|
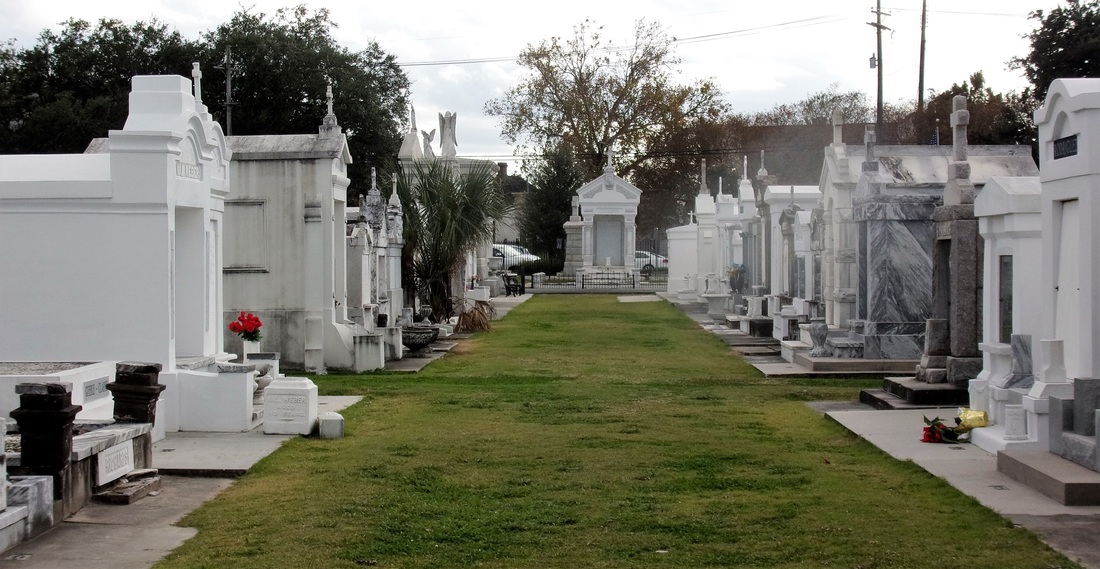
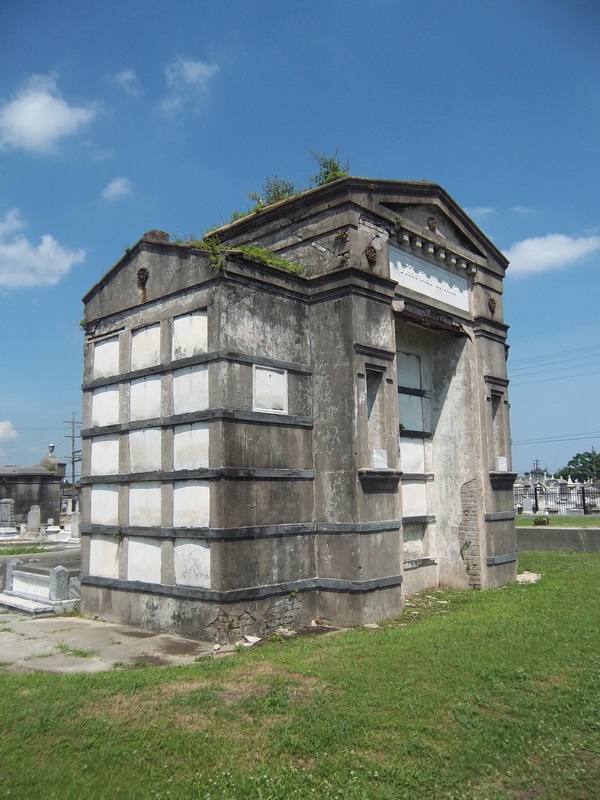
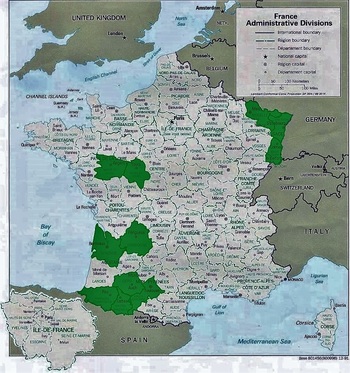
This blog post is Part Two of a two-part piece on the tomb of the Sociètè Française de Bienfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Jefferson, located in Lafayette Cemetery No. 1. To learn about the history of this French Society, check out Part One here. Recently, Oak and Laurel Cemetery Preservation, LLC transcribed the burial records of the tomb of the Sociètè Française de Bienfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Jefferson, located in Lafayette Cemetery No. 2, thanks in part to a grant from genealogist Megan Smolenyak. The Society was absorbed by the Sociètè Française de Bienfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Nouvelle Orléans in 1900. About the Record Books The records of the Sociètè are housed at LSU Special Collections, Hill Memorial Library, in Baton Rouge. (MSS 318, 1012) The burial books appear to have been included with the larger collection of papers from the Sociètè Française de Bienfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Nouvelle Orléans (French Benevolent and Mutual Aid Society of New Orleans) which absorbed its Jefferson City counterpart in 1900. The collection is comprised of two books, dating from the tomb’s construction in 1872 through 1900. While later interments were certainly made in the Lafayette Cemetery No. 2 tomb, their record appears to have been incorporated into another, as-yet unstudied document. Within these two books are the burial documents for 186 individuals. Among these records, 142 people were buried in the society tomb in Lafayette Cemetery No. 2, 32 were provided formal burial aid by the society and were interred in family tombs throughout the city, and 12 were not specified as to burial location.[1] Each burial record documents the date and place of the individual’s birth, date and place of death, as well as cause of death and information regarding membership. These documents shed light on the lives of hundreds of people. They allude to intricate familial and professional relationships, personal tragedies, and public calamities. They offer a window into a rich community, the vestiges of which stand silent in this stately yet neglected tomb in Lafayette Cemetery No. 2. Today we share the stories of those buried within. The Foreign French: Founding Members and their Origins The Sociètè Française de Bienfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Jefferson was organized in 1868 by native-born French men – eight of whom are buried in the Lafayette No. 2 tomb. Much like the New Orleans French society, these immigrants sought fraternity among their countrymen. Incidentally (or perhaps not so much so), most of these men were born in the same French provinces (départments), and often in the same village. The majority of adults buried in the Sociètè tomb originated from two primary areas in continental France: the department now known as Midi-Pyrenees, including Gers, Haute-Pyrenees, Haute-Garonne, and Bass Pyrenees (now known as Pyrenees-Atlantiques), and the eastern departments of Alsace-Lorraine, specifically Haut-Rhin, Bas-Rhin, and Moselle. These two areas are nearly as geographically disparate as can be, with the former nestled along the Pyrenees mountains at the Spanish border, and the latter at the Rhine River beside present-day Germany.
