|
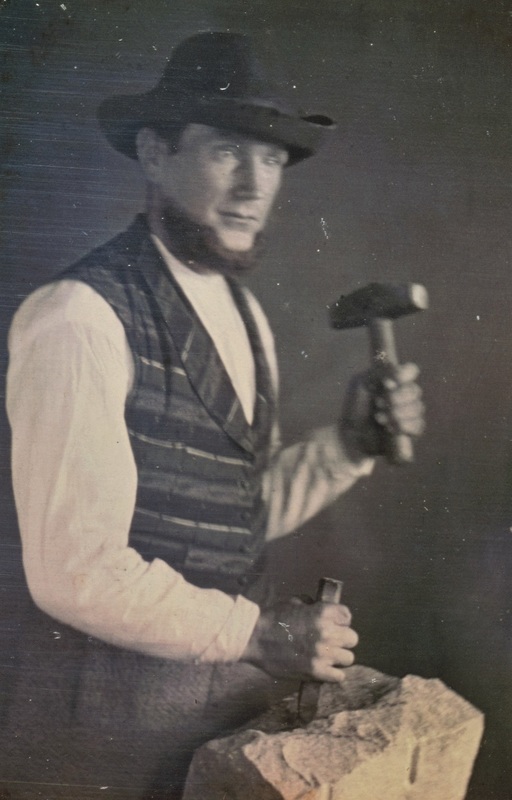
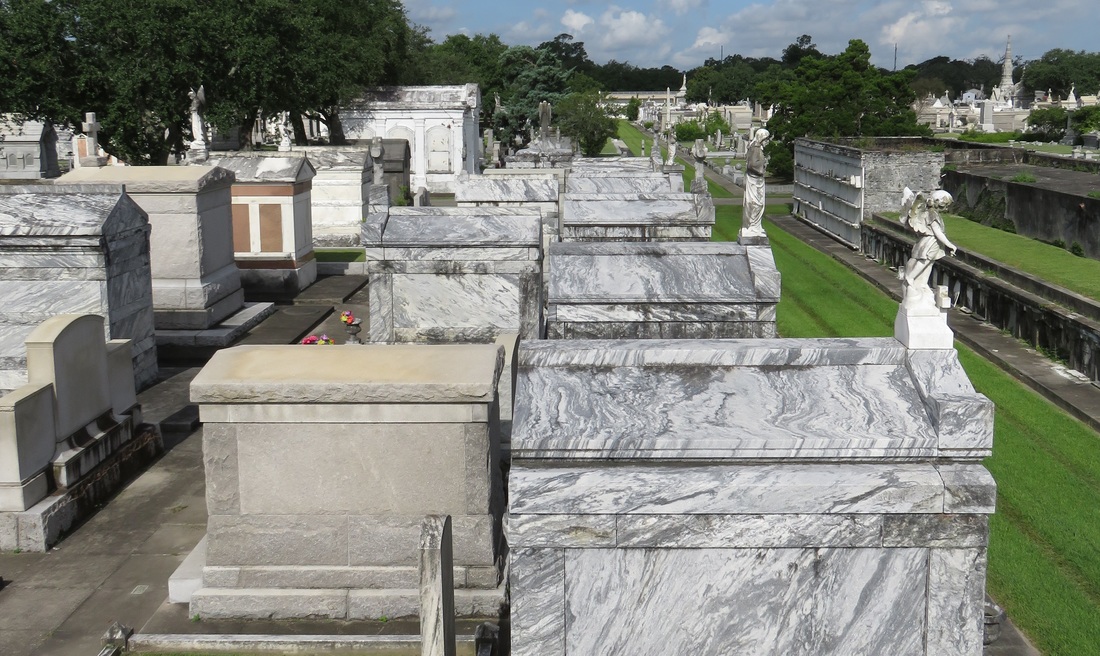
Adapted from Emily Ford, “The Stonecutters and Tomb Builders of Lafayette Cemetery No. 1, New Orleans, Louisiana,” Master’s Thesis, Clemson University, 2012. Full text can be found for free here. Beyond sweeping landscapes and imposing architecture – within the “stories in stone” that are so beloved in New Orleans cemeteries, are the stones themselves. Much like the long-dead people they memorialize, these slabs of honed and carved limestone, marble, and granite journeyed great distances to become part of an irreplaceable cemetery landscape. Whose hands drew that stone from its quarry? Why is the marble found in Greenwood Cemetery drastically different from what we find in St. Louis Cemetery No. 2? Today we share the stories of quarries, infrastructures, and materials that make up New Orleans cemetery stonework. Louisiana Lacks Workable Native Stone The geology of southern Louisiana is similar to that of other states along the Gulf of Mexico. Comprised of mostly sedimentary rock, clay, limestone, and sandstone, Louisiana has few stone resources that would be desirable for cemetery monuments.[1] Furthermore, the stone that is quarried in Louisiana has historically been of poor quality for building. For example, during the 1850s construction of the Washington Monument in Washington, D.C., requests were made that each state donate a block of native stone to be placed in the interior of the monument. Louisiana sent a block of sandstone that, within the decade, was so crumbling and decayed that it was replaced with a block of Pennsylvania marble.[2] Thus, from the eighteenth century onward, the stone used in New Orleans cemeteries was imported from elsewhere. Various types of slate, marble, and granite were made available as trade routes and quarries opened. By the mid-nineteenth century, New Orleans merchants and dealers offered stone from a number of different places. As time went on, the availability and sources of stone widened.
