on Ways and Means of the House of Representatives, Sixtieth Congress, 1908-1909, Vol. VIII (Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office, 1909), 7886-7888. In this year, cost to transport Alabama marble to New Orleans was 32 cents per cubic foot. [14] Leonard V. Huber et. al. New Orleans Architecture, Vol. III: The Cemeteries, 54-55. [15] Vermont Railroad Commissioner, Eleventh Biennial Report of the Board of Railroad Commissioners of the State of Vermont (St. Albans, VT: St. Albans Messenger Co., 1908), 308. [16] Daily Picayune, July 15, 1853, page1; Daily Picayune, June 16, 1855, 1. [17] Thomas Nelson Dale, The Commercial Marbles of Western Vermont (Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office, 1912), 117-122. [18] Tariff Hearings before the Committee on Ways and Means, Second Session, Fifty-Fourth Congress, 1896-97, Volume 1 (Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office, 1897), 275-279; “Random Notes,” The Reporter: The First and Only Journal Published in the World Devoted Exclusively to Granite and Marble, No. 1 (January, 1900): 33. [19] David Spence Hill, Industry and Education: Part Two of a Vocational Survey for Isaac Delgado Central Trades School (New Orleans: The Commission Council, 1916), 227. [20] “Science and Industry,” The Colfax Chronicle (Colfax, LA), November 3, 1888, 3. This was not an uncommon claim for many quarries to make. “Georgia Quarries,” The True Democrat (Bayou Sara, LA), January 30, 1897, 7. [21] Memoirs of Georgia, Vol. I (Atlanta: The Southern Historical Association, 1895), 211-217. [22] A. Oakley Hall, “Cities of the Dead,” in Louisiana Sojourns: Travelers Tales and Literary Journeys, Frank de Caro, editor. (Baton Rouge: LSU Press, 1998), 532-533; Arthur Wellington Brayley, History of the Granite Industry of New England, Volume I (Boston: National Association of Granite Industries of the United States, 1913), 114. [23] Ibid., 84. [24] Special thanks to Jonathan Kewley of Durham University, UK, for his knowledge and expertise in identifying the Hagan tomb as Scottish granite. [25] Soards’ New Orleans City Directory for 1895, Vol. XXII (New Orleans: L. Soards, Publisher, 1895), 1095. [26] “Notes from the Quarries,” Stone: an Illustrated Magazine Vol. 4 (1892): 496. Adapted from Emily Ford, “The Stonecutters and Tomb Builders of Lafayette Cemetery No. 1, New Orleans, Louisiana,” Master’s Thesis, Clemson University, 2012. Throughout the course of the nineteenth century, the New Orleans Jewish experience varied among individuals and families, from great successes to great defeats. For some, it was something one was born into: by mid-century, a number of families had developed deep roots in New Orleans commerce and culture. For men like Judah P. Benjamin and other merchants, lawyers, and factors, New Orleans was a place of opportunity among aristocrats and politicians. For others, however, New Orleans was a refuge, only slightly improved from the poverty and exclusion of the homeland from which they had fled. Among the Jews from Central and Eastern Europe who immigrated to New Orleans between 1840 and 1880, many found their new home to be wracked by destitution, disease, and an uncertain future. These immigrants formed their own communities, establishing a familiar cultural norm to ease their transition in the New World.[1] Two New Orleans stonecutters exemplify this wide spectrum of experience. Edwin I. Kursheedt, part of an influential Jewish family, was successful not only professionally but personally. Committed to charity and military service, he inherited his business from his father and carried it into the twentieth century. Alternatively, the carved signature of H. Lowenstein is nearly all that remains of this stonecutter’s legacy. It is likely that his time in New Orleans was brief, cut short by disease, war, or the search for better opportunities.
The address of H. Lowenstein’s business is recorded in directories and on his signed tablets as 195 and 197 Washington Avenue, which corresponds to the historic marble yard and shop located across Washington Avenue from Lafayette Cemetery No. 1. During the years Lowenstein held business there, other stonecutters and sextons advertised at the address, namely James Hagan and Philip Harty. Lowenstein also advertised himself as an undertaker at this address. Lowenstein’s carving style bears a resemblance to that of other contemporary German stonecutters, namely the Anthony Barret and his sons Charles and Frederick. These artisans carved in the German Fraktur style, or black-letter, and employed similar imagery of oak and laurel wreaths that are not found among the work of non-German craftsmen in Lafayette Cemetery No. 1. These scant traces of Lowenstein in New Orleans indicate that he was likely a German-Jewish immigrant who served the community of the Fourth District, once part of the suburb of Lafayette. A number of German newspapers, including the Deutsche Zeitung and the Louisiana Straatszeitung, may have been the venue for his advertising. Considering he frequently carved closure tablets in German, it is likely that he aided more established craftsmen like Hagan and Harty with their business in the German immigrant community. Yet, after 1869, documentation of H. Lowenstein evaporates completely, suggesting that, like many other Jewish immigrants in the South, he may have moved elsewhere, or possibly died young in New Orleans.