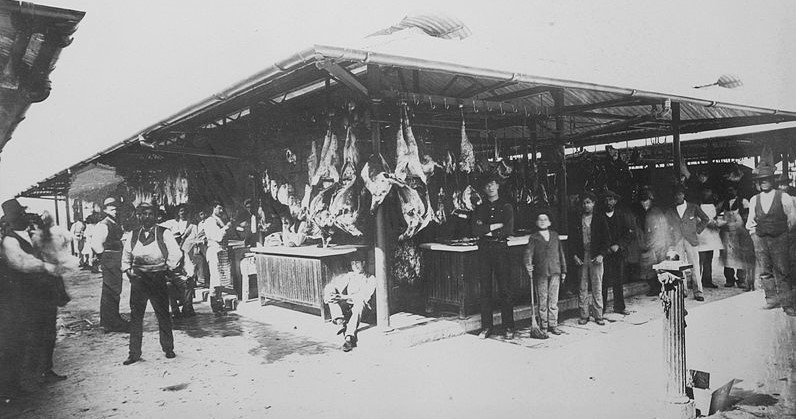
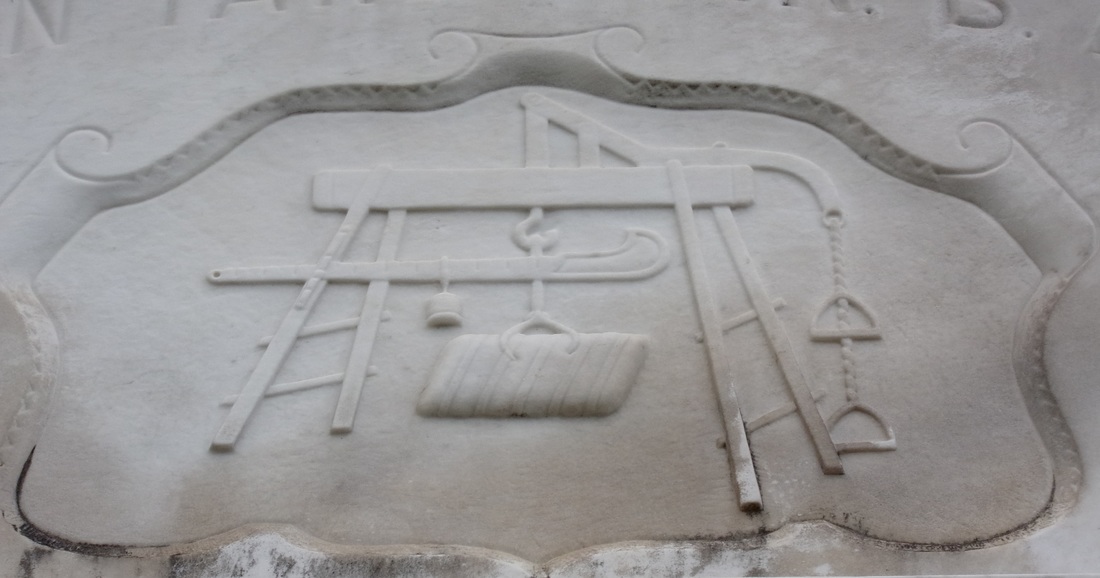
In Alsace-Lorraine, a different climate motivated the eventual members of the Sociètè to emigrate from their homes. The Franco-Prussian War (1870-1871) forced many Alsatians from their homeland when the controls of the provinces shifted from France to newly-nationalized Germany. For French-speaking Alsatians, both Jewish and gentile, German citizenship was a less than desirable option. New Orleans was an attractive alternative due to its Francophone tradition. Among these Alsatian emigrants were sisters Catherine and Marie Sonntag, both in their early twenties from Altinstadt, Alsace. Nieces of Sociètè member O.M. Redon, they both died of yellow fever within weeks of each other in October 1872. They were buried in vaults 20 and 22 of the Lafayette No. 2 society tomb. While the people buried in this tomb overwhelmingly shared a linguistic and cultural bond, there is no shortage of strangers among the burials in Lafayette Cemetery No. 2. Although the tomb was built for French society members, those members were not always French. Strangers in a Strange Land: Non-French Buried in the French Tomb A handful of foreign-born non-French people were laid to rest in the Lafayette Cemetery No. 2 society tomb. Their stories contribute to the greater narrative of the society which at its heart was thoroughly New Orleanean in its cultural interactions. From Germany, Catherine Deffenback and brothers John and Jacob Schwenck were buried in this tomb at their time of death. The Schwenck brothers owned a saloon together on Magazine Street.[3] Leon Vignes, from Mont-de-Marrast, France, mourned the death of his Irish-born wife, Margaret, in 1884. She is buried in vault 35. Leon died fifteen years later and was buried in vault 38. He was not the only person to join the matrimonial melting pot: The wife of J.M. Gelé was born in England and died in 1872, buried in vault 26. Perhaps the most interesting foreign-born member of the society is not buried in the Lafayette No. 2 tomb but instead only blocks away in Lafayette Cemetery No. 1, although no tablet remains to mark his name. Louis Savini was born in 1830 in Mortara, Italy. By the time he was eleven years old, he and his family had taken residence in New Orleans. From the very scant documentation remaining, Savini appears to have led a colorful life. He owned a saloon in what is now the Central Business District on Common Street, near the Mississippi River.[4] For reasons unclear from available records, Savini joined the Sociètè Française de Bienfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Jefferson in 1874. Only months after joining the group, however, Savini was struck down by a “cerebral fever,” which could indicate encephalitis, meningitis, or scarlet fever. He died on June 1, 1874 in his home on Poydras Street. The Sociètè not only furnished his burial in Lafayette Cemetery No. 1, but also provided a procession befitting a French society member. Savini was buried in the tomb of his brother, Paul Savini, in Quadrant 2 of Lafayette Cemetery No. 1. Today, the tomb is in a state of dangerous neglect and has lost the closure tablet bearing Louis Savini’s name. As the Sociètè aged, its members increasingly were New Orleans natives. Over time, both the children of members and other Francophone Louisianans joined, advancing the process of assimilation in a new country. The Family Tomb At least one hundred and forty-two individuals are buried in the Sociètè Française de Bienfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Jefferson tomb in Lafayette Cemetery No. 2. Some were recent immigrants with little or no family left behind. For a striking number of society members, however, the tomb was the final resting place for multiple generations. It has already been noted that Leon and Margaret Vignes rest near each other in this tomb. They are also interred with their son, Joseph, who drowned at the age of 14 in 1891. He is interred in the same vault as his mother. The Fortassin family likely also utilized the society tomb for the interment of multiple generations. In 1870, twenty year-old Gabriel Fortassin, Jr., arrived in New Orleans from Trie, France. His parents joined him as well. In 1882, he married Alexandrine Claverotte.[5] The two would briefly move to San Antonio, Texas before returning to New Orleans. In his lifetime, Gabriel would bury his parents in the society tomb, as well as five of his infant children. When he died in 1927, he was given a French Society burial in Lafayette Cemetery No. 2.[6] One of Gabriel’s adult sons, Baptiste Fortassin was also buried in Lafayette Cemetery No. 2, in 1929. Two years later, Baptiste’s widow Marie Maille joined him. With no Fortassin tomb in Lafayette Cemetery No. 2, it is very likely they joined their relatives in this tomb, making it the last resting place of three generations of one family, with at least nine burials.[7] Other families utilized the society tomb similarly. Surnames such as Tujague[8], Abadie, Mouledous[9], Vignes, and Carrare appear multiple times through the burial books, representing multiple generations. These records also show combinations of the above-mentioned names, linked by intermarriage. Eleanor Vignes Tujague and Pauline Mouledous Tujague are both buried in the Lafayette Cemetery No. 2 society tomb. Society members formed a strong, interdependent community. They even stood at each other’s deathbeds to witness a last will and testament.