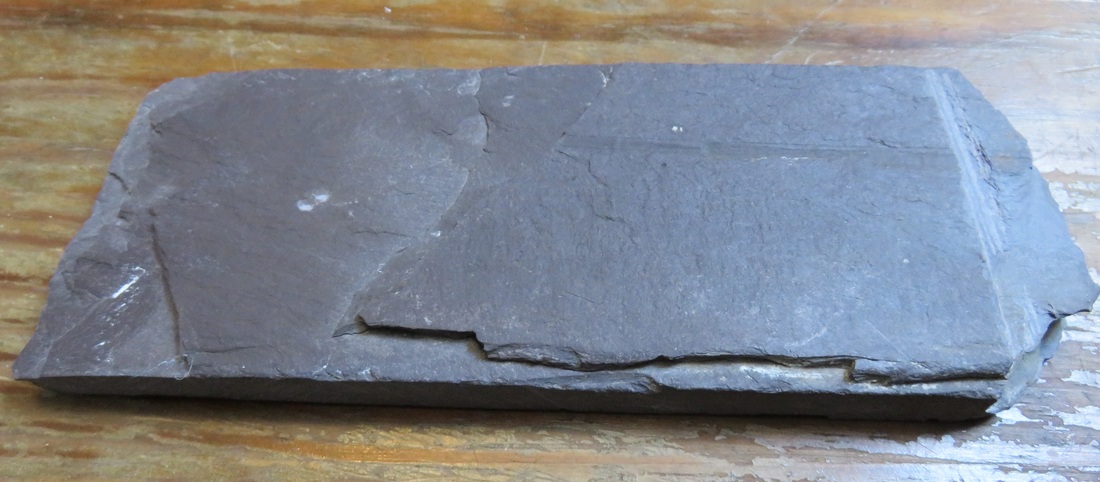
Arkansas slate was quarried from areas near the towns of Hot Springs, Little Rock, Benton, Malvern, or Mena. This small vein of quality slate, approximately 100 miles long, could produce stone of red, gray, green, or black appearance. Despite the availability of slate from Arkansas, Pennsylvania slate continued to be quarried and shipped to New Orleans. Historic Louisiana newspapers frequently mention the quality and availability of slate from the Bangor quarry in Northampton County. Given the same name as a slate quarry in Wales, the “Old Bangor” quarry had an office in New Orleans by the 1870s. Old Bangor slate is “very dark gray, and to the unaided eye has a fine texture and fine cleavage surface, almost without any luster. The sawn edge shows pyrite.” The Williamstown, Franklin, and Pen Arygl quarries of Pennsylvania also had retail agents in New Orleans, who advertised their slate to be of the same quality as that of Wales.[6]
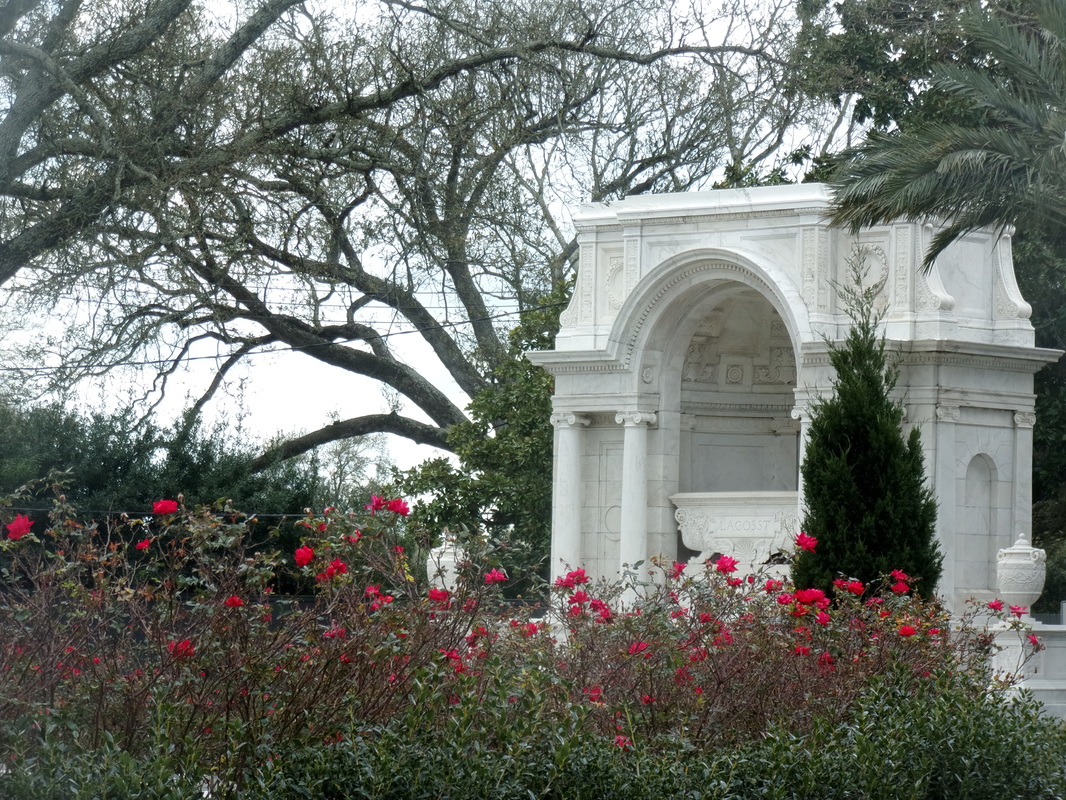
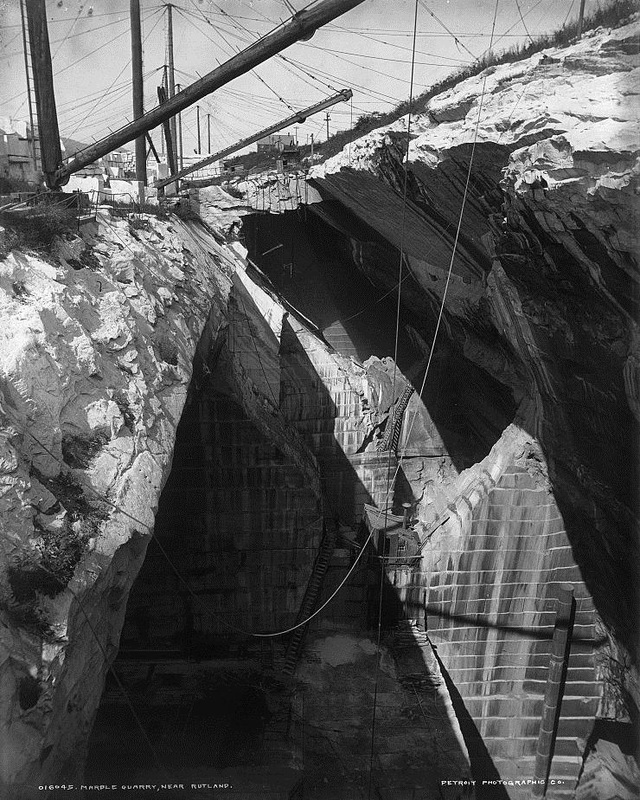
They form by the compression of these sediments, along with all the calcium-rich seashells within. They diverge when these sediments either compress and become sedimentary rock or, alternatively, are subject to higher pressures and become metamorphic. Limestone is sedimentary, marble is metamorphic. Limestone is most prevalent in the oldest remaining New Orleans cemeteries, namely St. Louis Cemetery No. 1 and 2, although precious isolated examples are found in other cemeteries. In this context, limestone was used for closure tablets. Limestone closure tablets are usually dark gray (likely quarried in Arkansas or Tennessee) and can be identified by the tiny fossilized shells included in the stone’s matrix. Around the mid-nineteenth century, whiter limestones were used in the same context as marble and are harder to identify. Some rough-faced stones that appear to be marble can be identified as limestone by spotting the shell inclusions within. These rare examples of white limestone were often quarried in Tennessee. Imported Marble: An Italian Commodity New Orleans was a primary hub for the import and export marble from both Europe and the United States. Used for closure tablets, shelves, memorial sculpture, apex sculptures, tomb cladding, and other decorative elements, marble was the medium in which cemetery stonecutters primarily worked throughout the nineteenth century. Based on documentary evidence, the quarries of Italy were the primary source of marble into the 1850s. Italian marble was either directly imported from Italy or arrived via northeastern ports like Boston or New York.