The business of Kursheedt & Bienvenu was among the most successful and prominent merchants of not only cemetery stonework and tombs but also hardware, commercial stonework, mantels, grates, and other items. By the 1880s, they owned not only a large show room on Camp Street but also a marble yard next door, at which at least thirty men were employed.
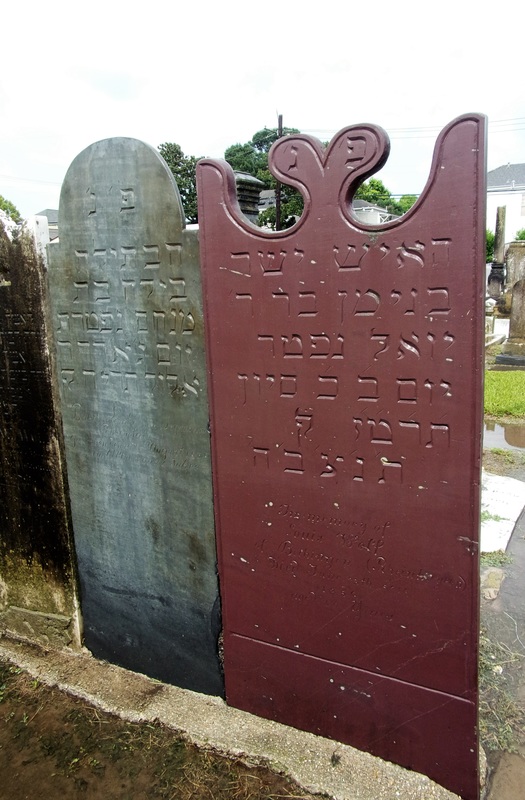
Much of Kursheedt & Bienvenu’s signed work can be found in Jewish cemeteries in New Orleans, Baton Rouge, Alexandria, and Plaquemine, among other Louisiana towns. Within Jewish cemeteries, this work consists of headstones, as Jewish tradition prohibits above-ground burial. Yet Kursheedt & Bienvenu served clients of all religions and traditions. Among their most visible commissioned works is the Sercy tomb in Lafayette Cemetery No. 1. Marked by a stone sarcophagus and located near the Washington Avenue cemetery gate, it is most notable for its epitaph: “Died of Yellow Fever,” a relic of the 1878 epidemic. J.G. Bienvenu left the business after 1888, and Edwin Kursheedt operated Kursheedt’s Marble Works until 1901.[8] Throughout these years, he served on various boards for Jewish Charities, including Touro Infirmary, the Hebrew Benevolent Association, and the Jewish Widows and Orphans Home.[9] He died in on February 21, 1906, at the age of sixty-seven, a veteran, merchant, benefactor, husband and father. He is buried in Dispersed of Judah Cemetery on Canal Street. It is unclear where or when H. Lowenstein died. The only tenuous hint points to an obituary published in the New Orleans Daily Picayune November 3, 1896, reporting the death of Henry Lowenstein, who died at the age of fifty-six in Cincinnati, Ohio. That a New Orleans newspaper reported his death suggests he once lived in the city, and may have been a young stonecarver on Washington Street in 1861, but no definitive documentation can support this possibility.[10] So these two artisans whose work is marked in New Orleans cemeteries died as they lived: one documented and memorialized, one lost in historic thin air, as were many immigrants who came and went from the Crescent City in the nineteenth century. [1] Bobbie Malone, “New Orleans Uptown Jewish Immigrants: The Community of Congregation Gates of Prayer,” Louisiana History: The Journal of the Louisiana Historical Association, Vol. 32, No. 3, Summer 1991, 239-287; Ellen C. Merrill, Germans of Louisiana (Gretna, LA: Pelican Publishing, 2005), 225, 236.