[10] Death and burial were only the final threads that tied these French-speaking New Orleaneans together. In life, they lived and worked beside one another. As the French Society of Jefferson, members lived predominately within the boundaries of the former Jefferson suburb (portions of present-day Garden District, Irish Channel, Central City, and Uptown neighborhoods). Burial records note the residences of a multitude of members as near the St. Mary’s Market and along Tchoupitoulas Street. Even more records note residence as simply “aux abbatoirs,” or “near the slaughterhouses.” Which is no surprise: the majorit of members were butchers. A Workingman’s Society The Sociètè Française de Bienfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Jefferson shared members and celebrated social events with the Sociètè de Bienfaisance des Bouchers, or the French Butchers Society. Their enormous, eighty-vault society tomb remains also in Lafayette Cemetery No. 2. Members of each society lived near the Mississippi River, where cattle were unloaded at river docks. Until the late 1860s, the City of New Orleans had little regulation regarding the slaughter of livestock. Butchers were free to practice their trade where they pleased, usually near a market where they could sell their wares. This changed with a municipal law that required butchers slaughter livestock exclusively in a city-owned slaughterhouse, the goal of which was to prevent public health hazards.[11] Opposition to this law among butchers of both French societies led to civil unrest and years of legal battles. The case finally reached the Supreme Court in a landmark ruling known as the Slaughterhouse Case. Among the French and Butchers societies, the butcher’s trade was passed through generations and within a tight-knit community. Members lived in close proximity to each other, with addresses at Louisiana, Camp, Chippewa, Annunciation, Constance, Josephine, St. Mary, Tchoupitoulas, St. Andrew, Washington, Magazine, and Rousseau Streets. The propensity to take on the butcher’s trade among these society members is truly overwhelming. One casual cross reference of members’ names with an 1878 directory revealed nine butcher/members alive and working at the time: Gabriel Fortassin, Jr., Jean Abadie, Joseph Barrere, Pierre Lacaze, Bernard Lacoste, John William Lannes (Lannis), Pierre Sabatte, and Leon Vignes. The other three members searched, Victor Brisbois, Ulysses Mailhes, and Jacob Schwenck, were all listed as saloon owners or bartenders. Causes of Death If cursory research is to be trusted, the Sociètè Française de Bienfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Jefferson was populated by close friends who slaughtered animals and served alcohol for a living. When this living ended for each individual, however, the causes varied. It should be noted that 65 of the 142 burials (45%) in the Lafayette Cemetery No. 2 tomb were for children under six years of age. The Fortassin family, who buried five children in this tomb, were by no means unusual in their parental grief. Joseph Bararre and his wife Amanda Mailhes buried four children as well, all of whom were interred in vault 8. The high concentration of child burials in this tomb has a dual explanation. In addition to the well-understood status of childhood illness and mortality in the late nineteenth century, it was also much more likely for a family to bury a child in a society tomb than one built for a family. Married couples without their own family tomb were unlikely to purchase a lot for the burial of a child or stillborn infant. Instead, it was much more affordable to inter the child in a wall vault or society tomb, if available. Furthermore, the spiritual and emotional benefits of society-supported burial of a child were likely comforting. A significant percentage of the 65 infant/child burials were the stillborn or nonviable infants of society members. The other children of the Sociètè died of many common childhood maladies, including lockjaw (tetanus), cholera, croup, seizures, and whooping cough. Six children were listed as having died either of “bad teething” or a jaw ailment. In the nineteenth century, a range of many ailments was attributed to the process of teething in toddlers, including intestinal disease, seizures, meningitis, or even crib death. About half of the burial records in the Sociètè burial book list a cause of death. Among the adult members, most causes of death of typical of the time period: apoplexy, Bright’s disease, consumption (tuberculosis), and yellow fever. Surprisingly, only four burial certificates mark yellow fever as cause of death. This statistical anomaly may be explained by society members being buried hastily during times of epidemic, either in other tombs or too quickly to fill the burial form completely. “A Mort et Sans Espoir de Guerison” A few members, however, appear to have died in a slightly more unusual manner. Among them are:
All of the above-listed men were members of the Sociètè who were buried in the Lafayette Cemetery No. 2 tomb alongside lost children, fellow butchers, and more than a few bartenders, as well as many wives, nieces, and grandchildren. A Community Buried Together Nearly all vestiges of Sociètè Française de Bienfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Jefferson have faded from popular memory. The tomb itself does not have a single carved name on any of its forty marble vault tablets. Yet within the decaying stucco vaults of this tomb in Lafayette Cemetery No. 2 are the relics of a great communal history that remains vitally significant to New Orleans cultural heritage. It is the hope that this research might connect the descendants of those buried in this tomb with their ancestors. The full burial rolls of interments into this tomb from 1872 to 1900 (up to the society’s merger with Sociètè Française d’Assistance Mutuelle de Nouvelle Orléans) have been uploaded to FindaGrave, in hopes their descendants may find them. The burial books are also available as an Excel Spreadsheet , MS Access Database, or PDF Document. Click here for burials listed by vault number. [1] Unless otherwise noted, all content is referenced directly from the original burial books as transcribed and documented by Oak and Laurel Cemetery Preservation, LLC. Links to these materials can be found at the end of this blog post.
[2] Arnold R. Hirsch and Joseph Logsdon, editors. Creole New Orleans: Race and Americanization (Baton Rouge: LSU Press, 1992), 112. [3] Edwards’ Annual Directory…in the City of New Orleans, for 1872 (New Orleans: Southern Publishing Company 1872), 366. [4] New Orleans City Directory 1870, 531. [5] State of Louisiana, Secretary of State, Division of Archives, Records Management, and History. Vital Records Indices. Baton Rouge, LA, USA. [6] Times-Picayune, August 28, 1927, 2. [7] Times-Picayune, January 18, 1929, 2; [8] To our knowledge, if this family is related to Guillaume Tujague, restauranteur, it is only distantly. [9] Alternately spelled Moledous, Mouledoux, etc. [10] Pierre Lacaze, also from Trie, witnessed Sylvain Tujague’s final will in 1882. Louisiana Will Book, Vol. 21 (1880-1883). [11] “City Litigation,” Morning Star and Catholic Messenger, May 30, 1869, 5. In this article regarding the Butchers’ filed injunction against the City, the author notes their injunction as “a string of reasons as clear and cutting as the keenest cleaver could demonstrate.”
1 Comment
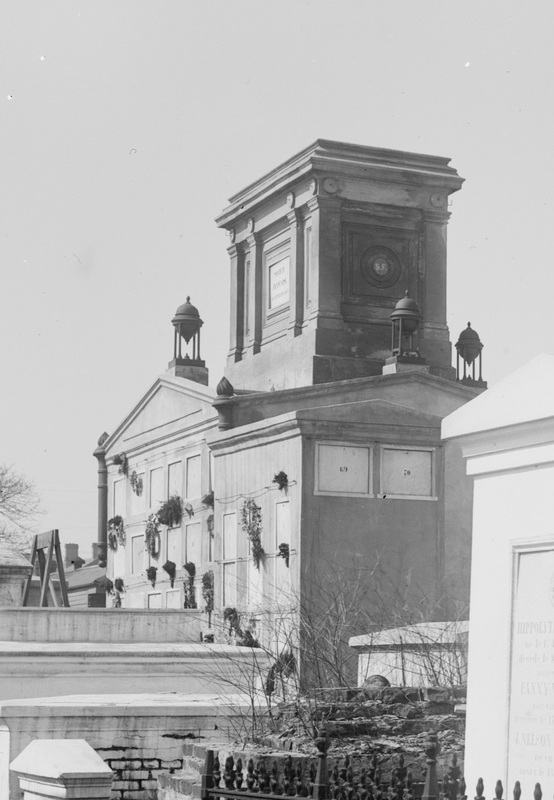
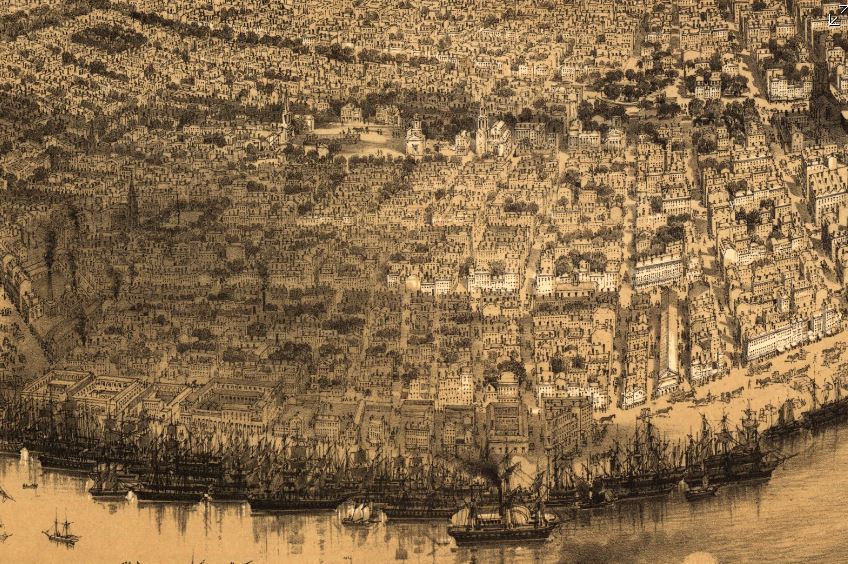
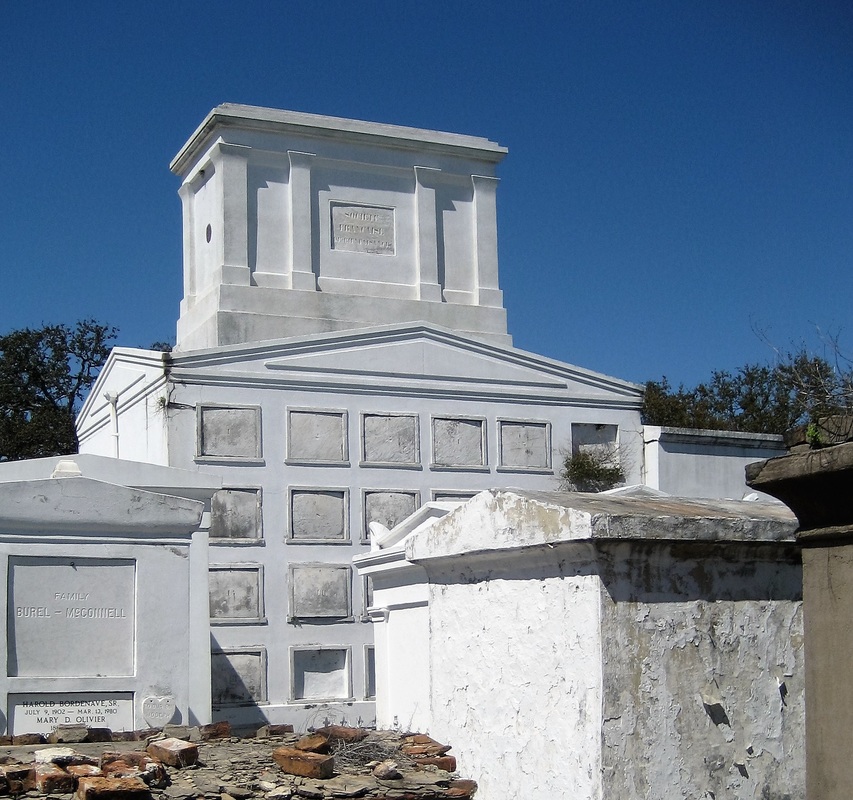
Recently, Oak and Laurel Cemetery Preservation, LLC transcribed the burial records of the tomb of the Sociètè Française de Beinfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Jefferson, located in Lafayette Cemetery No. 2, thanks in part to a grant from genealogist Megan Smolenyak. The Society was absorbed by the Sociètè Française de Beinfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Nouvelle Orléans in 1900. Through this research and through extended investigation into the history of the society, its members, predecessors, and descendants, a rich portrait of the life of French-speakers in nineteenth- and twentieth-century New Orleans emerged. Today, we share the history of that society and its many milestones, members, and tombs. ARTICLE I: The association aims to improve physical, moral, and political fitness of its members; to lend each other assistance and relief in misery; to promote each other’s wellbeing, by council and by example; to collectively inspire the rights and freedoms of the home in all countries, and the practice of the duties, which alone can make them worthy; these are the primary obligations as members define them. – from the original constitution of the Sociètè Française de Beinfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Nouvelle Orléans, 1843 (translated from French).[1] The First French Benevolent Society in New Orleans On March 14, 1843, after four years of preliminary incorporation, the Sociètè Française de Beinfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Nouvelle Orléans (French Benevolent and Mutual Aid Society of New Orleans) was formally established with twenty-seven members. In its own words, the society formed as a result of increasing Americanization of the French colonial city after the Louisiana Purchase and into the Antebellum Era. The Sociètè Française was the first of many organizations in New Orleans with the aim of preserving French language and identity among its members. The Sociètè in New Orleans crafted their organization in the image of fraternal and masonic organizations in France, exemplified by the Grand Orient de France.[2] Similar values were emphasized: brotherhood, charity, social solidarity, and citizenship. The French model of freemasonry also emphasized laicity, or secularism. Among the founding members of the Sociètè in 1843 was a man who himself embodied the political nature of French freemasonry. Pierre Soulé (1801 – 1870) a French native and revolutionary who settled in New Orleans in the 1830s, shaped the early goals and tone of the Sociètè. However, he was elected to the United States Senate in 1847 and thus truncated his involvement. In this year, the Sociètè merged with the French Consulate. Minute books and histories of the Sociètè suggest that after Soulé’s departure, the political aims of the organization were abbreviated in favor of a charitable and social mission.