[7] Florville Foy, who advertised aggressively throughout his career, frequently promoted his most recent shipment from Carrara or Genoa, cut into one, two, and three inch slabs. Paul Hippolyte Monsseaux similarly advertised his Italian marble stock.[8] New Orleans stonecutters dealt in and imported Italian marble through the nineteenth century. In the 1870s, stonecutter John Hagan (active 1854 – 1890s) stocked Italian marble “for sale at a small advance on New York prices.” George Stroud (active 1866 – 1899) cut his own Italian marble at Monsseaux’s steam cutting plant. James Reynolds (active 1866 – 1880) not only sold his Italian marble in New Orleans but also in Vicksburg, Mississippi.[9] Italian marble, often vernacularly referred to as “Carrara marble” regardless of its quarry of origin, is a stone of high-grade, consistent quality, and a variety of colors including cream, pure white, and blue. As one Alabama quarry owner conceded in 1909, “Italian marble has long been a standard, not only because the stone is undeniably high grade, but also because the blocks are so uniform in quality that all the slabs or pieces from a block can be used together.”[10] The cost of importing marble in New Orleans varied over the course of the nineteenth and twentieth century; at times, it actually cost less to import than marble from Vermont or Tennessee. Protective tariffs helped to stabilize the marble industry during the 1880s and 1890s, but the presence of the famed marble remained a factor among monumental craftsmen into the present. For example, in 1914, before Albert Weiblen purchased his own marble quarry in Georgia, he received a shipment of Italian marble so substantial it took two large derricks to lift the fifteen-ton blocks from the steamship in which it arrived.