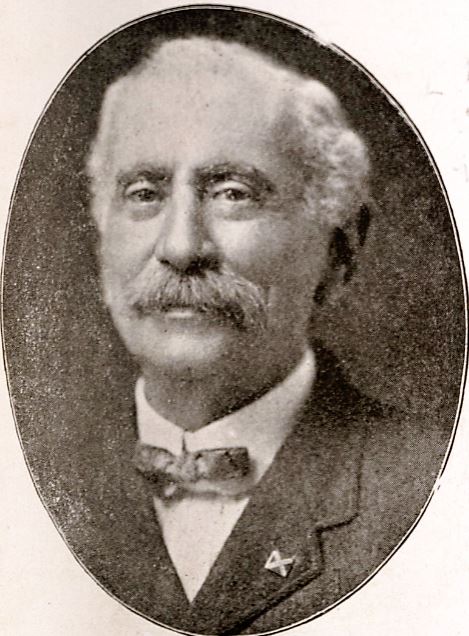
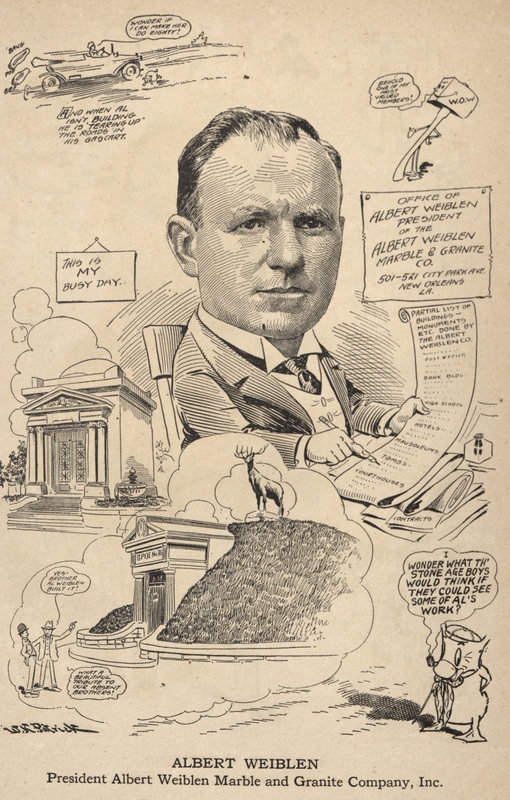
[2] The signature “Löwenstein” can be found on the Fridolin Hottinger tomb, Quadrant 2, Lafayette Cemetery No. 1; Gardner’s New Orleans Directory for 1861 (New Orleans: Charles Gardner, 1861), 282; Gardner’s New Orleans Directory for 1866 (New Orleans: True Delta Book and Job Office, 1866), 279; Gardner’s New Orleans Directory for 1869 (New Orleans: Southern Publishing Company, 1868), 399. [3] Bertram Wallace Korn, The Early Jews of New Orleans (American Jewish Historical Society: 1969), 247-249; “Mr. Israel Baer Kursheedt,” The Occident and American Jewish Advocate, Vol. X, No. 3, June 1852, 1. [4] Robert N. Rosen, The Jewish Confederates (Columbia: University of South Carolina Press, 2000), 111-116. [5] Andrew Morrison, The industries of New Orleans: her rank, resources, advantages, trade, commerce and manufactures, conditions of the past, present and future, representative industrial institutions, etc. (New Orleans: J.M. Elstner & Co., 1885), 144. [6] Louisiana Capitolian (Baton Rouge, LA), August 21, 1880, 5; “The Other Side: The Report Adopted by the State-House Commission Respecting the Work Done,” Louisiana Capitolian (Baton Rouge, LA), August 28, 1880. [7] Soards’ New Orleans City Directory for 1887 (New Orleans: L. Soards & Co. Publishers, 1887), 513. [8] Soards’ New Orleans City Directory for 1889 (New Orleans: L. Soards, Publisher, 1889), 532; Soards’ New Orleans City Directory, for 1901, Vol XXVIII (New Orleans: Soards Directory Co., Ltd., Publishers, 1901), 501. [9] W.E. Myers, The Israelites of Louisiana: Their Religious, Civic, Charitable and Patriotic Life (New Orleans: W.E. Myers, 1904), 103. [10] Daily Picayune, November 3, 1896, 4. See also, Emily Ford and Barry Stiefel, The Jews of New Orleans and the Mississippi Delta: A History of Life and Community Along the Bayou (History Press, 2012). On May 1, 1957, and only a few months shy of his 100th birthday, Albert Weiblen passed away in New Orleans. In his lifetime, Albert Weiblen was a revolutionary figure in New Orleans cemetery architecture. Under his carving hand, the craft of tomb building would expand from a hyper-local, individual cottage profession into a modern industry – spanning the eastern United States and powerfully altering the landscape of New Orleans cemeteries. A German Immigrant in New Orleans Albert Weiblen was born in 1857 in Metzingen, Wurttemberg, Germany. Sources suggest that he began his work as a sculptor in his homeland, apprenticing in the manner that was traditional for the time.[1] Weiblen immigrated to the United States in 1883 and soon afterward began work with local marble company Kursheedt and Bienvenu. Operational from 1867 to 1901, the company was co-owned by Edwin I. Kursheedt, a prolific stonecutter in his own right who, in addition to work in New Orleans’ Jewish cemeteries and other cemetery stonework, supplied the stone for the reconstruction of the Old State Capitol in Baton Rouge in the late 1880s.[2] At this time, New Orleans’ cemetery stonecutting industry was already changing. The florid, individualized Classical-revival tombs popular from the 1840s through the 1860s had given way not only to new styles inspired by Gothic and Italianate revival aesthetics, but also to economies of scale. The Yellow Fever epidemic of 1878 galvanized this trend. In this year, the construction of tombs shifted more to “cookie cutter” and slightly simplified styles, replicated by numerous carvers and builders.