[3] The Sociètè would come to be known for many things – its Bastille Day celebrations, its protection of the French language, its role as the French consulate for some time – but it was likely best known for its Hospital, which was an institution for over a century. French Hospital In the same year as the Sociètè’s founding, a French visitor to New Orleans donated thirty thousand bricks for the construction of a place in which the members could gather. The material was used to build the first French Hospital on Bayou Road near North Robertson Street, described by historians as “a center-hall, gable-sided, double galleried residence.[4]” The hospital, or Asile de la Société Française, cared for Sociètè members and their families. From 1847 to the early 1860s, the organization weathered multiple yellow fever epidemics in which as much as half of the membership was hospitalized.[5] In the early 1860s, the Hospital moved to St. Ann Street, a property donated by then-President Olivier Blineau. Blineau died shortly thereafter and was given the posthumous title of “Father of the French Society.” Originally meant only for society members, French Hospital was opened to all sailors of the French fleet in November 1862, in the event that an illness may require a stay on land.[6] With few exceptions, the Hospital was expressly for the use of members, their families, and those sponsored by members until 1913. In 1913, French Hospital expanded under the decision that “it was finally decided to build a clinic to treat strangers.[7]” Over the next thirty years, the Hospital would include a maternity ward, modern X-ray machines, and operation rooms. The original 1913 building became a well-known edifice on Orleans Street near Claiborne Avenue.[8] Tombs and Burial Benefits Throughout New Orleans history, it was common for societies to form around commonalities of nationality, profession, or background. Most societies would provide benefits similar to those provided by fraternal orders or by modern-day insurance companies. Among these benefits was frequently the option of burial in a society tomb, as well as funereal benefits for survivors. The Sociètè Française de Beinfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Nouvelle Orléans spared little time in establishing a society tomb for itself. On March 14, 1850, the Sociètè acquired a large lot in St. Louis Cemetery No. 1 on Basin Street with the financial aid of the French Consul, M’r Roger. By August of the next year, the first stone of the tomb was laid at a formal ceremony. Beneath this stone, Sociètè officers laid a lead box, in which a copy of the organization’s Constitution, and parchment containing “the names of the President, members of the Consulate, and all members of the society” were placed.[9] The Classically-inspired tomb with an intricate sarcophagus at its apex was completed in the following years. In the early 1850s, the size of the tomb would have overwhelmed the landscape of St. Louis Cemetery No. 1. The similarly-imposing Italian Benevolent Society tomb would not be built until 1857. The cross-gable roof of the tomb supported four cast-iron lamps (now missing), in addition to its large sarcophagus, giving it the appearance of a temple. Each corner of the tomb featured an upright torch fashioned of cast plaster. In historic photographs of the tomb, these torches were painted black.[10] In 1853 and 1856, President Blineau donated two additional lots in St. Louis Cemetery No. 1 to the Sociètè. Either one of these donations may have been for the purpose of building an addition to the tomb. As is visible in the 1895 Library of Congress photograph, a smaller structure was built to adjoin the original tomb, comprised of fifteen vaults. This expanded the Sociètè’s burial capacity to seventy vaults, all of which could be reused over time.[11] Possibly as a result of a yellow fever epidemic in that year, rumors flew in 1867 that St. Louis Cemetery No. 1 would be permanently closed. In response, the directors of the Sociètè organized a picnic fundraiser to construct a new tomb in St. Louis Cemetery No. 3. The nearly $1,000 raised was utilized for the purchase of a lot, which was donated to the Sociètè. Mentions in Sociètè records as well as newspaper resources suggest that a society tomb was in fact built in St. Louis Cemetery No. 3 for the use of the Sociètè Française de Beinfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Nouvelle Orléans. However, no tomb today bears the society name. The Sociètè maintained and repaired their tombs regularly, as was (and is) necessary with New Orleans tomb structures. In 1897 alone, the organization set aside nearly $500 por le fonds du Tombeau.[12] Regular limewashing, painting of plaster elements, cleaning of lamps and urns, and filling inscriptions with copper-based paint were annual expenses that contributed to the well-kept, beautiful structure seen in the 1895 Library of Congress photograph above. Funeral expenses were also part of member benefits. In an 1897 annual report, the Sociètè outlined these benefits specifically, including:
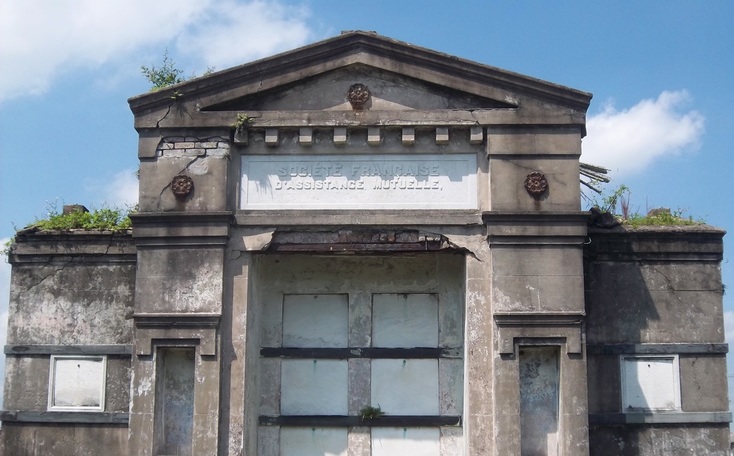