[11] Domestic Marble: Vermont, Alabama, Georgia, and Others The slow development of infrastructure and quarry technology prevented American quarries from competing with Italian marble in New Orleans until the 1850s. In 1845, one of the first marble quarries opened in Talladega County, Alabama. Five years later, another opened nearby, operated by J.M.N.B. Nix. Using a publicity tactic that would become common among quarry operators in the United States, the New Orleans Daily Picayune announced that “Alabama produces marble equal in fineness – that is, purity or clearness and susceptibility of polish – to any in the world, not excepting the most beautiful Italian, Vermont, or Egyptian.” It was Nix’s quarry that sent Alabama’s contribution to the Washington Monument.[12] Talladega marble can appear white, blue, or cream, and often displays black, green, or grey veins, although it is consistently characterized by the fineness of its grain. Its unpredictability in quality and appearance, however, made it costly to extract.[13] Alabama marble remained a presence among New Orleans cemetery craftsmen well into the twentieth century. One of the most recognizable and imposing monuments within Metairie Cemetery, the ornate sarcophagus of Eugene Lacosst, was crafted by Albert Weiblen from pure white Alabama marble.[14] As always, infrastructure dictated which materials were available in New Orleans at a given time period. In 1851, The Vermont Valley Railroad Company connected towns like Rutland to the greater markets in the East and South.[15] Only two years later, sources in New Orleans commented on the great productivity of the Rutland quarries, remarking that their product had gained “a reputation abroad as well as at home.”[16] Rutland and other Vermont marbles can be white, blue, or black. These quarries also produced pure-white sculpture-grade marble.[17] By 1900, Vermont produced more marble than any other American state, and the Rutland quarry was the highest-yielding quarry. Blocks of Vermont marble were sold for between $1.00 and $3.00 per cubic foot in New Orleans, where agents received shipments and distributed order throughout the South and West.[18] Like Alabama marble, marble quarried in Vermont remained in the stockpiles of New Orleans craftsmen into the mid- and late twentieth century. Vermont not only exported its marble to New Orleans, but its marble cutters as well. One account reflected that the stone cutting yards of New Orleans primarily employed skilled sculptors and polishers from the states of Vermont and Georgia.