[3] Weiblen stepped into the cemetery craft scene in New Orleans at a time when this streamlining of tomb construction was in its infancy. New industrial technology, such as saws and machinery to cut granite and marble, new types of stronger hydraulic cements, and stonecutting technology powered by pneumatic chisels and even sandblasting, had been adopted elsewhere in the country, but were a long way off from making their debut in New Orleans cemeteries.[4] When these new tools and methods did arrive, though, it was often Weiblen who spearheaded their use. In 1887, Weiblen left Kursheedt & Bienvenu’s and started his own marble and granite company.[5] His first office and show room was located at 233 Baronne Street, a location he expanded by 1893.[6] Weiblen’s big break came in 1891 when his company won the contract to construct the memorial obelisk to New Orleans Superintendent of Police David Hennessy. Hennessy was murdered on October 15, 1890, an event which sparked riots in New Orleans and led to the lynching of eleven Italian-Americans. The contest had been open to many New Orleans monument men, including Charles A. Orleans, the city’s prominent monument builder at the time.[7] The monument was described by national trade periodical Stone magazine as “one of the handsomest monuments in New Orleans”:
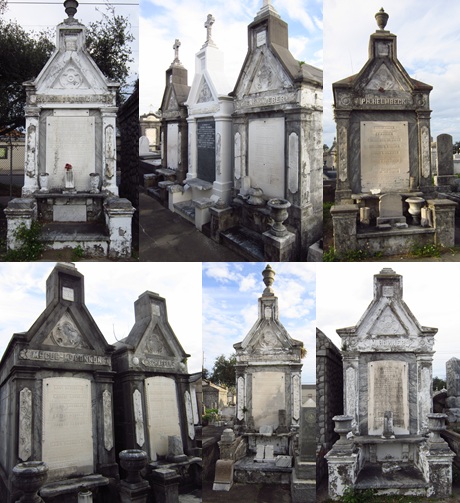
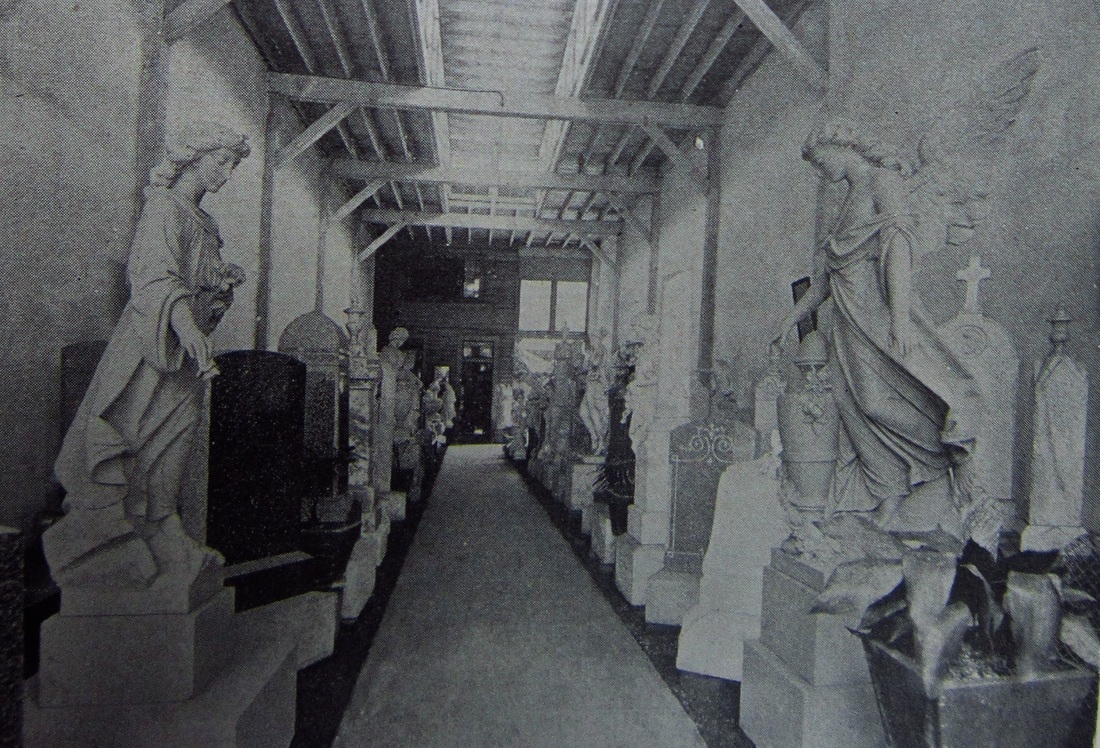
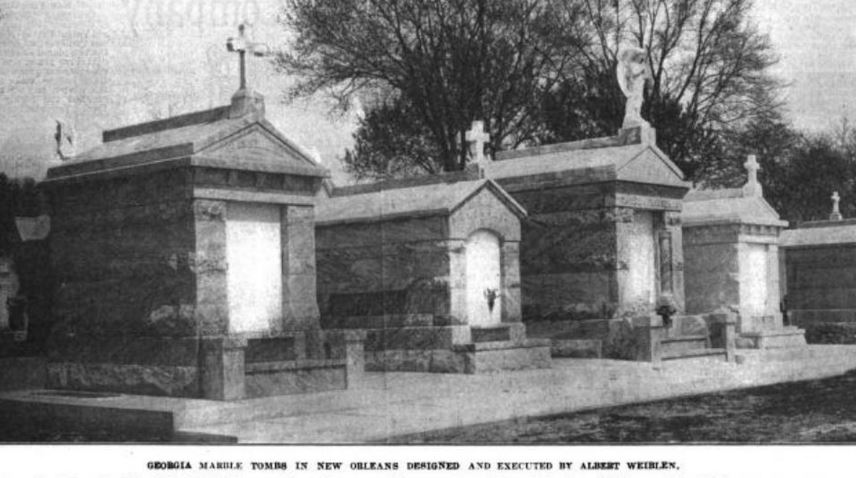
From this location, Weiblen had a workshop complete with powerful equipment to cut, shape, polish, and engrave marble and granite slabs. At the turn of the century, Weiblen’s equipment was not only state of the art (the largest in the South), but was also one-of-a-kind in New Orleans, where technologies were relatively slow to catch on.[10] A skilled marketer and self-advertiser, Weiblen described this equipment in detail in his advertisements, spending nearly half of one circa 1900 advertising booklet explaining its advantages over “the old-time and very laborious manner of cutting by hand.”[11] That Weiblen frequently looked outside of New Orleans for materials and technologies made him, in general, a man of his time. By 1900, the monument industry in the United States was galvanizing as a national trade. Periodicals and trade magazines illustrating the newest and best quarries, saws, cutting methods, and others flourished. Even in New Orleans, Charles Orleans and others had begun to reach outward to peers in the east, newly accessible by infrastructure. Yet Weiblen certainly had a flare for this type of resourcefulness. In 1905, he recruited stonecutters directly from Barre, Vermont, for his shop in New Orleans.[12] The stonecutting shop on City Park Avenue holds in itself a history as visible as any of Weiblen’s tombs. Expanded into the company’s primary sales office in 1907, by the 1920s Weiblen came into possession of five marble sculptures that were once part of the old New Orleans Cotton Exchange. Two of these sculptures, caryatids from the Exchange entranceway, were incorporated into the showroom entrance. The other three, representing Commerce, Industry, and Agriculture, were scrapped for their marble, fell victim to vandalism, or were used as road fill, respectively. The caryatids, however, remain in the Weiblen building, which now houses the Orleans Parish Communication District.