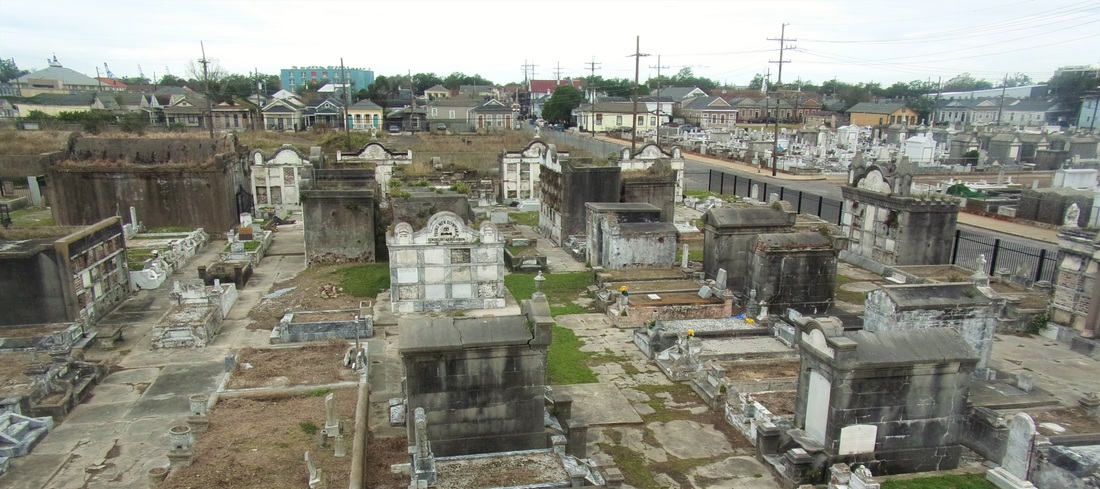
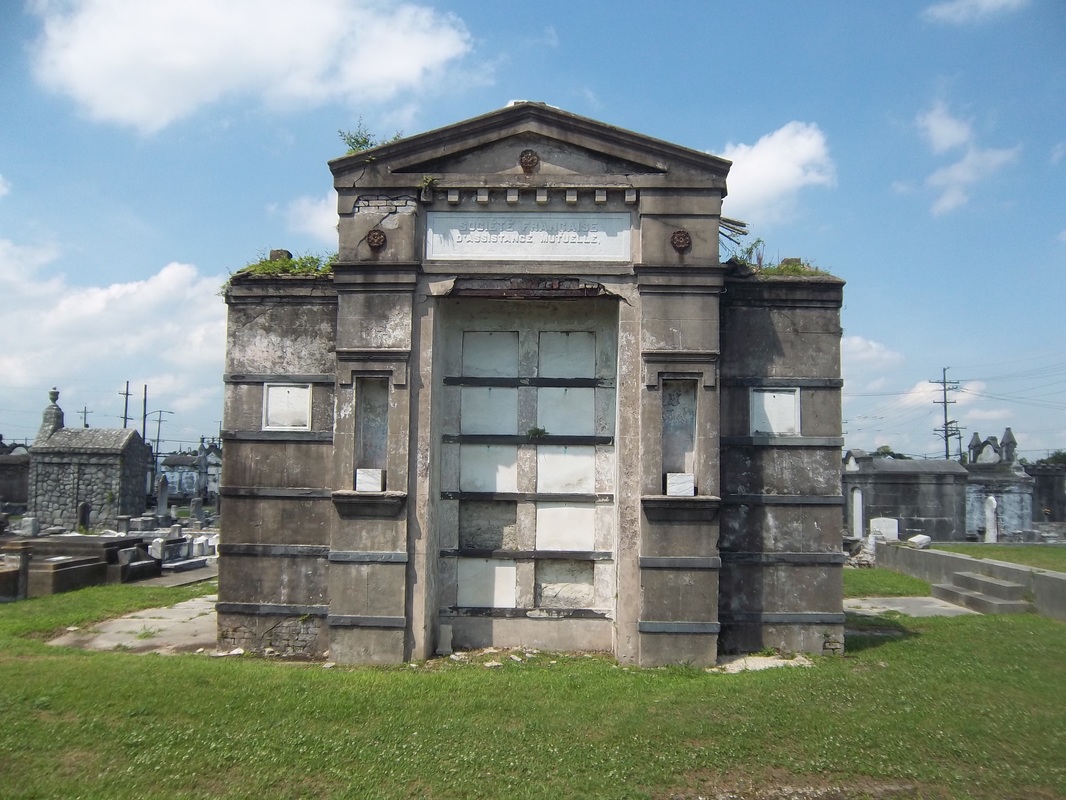
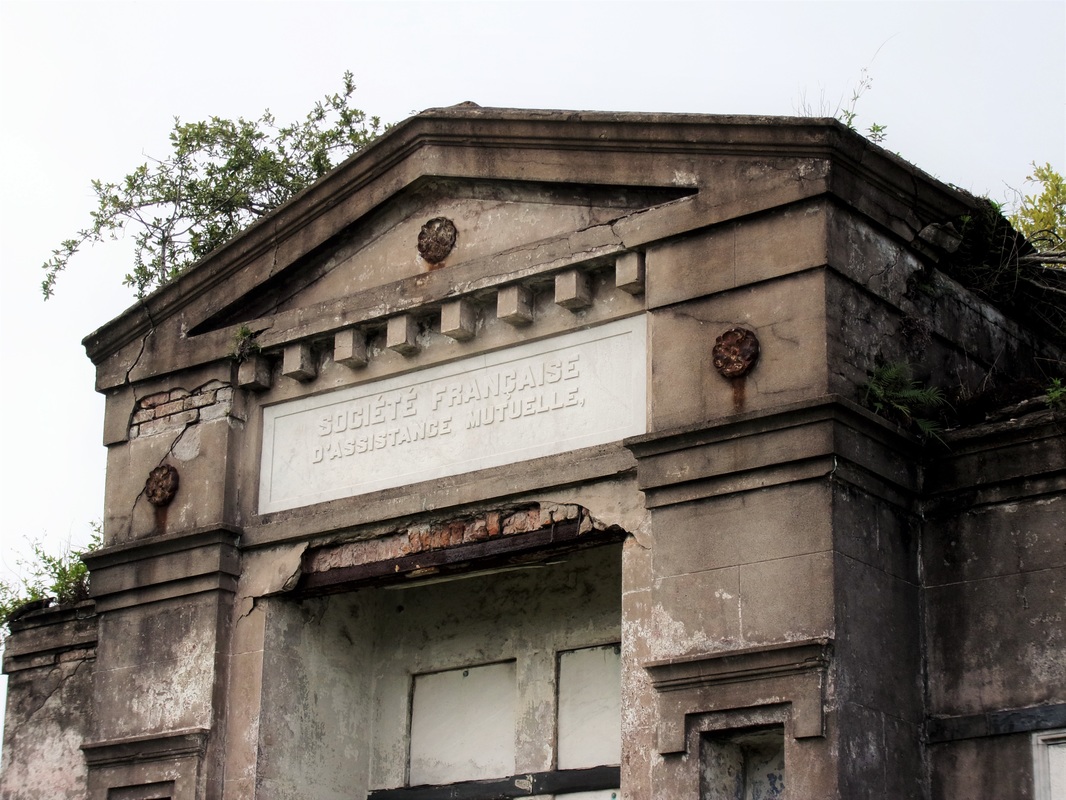
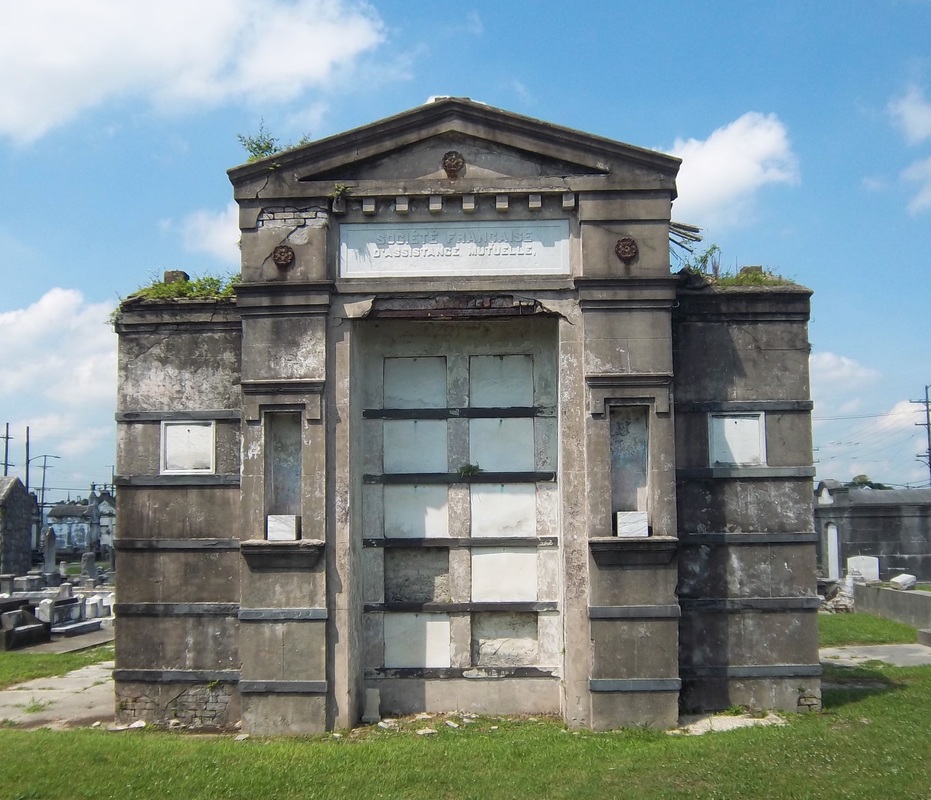
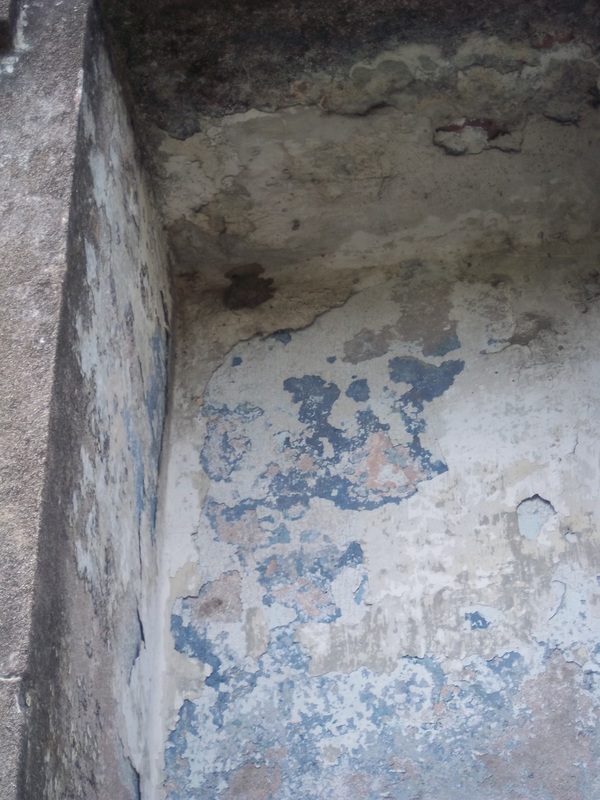
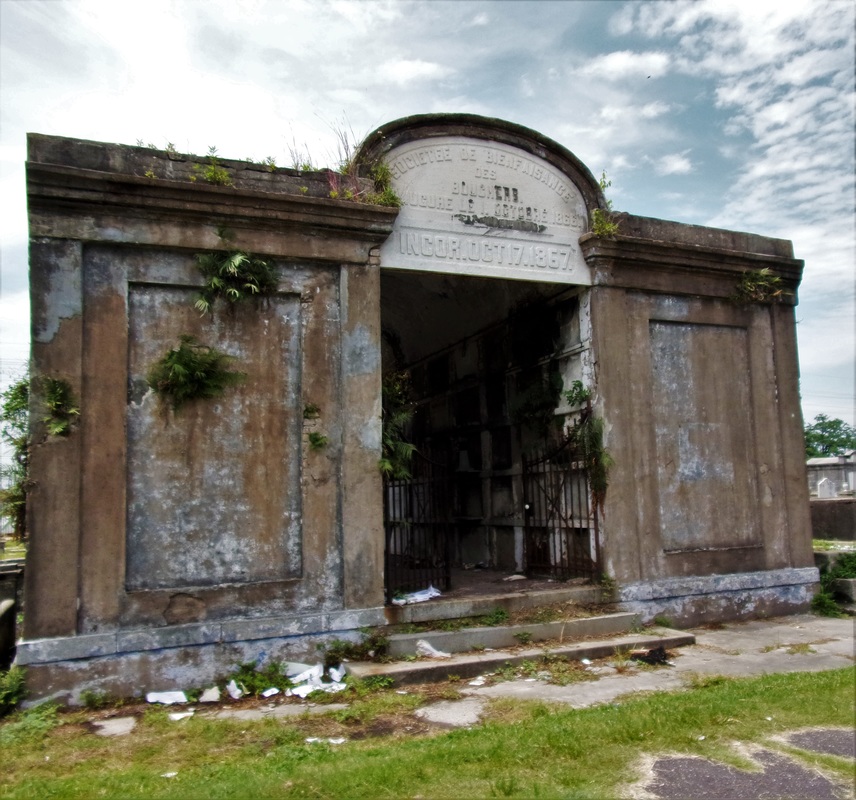
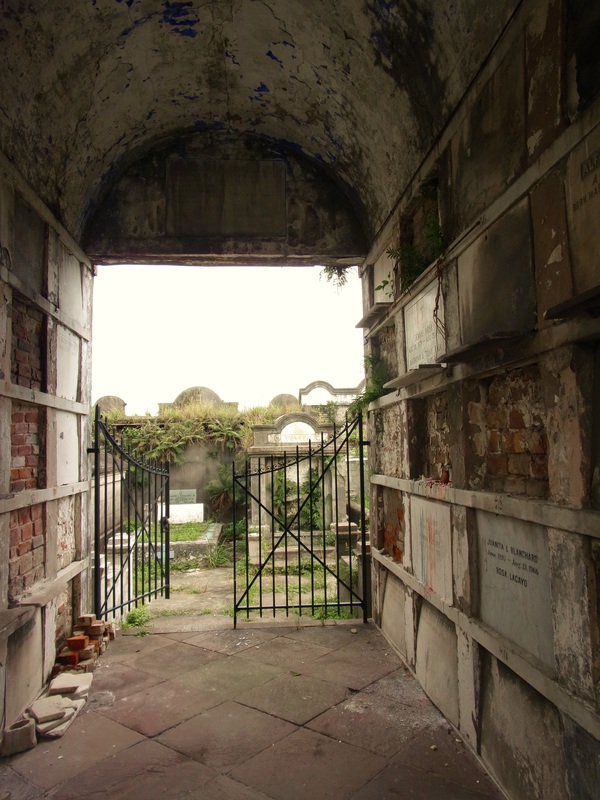
A Sister Society in Jefferson As the Sociètè Française de Beinfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Nouvelle Orléans flourished through the 1850s and 1860s, an additional population of French-speaking people in what was then the City of Jefferson organized their own benevolent society. In the 1850s, the City of New Orleans was much smaller, and bounded on its upriver side by the Faubourg St. Mary and, farther upriver, the City of Lafayette. Over the course of the nineteenth century, New Orleans successively incorporated these municipalities into itself, creating the modern landscape of the city. Between modern-day Toledano and Joseph Streets, and bounded on the downriver side by the former City of Lafayette, the City of Jefferson was incorporated in 1850. Comprised of the Faubourgs Plaisance, Delassize, Bouligny, and others, the city would only remain independent for twenty years before being incorporated into the larger City of New Orleans.[13] It was here that the Sociètè Française de Beinfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Jefferson formed in 1868. The French speakers who lived Jefferson Parish and formed the Sociètè Française de Beinfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Jefferson were in many ways similar to their counterparts in New Orleans proper. In fact, in many cases they were related. Members of the Tujague and Carerre families joined and served as officers in both societies. Members of each group were often natives of the same departments in France, primarily the Pyrenees and Gers. Many had family in St. Bernard Parish as well as Orleans and Jefferson.[14] The Jefferson Sociètè was comprised of men who lived with their families “near the slaughterhouses,” or who lived on Tchoupitoulas, or near the St. Mary’s Market. They collaborated with and shared members with the Sociètè de Bienfaisance des Bouchers (the Butcher’s Society) who in 1873 brought the famous Slaughterhouse Case to the Supreme Court. A number of Jefferson Sociètè members were buried in the Butcher’s tomb in Lafayette Cemetery No. 2. The Jefferson Sociètè built its large, Classically-inspired, forty-vault tomb in Lafayette Cemetery No. 2 around 1872. The tomb is of extraordinary height, particularly in the landscape of this cemetery. Its primary gable pediment was carved with the name of the society, which once read “Sociètè Française de Beinfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de la Ville de Jefferson,” although the “de la Ville de Jefferson” portion of the inscription appears to have been chiseled away after 1900. Below the pediment are stucco dentils, and on each side are cast-iron florets which likely cover structural tie-rods. The tomb has a number of unique additional features. On each side of its primary façade are niches which were once painted a brilliant Prussian blue, a historic pigment made with iron oxide. In each of these niches were marble statues of kneeling women, one of which had her hands raised in prayer, the other’s hands were crossed on her chest. Both of these statues were stolen between the 1950s and 1980s. The tombs gable-roof side projections hold most of its burial vaults, each enclosed in marble tablets and divided by slate slabs. All tablets of this tomb are uninscribed, leaving the names of those buried within to mystery until the recent transcription of burial books – which revealed the names of at least 150 people buried in this tomb between 1872 and 1900. The Sociètè Française de Beinfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Jefferson participated in the celebrations of a number of French societies in the city. In addition to the New Orleans Sociètè, the Jefferson Sociètè was frequently documented in relationship with the Fourteenth of July Society and the Children of France. 1900: Merging of the Societies By 1896, at its twenty-seventh anniversary, the Jefferson Sociètè had “fifty or sixty” members – a roster that the Daily Picayune regarded as “not quite so large a membership now as at other times in its history.”[15] Officers from the Butcher’s Society and the New Orleans Sociètè, the French Orpheon, and the Fourteenth of July Society raised glasses of wine to the Jefferson officers B. Tujague, O.M. Redon, F. Desschautreaux, T. Abadie, and M. Despaux – most of whom would eventually be buried in the Lafayette Cemetery No. 2 society tomb. It was only four years later that the dwindling numbers of the Jefferson Sociètè merged with their older counterparts at the Sociètè Française de Beinfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Nouvelle Orléans. The merger was completed on January 3, 1901, which records report “brought 41 new members to the society. It also brought to the Society a tomb of forty vaults, nearly new, located in Lafayette Cemetery No. 2.”[16] The New Orleans Sociètè had merged with other organizations before, beginning with the French Consulate in 1847. In 1895, they also absorbed the Philanthropic Culinary Society of New Orleans, who brought with them an additional burial place: a five-vault tomb located in St. Vincent de Paul Cemetery on Louisa Street.