[19] By 1916, Georgia was second only to Vermont in its production of quarried marble. Although marble quarrying had existed in Georgia long before, it appears to only have gained prevalence in the New Orleans market after the Civil War. By 1888, the Georgia Marble Company in Pickens County claimed to be the largest marble quarry in the world.[20] Georgia marble is typically coarse-grained and appears in blue-gray, black, white, and Creole, which has dramatic sweeping shades of dark gray, black, and white.[21] Ubiquitous Georgia Creole Marble Between 1890 and the 1930s, Georgia Creole marble exploded in the New Orleans cemetery market and made an enormous mark on the landscape. This explosion was the result of expert marketing, improved infrastructure, and enormous supply. Modern monument men during this period utilized Georgia Creole marble in nearly every aspect of their work, from tomb cladding to headstones to vases and urns. The streamlined process of tomb building, now executed in a more “cookie cutter” style than previous generations, allowed many more tombs to be built in a short period of time, and Georgia Creole marble was the medium of choice.
Additionally, as marble is a metamorphosed type of limestone, it is naturally alkaline in quality. Thus, exposure to rain, which is naturally slightly acidic, or any other acidic substance (for example, hydrochloric acid mistakenly intended to clean the stone) will cause marble to granulate and “sugar” over time. An extreme example of marble deterioration can be found in St. Joseph’s Cemetery No. 1. The failure that likely occurred with this stone was related to moisture entrapment within the tomb itself. This, paired with the tight, compressive position of the tablet within the opening, caused the closure tablet to bow and “bubble” outward.
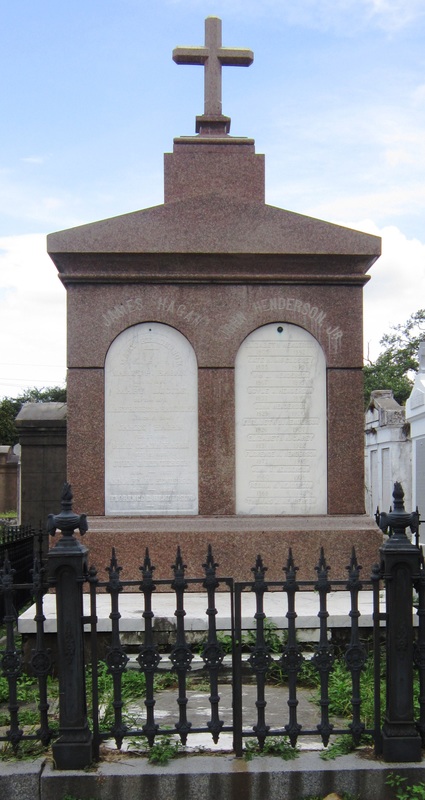
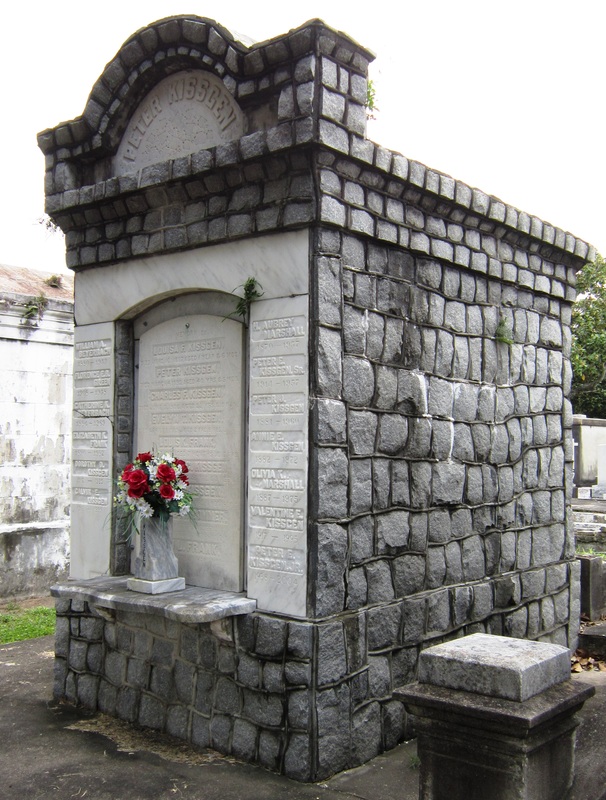
One of the most noticeable granite tombs in Lafayette Cemetery No. 1 is that of stonecutter and sexton James Hagan. This remarkable tomb was built of red-colored Scotch granite in 1872. Around the same time, Hagan also constructed the monument of Governor Henry Allen, which was also located in Lafayette Cemetery No. 1 until it was moved to the Old State Capitol in Baton Rouge in the 1880s. This monument, too, was carved from Scotch granite.[24]
[1] Louisiana Geological Survey, Geology and Agriculture: A Report on the Geology of Louisiana (Baton Rouge: 1902), 133-134.