[13] The Quarry Man In 1911, Albert Weiblen and his son George leased an interest in a quarry at Stone Mountain, Georgia, from the Venable Brothers company. This was one of a number of savvy moves by the elder Weiblen that helped him cut down his supply chain. By the 1930s, Weiblen would lease another quarry in Elberton, Georgia. His sons, George, Frederick, and John, would all live at the Georgia quarries.[14] In the 1920s, the Weiblens – specifically George and Frederick (who died in 1927) – would begin a long journey of involvement in the carving of the Confederate monument at Stone Mountain, which would not be completed until 1970, the year of George’s death. At these quarries, Weiblen further expanded his infrastructural advantage. By 1936, Weiblen had constructed a full-service carving shop on-site at his Elberton quarry – complete with one of the largest air compressors in the country.[15] Paired with the rail spur he had also built, this permitted Weiblen Marble and Granite to streamline its orders directly from the source. In 1940, Weiblen moved all of his manufacturing operations to Elberton. From this point on, tombs, monuments, and other orders would be ordered from catalogs by customers in New Orleans, manufactured in Elberton, and sent direct by rail to Louisiana, ready for assembly.[16] This advantage also allowed Weiblen to flood the New Orleans market with the products of his quarries, directly transported by rail from their source. Between 1900 and 1940, Weiblen's activities bolstered a stylistic and material shift in New Orleans cemetery architecture. Granite was much more accessible than in the past, and led to new uses as facing and coping material. Georgia marble overtook other sources for new closure tablets, copings, tomb claddings, and other elements. Ever on the marketing edge, Weiblen Marble and Granite even coined a new name for a specific type of Georgia marble, distinguished by sweeping gray and white color patterns: Georgia “Creole” marble (now called “solar gray”). Other burgeoning New Orleans suppliers took up the source, leading Creole marble to be found in large sections of cemeteries like Greenwood, Masonic, and Metairie. Weiblen also attached his name to the granite his company supplied, which is known even today in some circles as “Weiblen gray.” A Cemetery Family Weiblen’s success was passed on to his surviving sons, George and John. George Weiblen operated the Stone Mountain and Elberton interests until his death in 1970. John Weiblen, alternately, assumed his father’s mantle as president of Weiblen Marble and Granite, after Albert Weiblen’s retirement. It was at this time, between 1948 and 1951, that the family company assumed controlling interest in Metairie Cemetery Association. While the purchase of arguably the most prestigious cemetery in New Orleans would have been a grand accomplishment, it also coincided with a larger trend among New Orleans stonecutters in the 1940s.