[17] A Centennial Celebration and Gradual Decline While the New Orleans Sociètè had gained the members of its Jefferson counterpart, its own members were dwindling. This was the case for many benevolent societies in New Orleans after the 1930s. As the need for private hospitals waned, so did French Hospital. In the case of other societies who supported other causes such as orphanages or schools, the need for their ministries decreased with the rise of social services. As insurance corporations developed, private societies no longer fulfilled a necessity. For the French society, decreased interest in the French language likely took a toll, as the New Orleans Sociètè operated exclusively in that language. In 1943, the Sociètè Française de Beinfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Nouvelle Orléans (and, by merger, de la Ville de Jefferson) celebrated its 100th Anniversary.[18] A celebration was held at the French Hospital at 1821 Orleans Avenue, with a dance to follow at the American Legion. The festivities appeared to hold true to the organization’s civic dedication. French leader Andre Lefargue addressed the crowd with patriotic notions of the French and Americans once again fighting in a war together. Appeals were made to the crowd to donate to the Red Cross for the war effort. Nine French cadets training at the New Orleans Naval Air Station were special guests of honor.[19] Said society president Henry Bernissan at the centennial celebration, “the first 100 years of the society is merely the initial performance. We expect to improve our methods with every passing day.”[20] Yet the Centennial pamphlet published by the society seemed to suggest a different prescience: The current charter does not expire until the year 1972. Therefore, the Society has 29 years to run. It is hoped that the majority of the current members celebrating our centennial will prosper alongside the society until the end of its charter.[21] On October 31, 1949, only six years after its centennial, the closure of French Hospital on Orleans Avenue was announced.[22] The building was sold to the Knights of Peter Claver, an African-American Catholic Society, who utilized the building until the 1970s, when an adjacent structure was built. The French Hospital/Peter Claverie Building was demolished in 1986. The Knights of Peter Claver buiding remains on this site. The exact year in which the Sociètè Française de Beinfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Nouvelle Orléans formally disbanded is unclear. Unlike their various balls, benefits, picnics and celebrations, this milestone in the organization’s history was not published in newspapers. However, it does not appear as if the Sociètè survived to the end of its charter in 1972. In a 1972 newspaper article, a passing reference was made to the Sociètè, “which for many years maintained the old French hospital on Orleans Street. The French Society folded a number of years ago.”[23] A Legacy of Burial Places Physical evidence of the Sociètè Française de Beinfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle is scant in the landscape of modern New Orleans – except for in the cemetery. Each day, hundreds of visitors pass the Sociètè Française tomb in St. Louis Cemetery No. 1. Without its cast-iron lamps and jet-black torches, it fades into the cemetery scene a little more than it once did, but it remains. For the more than 150 people buried in the Sociètè Française de Jefferson tomb in Lafayette Cemetery No. 2, that memory is much more tenuous. A number of trees that began growing in the tomb roof in the 1940s were cut down only this year, leaving a structure in significant need of repair. The brilliant colors of the blue tomb niches, the contrast of its white walls against black slate, its green copper drain pipes, have all faded to flat greys and exposed brick. Without names on the tomb tablets, it has been difficult for families to realize their ancestors are buried within. Yet with this project it is our hope that new resources will supply stakeholders with important information with which to regrow a connection to this remarkable structure, which represents more than a century of French fellowship in New Orleans. In our next blog post, we will share the lives of the people buried in this tomb in Lafayette Cemetery No. 2. The full burial rolls of interments into this tomb from 1872 to 1900 (up to the society’s merger with Sociètè Française d’Assistance Mutuelle de Nouvelle Orléans) have been uploaded to FindaGrave, in hopes their descendants may find them. The burial books are also available as an Excel Spreadsheet , MS Access Database, or PDF Document. Click here for burials listed by vault number. [1] Abrege Historique de la Societe Francaise d’Assistance Mutuelle de la Nouvelle-Orleans, c. 1903, Williams Research Center, Historic New Orleans Collection. This and nearly all documentation of the Jefferson and New Orleans societies are entirely written in French. All translations by Emily Ford, who is by her own admission not fluent in French. Difficult phrases are presented in their original French in [brackets].