[2] National Park Service, Department of the Interior, Northeast Region, Architectural Preservation Division, The Washington Monument: A Technical History and Catalog of the Commemorative Stones (Washington, DC: National Park Service, 2005), 28. “Washington National Monument,” The Pittsfield Sun (Pittsfield, Massachusetts), August 22, 1850, page 1. The stone is referred to as “freestone,” meaning a soft, friable sedimentary stone. [3] Graham R. Thompson and Jonathan Turk, Introduction to Physical Geology (Rochester, NY: Saunders College Publishers, 1998), 133-137. Slate headstones are found commonly in the Northeast dating to the colonial period. Slate headstones are also present in cemeteries as far south as Charleston, South Carolina and Savannah, Georgia. However, no slate headstones are visible in the cemetery landscapes of New Orleans. [4] Mary Louise Christovich, Roulhac Toledano, and Betsy Swanson, New Orleans Architecture, Vol. I: The American Sector (Gretna, LA: Pelican Publishing, 1998), 57. [5] Daily Picayune, September 27, 1850, 2; Daily Picayune, May 2, 1853, 1; Daily Picayune, February 28, 1869, 11. [6] “Alexander Hill, Welsh and American Slates, Slabs, etc.” Morning Star and Catholic Messenger, July 4, 1875, 6. These slates priced from $6.50 to $10 per square; “Slates! Slates! Slates!” Ouachita Telegraph (Monroe, LA), July 22, 1872, 2. [7] “Brig Casket arrives from New York with sundry marble slabs,” Louisiana Advertiser, April 29, 1820, 3. “Barelli & Company, commission merchants, selling blocks of Italian marble,” Daily Picayune, March 21, 1845, 3. [8] Daily Picayune, November 10, 1848, 7; Daily Picayune, February 17, 1848, 3; Cohen’s New Orleans and Lafayette Directory for 1851 (New Orleans: Cohen’s Directory Company, 1851), page AT. [9] Edwards’ Annual Director to the Inhabitants, Institutions….etc., etc., in the City of New Orleans for 1871 (New Orleans: Southern Publishing Company, 1870), 275; Daily Picayune, May 18, 1871, 3. [10] Committee on Ways and Means, United States Congress, “Marble: The Alabama Marble Company, Gantts Quarry, Ala., Urges Retention of Duty on Marble,” in Tariff Hearings Before the Committee on Ways and Means of the House of Representatives, Sixtieth Congress, 1908-1909, Vol. VIII (Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office, 1909), 7886-7888. [11] “Ship Brings Cargo of Italian Marble,” Times-Picayune, July 27, 1914, 8. [12] “Alabama Marble,” Daily Picayune, October 1, 1845, page 2; Daily Picayune, May 18, 1871, 