[17] With the monument industry widening to a national scale, and paired with other factors surrounding cemetery management and use, the traditional model of the New Orleans stonecutter that once suited in the nineteenth century was no longer adequate after World War II. This trend was present across all New Orleans cemeteries. In Protestant Girod Street Cemetery, the position of sexton (caretaker), historically held by a stonecutter, was eliminated. This was true also of City-owned cemeteries like Lafayette, Carrollton, Holt, and Valence, in which the position of sexton was eliminated and the management of cemeteries delegated to the City Department of Property Management. The role of the stonecutter, then, was no longer supported by specific cemeteries.[18] Across New Orleans, it became more economically feasible for stonecutters and monument men to shift paradigms from being caretakers of cemeteries to owning the cemeteries outright. Sextons of the Lafayette Cemeteries for three generations, the Alfortish family moved to Gretna and opened Westlawn Cemetery. Victor Huber, monument dealer and caretaker of St. John Cemetery, assumed controlling interest of that burial ground and opened Hope Mausoleum. In 1951, the Stewart family purchased property adjoining Metairie Cemetery and opened Lake Lawn Park and Mausoleum.[19] In this sense, Weiblen’s shift from producer of Metairie’s monuments to owner of Metairie’s business was a natural one. John Weiblen preceded his father in death in 1956, leaving his widow, Norma Merritt Weiblen, to manage Metairie Cemetery, which she did so until the property was purchased by Stewart Enterprises, Inc., in 1968.[20] Passing the Torch According to son George, on the morning of May 1, 1957, Albert Weiblen “said he wanted to lie down before breakfast… took one deep breath and he was gone.” At the age of 99 years, Albert Weiblen died, leaving a legacy of innumerable monuments, buildings, statutes, and sculptures behind him. Still working on the Stone Mountain sculpture in the 1960s, George Weiblen noted that he wanted to find a way to carve his father’s name into the stone, “I don’t know how I will work his name in, but there is a way.” Long after Weiblen’s death, the cemeteries of New Orleans bear the mark of his work at nearly every turn. One estimate suggests that nearly half the tombs and monuments in Metairie Cemetery were constructed by Weiblen’s company.[21] In fact, a street off of Canal Boulevard near Greenwood Cemetery is even named after the great monument man. Albert Weiblen was buried in Metairie Cemetery, under a red granite monument. Weiblen's monuments, tombs, buildings, and other projects are innumerable. Weiblen even designed and built the Cuban capitol at Havana. The collection of images below is only a small example of the work of his lifetime.
[1] Leonard V. Huber, Peggy McDowell, and Mary Louise Christovich, New Orleans Architecture, Vol. III: The Cemeteries (Gretna: Pelican Publishing, 2004), 55, 62; “Time Marches On, but Weiblen Memorials Remain to Remind,” Times-Picayune, January 25, 1937, 170.
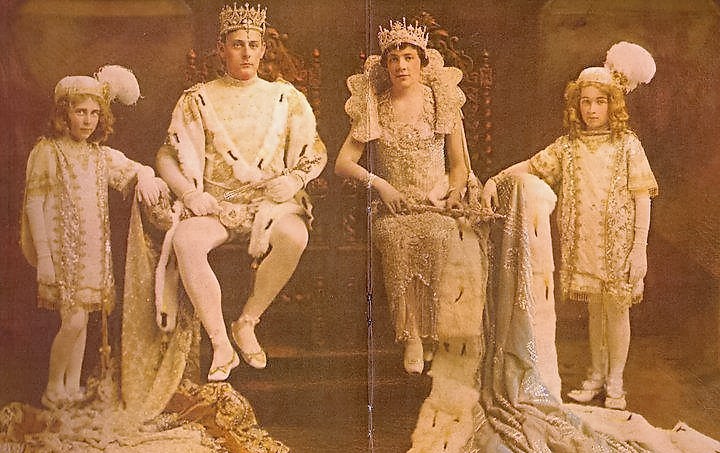