[2] Founded in the 18th Century, the Grand Orient de France permitted female membership by 1773. Documents of the Sociètè Française de Beinfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Nouvelle Orléans and of Jefferson suggest that neither society permitted female membership at any time. [3] Centenaire: Societe Francaise de Bienfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de la Nouvelle-Orleans, 1843-1943, published 1943 by the Sociètè, 9. Louisiana State University Special Collections, MSS 318, 1012. [4] Roulhac Toledano, Mary Louise Christovich, and Robin Derbes, New Orleans Architecture: Faubourg Tremé and the Bayou Road (Gretna: Friends of the Cabildo, 2003), 82. [5] Centenaire: Societe Francaise de Bienfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de la Nouvelle-Orleans, 1843-1943, 19-21. [6] Ibid., 21. [7] Ibid., 39. [8] “New French Hospital Dedicated Yesterday,” Times-Picayune, February 24, 1913, 13. [9] Ibid., 15. [10] Leonard Victor Huber, Peggy McDowell, Mary Louise Christovich, New Orleans Architecture, Vol. III: The Cemeteries (Gretna: Pelican Publishing, 2004), 9. [11] Centenaire: Societe Francaise de Bienfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de la Nouvelle-Orleans, 1843-1943, 19. [12] “Societe Francaise de Bienfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de la Nouvelle-Orleans, Rapport annuel, 1897,” Williams Research Center, Historic New Orleans Collection. [13] Richard Campanella, Bienville’s Dilemma: A Historical Geography of New Orleans (Lafayette: University of Louisiana at Lafayette, 2008), 290. [14] From the records of Sociètè Française de Beinfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Jefferson burial books, Louisiana State University Special Collections. [15] “The Old Jefferson Society Celebrates its 27th Birthday,” Daily Picayune, November 16, 1896, 10. [16] Centenaire: Societe Francaise de Bienfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de la Nouvelle-Orleans, 1843-1943, 37. [17] Ibid., 35. [18] “French Unit Will Fete Centennial,” Times-Picayune, March 14, 1943, 11. [19] “Society Marks Centennial Day,” Times Picayune, March 15, 1943, 25. [20] Ibid. [21] Centenaire: Societe Francaise de Bienfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de la Nouvelle-Orleans, 1843-1943, 51. [22] “25 years ago,” Times-Picayune, October 17, 1974, 19. [23] Times Picayune, September 24, 1972, 6. Labor Day was established in the 1880s as a holiday in which to appreciate and remember the contributions of organized labor in our communities. New Orleans is not always readily associated with labor history, but one walk through a quiet, historic cemetery and the significance of workingmen’s societies is clear. Established in 1850 along Washington Avenue at Saratoga Street, Lafayette Cemetery No. 2 is the site of many different expressions of the drive of individuals to organize and collect for the greater benefit. Social aid societies such as the Société Française de Bienfaisance et D'Assistance Mutuelle built tombs for their members here – tall, wide, multi-vault tombs into which numerous burials could be made at once. Members of these societies paid monthly or yearly dues, the benefits of which included a funeral, tomb burial, and often monetary support for widows and orphans. The most prominent of these societies in both history books and the landscape of Lafayette Cemetery No. 2 is that of the Butchers’ Benevolent Society, who contracted James Hagan and L.E. Lohes to build their eighty-seven vault tomb in Square 19. It cost $5,000 and was completed in 1868.[1] The Butchers’ Benevolent Society charged its members each $1 in the event of a member’s death, the proceeds of which were given to surviving family. If any member failed to attend the burial of the deceased butcher, he was fined fifty cents (one dollar for board members). Members attending a butcher’s funeral were prohibited from smoking cigars and cigarettes while processing to the tomb, but were allowed to do so when processing away.[2] The Butcher’s association tomb is distinctive, but is not nearly the most significant aspect of the society’s history. Shortly after the dedication of the tomb, the Butchers’ Benevolent Association brought suit against the City of New Orleans in a case that challenged the interpretation of the newly-drafted Fourteenth Amendment. The Slaughterhouse Case became a landmark Supreme Court case in 1873, and continues to be argued and revisited today. The Slaughterhouse Case challenged the language of the Fourteenth Amendment, which was intended to establish the rights of emancipated slaves as the same rights, privileges and immunities of all American citizens. Beyond the Butchers’ tomb, the exercise of these rights by African American laborers is visible in high relief across the landscape of Lafayette Cemetery No. 2. African-American Labor Societies Along the Sixth Street and Loyola Street fences of Lafayette Cemetery No. 2 are numerous society tombs dedicated to the members of African American labor organizations. Many of them were associated with the transport, weighing, and moving of goods along New Orleans’ waterfront: the Coachmen Benevolent Association, the Teamsters and Loaders Union Benevolent Association, the Cotton Yardmen No. 2, and others. In the late 1870s and through the 1880s, these associations formed to protect the rights and opportunities available for African American workingmen. Organizations were racially segregated but frequently worked in tandem with white organizations. The Cotton Yardmen Benevolent Association No. 2 is an example of this. From Eric Arnesen’s Waterfront Workers of New Orleans: “Leading the new union drive was the white Cotton Yardmen’s Benevolent Association formed in December 1879 under the direction of Democratic party ward boss and Administrator of Police, Patrick Mealy; two years later it boasted a membership of 986 and a bank account of $13,000. Black cotton rollers, with the assistance of the leaders of the white yardmen, formed the Cotton Yardmen’s Benevolent Association No. 2, in January 1880, and both organizations agreed to work ‘in full harmony’ with each other. In April 1880, the black teamsters and loaders established their benevolent association, as did coal wheelers the following month…In September 1880, cotton weighers and reweighers formed a mutual aid association that aimed to secure a uniform system for weighing and re-weighing cotton and to regulate wages and arbitrate disputes.[3]” Organizations like those represented in Lafayette Cemetery No. 2 navigated the twin hardships of labor injustice and racial prejudice. Yet the establishment of such unions was accomplished, despite acute awareness of the possibility of violence. Events like the 1887 Thibodaux Massacre and other bloody labor conflicts would have surely weighed upon laborers as they worked toward fair treatment.
While these treatments appear to offer a maintenance-free solution to crumbling tombs, such materials can be harmful to the soft brick beneath. Of the twenty-two society tombs of Lafayette Cemetery No. 2, only a few are not abandoned, and active decay is the dominant force.
This Labor Day, we take part in the intention of this memorial architecture and appreciate the achievements that the society tombs of Lafayette Cemetery No. 2 represent. For further reading: Daniel Rosenberg. New Orleans Dockworkers: Race, Labor, and Unionism 1892-1923. New York: SUNY Press, 1988. Eric Arnesen. Waterfront Workers of New Orleans: Race, Class, and Politics, 1863-1923. Chicago: University of Illinois Press, 1994. Steve Striffler and Thomas Jessen Adams. Working in the Big Easy: The History and Politics of Labor in New Orleans. Baton Rouge: University of Louisiana Press, 2014. Paul D. Moreno. Black Americans and Organized Labor: A New History. Baton Rouge: LSU Press, 2008. PBS: Landmark Supreme Court Cases related to Labor. New Orleans Dockworkers and Unionization, Wikipedia New Orleans 1892 General Strike, Wikipedia [1] New Orleans Republican, November 2, 1868, 1; “The Butchers’ Benevolent Association,” New Orleans Crescent, October 13, 1868.
[2] Butchers’ Benevolent Association, Constitution et règlements de la Société de bienfaisance des bouchers de la Nouvelle-Orléans (New Orleans: Imprimerie Franco-Americaine), 1883, Articles Fourteen and Sixteen. [3] Arneson, Eric, Waterfront Workers of New Orleans: Race, Class, and Politics, 1863-1923 (Chicago: University of Illinois Press, 1994), 61-63. |
About the Author:Emily Ford owns and operates Oak and Laurel Cemetery Preservation, LLC. Archives
November 2019
Categories
All
|
- About
-
Restoration
- Services
-
Portfolio
>
- Turning Angel Statue, Natchez, MS
- Ledger Monument, Baton Rouge, LA
- Pyramid Statuary, New Orleans, LA
- Bronze and Granite Monument, Carville, LA
- Box Tomb, New Orleans, LA
- Vernacular Concrete Monument, Pensacola, FL
- 1830s Family Tomb, Covington, LA
- 1850s Family Tomb, New Orleans, LA
- 1880s Family Tomb, New Orleans, LA
- Headstone and Monument Restorations, Pensacola, FL
- Society Tomb, New Orleans, LA
- Education
- Blog
- Contact
|
Oak and Laurel Cemetery Preservation, LLC is a preservation contractor in New Orleans, Louisiana, specializing in historic cemeteries, stone conservation, educational workshops and lectures. Oak and Laurel serves the region of the Southeastern US.
|
QUICK LINKS |
CONNECT |
Proudly powered by Weebly