[2] Emily Ford, The Stonecutters and Tomb Builders of Lafayette Cemetery No. 1, New Orleans, Louisiana (MS Thesis, Clemson University, 2013), http://tigerprints.clemson.edu/all_theses/1613/, 96. [3] Ibid. 121-132. [4] Ibid. 164-181. [5] “Time Marches On, but Weiblen Memorials Remain to Remind,” Times-Picayune, January 25, 1937, 170; Soards’ New Orleans Directories, 1885-1910, these directories discourage the notion that Weiblen actually purchased Kursheedt & Bienvenu, which continued until 1901. [6] “Albert Weiblen Marble and Granite Co., Inc.” Times-Picayune, January 25, 1937, 170. [7] Huber et. al., New Orleans Architecture, Vol. III: The Cemeteries, 61-62. [8] “The Hennessy Monument,” Stone – An Illustrated Magazine, Vol. V (June-November 1892), 142. [9] “Ship Brings Cargo of Italian Marble,” Times-Picayune, July 27, 1914, 8; “A Big New Orleans Plant,” Rock Products, Vol. VII, No. 7 (January 1908), 23. [10] “A Prominent Southern Establishment,” The Reporter, Vol. 32 (August 1899), 7. [11] c. 1900 advertising pamphlet, Weiblen Marble and Granite Company, from Tulane University Southeastern Architectural Archive, Collection 39. [12] “Wanted,” Barre Daily Times, July 26-30, 1905, 7. [13] “More about the caryatids,” Times-Picayune, November 17, 1987, 12. [14] “Fred. E. Weiblen Succumbs Here: Was Executor of Granite Work on Confederate Monument,” Times-Picayune, April 12, 1927, 3. [15] 1936 advertising brochure, Tulane University Southeastern Architectural Archive, Collection 36. [16] 1946 advertising brochure, Tulane University Southeastern Architectural Archive, Collection 36; “Marble Works as New Policy,” Times-Picayune, October 2, 1940, 11. [17] “Stone Company Executive Dies,” Times-Picayune, March 23, 1956, 5; Huber, et. al., 59. [18] “Girod Cemetery Vandals Hunted,” Times-Picayune, June 7, 1952, 3; “A Strong Fund,” Times-Picayune, August 23, 1942, 10; Ford, 116. [19] “Lake Lawn Park Plans Revealed: One of Largest Mausoleums in US Promised,” Times-Picatune, March 8, 1950, 42. [20] “He brings city of dead to life,” Times-Picayune, April 14, 1985, B-8. [21] Huber, et. al., 55. During Mardi Gras season, New Orleans sees increased tourist traffic to one of its most popular attractions: its cemeteries, particularly Lafayette Cemetery No. 1 and St. Louis Cemetery No. 1. It nearly seems counterintuitive to visit a place of death and remembrance on a trip so populated with mirth and celebration. Yet the relationship of New Orleans cemeteries to its carnival celebrations is much richer than simply beads on wrought iron or the odd Muses shoe left on a tomb shelf. While the Carnival celebration is one of life and vivacity, the themes of mortality and cemeteries often creep into the mix. From death-themed floats, krewes, and costumes to actual celebrations in the cemeteries themselves, our cities of the dead have been part of the Mardi Gras stage since the 19th century.
The first (and last) Jewish man to serve as Rex in New Orleans’ Mardi Gras, Salomon later moved to New York, although he visited New Orleans each year for Mardi Gras for decades after his reign. He died in 1925 and, surprisingly, it appears as if no one knows where he was buried. His final resting place seems to remain a mystery. His sister Delia, however, married local liquor dealer Otto Karstendiek and, upon her death in 1866, was buried in the only cast-iron tomb in Lafayette Cemetery No. 1. Lewis Salomon was remembered as the first Rex for decades after his great parade. And although his final resting place may remain a mystery, it stands to reason that it does, in fact, exist someplace. Unfortunately, neither of these things were true for the third King of Carnival, Rex 1874, A.W. Merriam.
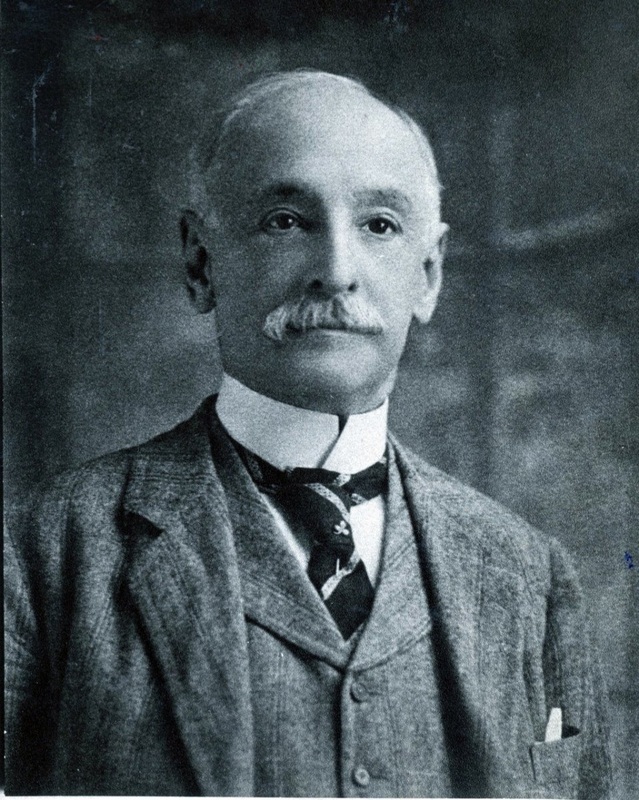
Merriam’s funeral was held days later and, in an even more tragic turn of fortune, his moral remains were paraded to Girod Street Cemetery, where he was interred.[1] While the old king may have rested in peace for as long as seventy years, Girod Street Cemetery was demolished in 1957. Whether the remains of A.W. Merriam were transferred to Hope Mausoleum (as all unclaimed remains of white people reportedly were) or elsewhere, or at all, is anyone’s guess. No record concerning Girod Street Cemetery includes his name. Rex rules his chaotic kingdom for a day. He is emblematic of both disarray and refinement, satire and grace. Upon the close of the evening on Shrove Tuesday, when Rex has met with the Court of Comus and the curtain is drawn on the season, Rex relinquishes his rule until next year, when he returns in the guise of another man. For most of those who served as Rex, death and burial was a rather uneventful affair. Yet one King of Carnival would have a much greater impact on the cemeteries of New Orleans than simply being buried there. The Builder King In 1915, Mardi Gras took place on February 16. Rex this year was Ernest Lee Jahncke, who “headed the procession on a golden chariot of state symbolic of his imperial power… crowned with jewels and wearing a mantle of cloth of gold, [sitting] upon the throne in the center of the car, gracefully acknowledging the plaudits of his subjects.” The theme that year was “Fragments from Sound and Story,” and featured such floats as “The Fatal Kiss of Undine (the water nymph)” and “The Barter of Mephistopheles,” illustrating the bargain of Dr. Faust with the devil.[2] Rear Admiral (USNR) Ernest L. Jahncke (1878-1960) served as assistant secretary of the Navy from 1929 to 1933 and was himself a “renowned yachtsman.[3]” He was the son of Fritz Jahncke (1847-1911), a German immigrant and founder of Jahncke Navigation Company. The elder Jahncke was instrumental in one of the greatest shifts in tomb construction in New Orleans history. Beginning in 1879, Jahncke was one of the first building supply dealers to make Portland cement available for his clients. While Portland cement had been available elsewhere in the country as early as the 1860s, its use was nearly unheard of in New Orleans prior to Jahncke’s business. Since the 1700s, builders in New Orleans cemeteries used mortars, stuccoes, and renders mixed from hydrated lime, a material procured from burning limestone or oyster shells in a kiln. These materials required protection from the elements, usually achieved by limewashing tombs on a regular basis.
The materials which Fritz Jahncke had made available to New Orleans cemetery builders would eventually replace lime-based stuccoes and shift the way tombs were constructed. Just as importantly, Jahncke established himself as a great paver, paving sidewalks and streets using new cement mixes and replacing the brick and shell-lined avenues that once marked neighborhoods and cemeteries. These materials in cemeteries cut down on the need to mow grass or perform other landscaping. An unintentional consequence of this paving process was the exacerbation of drainage issues in cemeteries which continue to this day. The Jahncke family expanded from serving as Mardi Gras royalty a century ago to owning a shipyard and a dry dock in addition to the cement company. Ernest continued these businesses into the twentieth century and long after his reign as Rex. He was, however, the Rex spokesperson who, in 1942, announced that Mardi Gras would be cancelled that year in the spirit of solemnity and frugality in the face of World War II. Both Ernest and Fritz Jahncke are buried in Metairie Cemetery. In the next installment of our examination of New Orleans cemeteries in Mardi Gras history, we bring death to the party itself and check out cemetery and mortality-themed floats, krewes, and costumes.
|
About the Author:Emily Ford owns and operates Oak and Laurel Cemetery Preservation, LLC. Archives
November 2019
Categories
All
|
- About
-
Restoration
- Services
-
Portfolio
>
- Turning Angel Statue, Natchez, MS
- Ledger Monument, Baton Rouge, LA
- Pyramid Statuary, New Orleans, LA
- Bronze and Granite Monument, Carville, LA
- Box Tomb, New Orleans, LA
- Vernacular Concrete Monument, Pensacola, FL
- 1830s Family Tomb, Covington, LA
- 1850s Family Tomb, New Orleans, LA
- 1880s Family Tomb, New Orleans, LA
- Headstone and Monument Restorations, Pensacola, FL
- Society Tomb, New Orleans, LA
- Education
- Blog
- Contact
|
Oak and Laurel Cemetery Preservation, LLC is a preservation contractor in New Orleans, Louisiana, specializing in historic cemeteries, stone conservation, educational workshops and lectures. Oak and Laurel serves the region of the Southeastern US.
|
QUICK LINKS |
CONNECTNew Orleans, Louisiana
restoration@oakandlaurel.com (504) 602-9718 |
Proudly powered by Weebly