3. [13] Committee on Ways and Means, United States Congress, “Marble: The Alabama Marble Company, Gantts Quarry, Ala., Urges Retention of Duty on Marble,” in Tariff Hearings Before the Committee on Ways and Means of the House of Representatives, Sixtieth Congress, 1908-1909, Vol. VIII (Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office, 1909), 7886-7888. In this year, cost to transport Alabama marble to New Orleans was 32 cents per cubic foot. [14] Leonard V. Huber et. al. New Orleans Architecture, Vol. III: The Cemeteries, 54-55. [15] Vermont Railroad Commissioner, Eleventh Biennial Report of the Board of Railroad Commissioners of the State of Vermont (St. Albans, VT: St. Albans Messenger Co., 1908), 308. [16] Daily Picayune, July 15, 1853, page1; Daily Picayune, June 16, 1855, 1. [17] Thomas Nelson Dale, The Commercial Marbles of Western Vermont (Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office, 1912), 117-122. [18] Tariff Hearings before the Committee on Ways and Means, Second Session, Fifty-Fourth Congress, 1896-97, Volume 1 (Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office, 1897), 275-279; “Random Notes,” The Reporter: The First and Only Journal Published in the World Devoted Exclusively to Granite and Marble, No. 1 (January, 1900): 33. [19] David Spence Hill, Industry and Education: Part Two of a Vocational Survey for Isaac Delgado Central Trades School (New Orleans: The Commission Council, 1916), 227. [20] “Science and Industry,” The Colfax Chronicle (Colfax, LA), November 3, 1888, 3. This was not an uncommon claim for many quarries to make. “Georgia Quarries,” The True Democrat (Bayou Sara, LA), January 30, 1897, 7. [21] Memoirs of Georgia, Vol. I (Atlanta: The Southern Historical Association, 1895), 211-217. [22] A. Oakley Hall, “Cities of the Dead,” in Louisiana Sojourns: Travelers Tales and Literary Journeys, Frank de Caro, editor. (Baton Rouge: LSU Press, 1998), 532-533; Arthur Wellington Brayley, History of the Granite Industry of New England, Volume I (Boston: National Association of Granite Industries of the United States, 1913), 114. [23] Ibid., 84. [24] Special thanks to Jonathan Kewley of Durham University, UK, for his knowledge and expertise in identifying the Hagan tomb as Scottish granite. [25] Soards’ New Orleans City Directory for 1895, Vol. XXII (New Orleans: L. Soards, Publisher, 1895), 1095. [26] “Notes from the Quarries,” Stone: an Illustrated Magazine Vol. 4 (1892): 496.
17 Comments
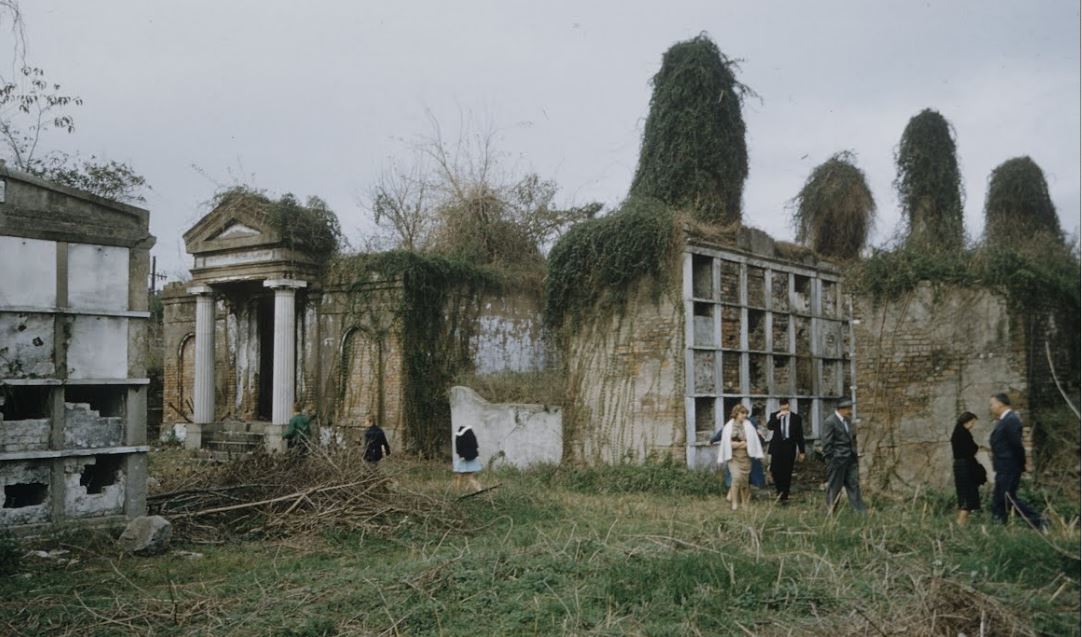
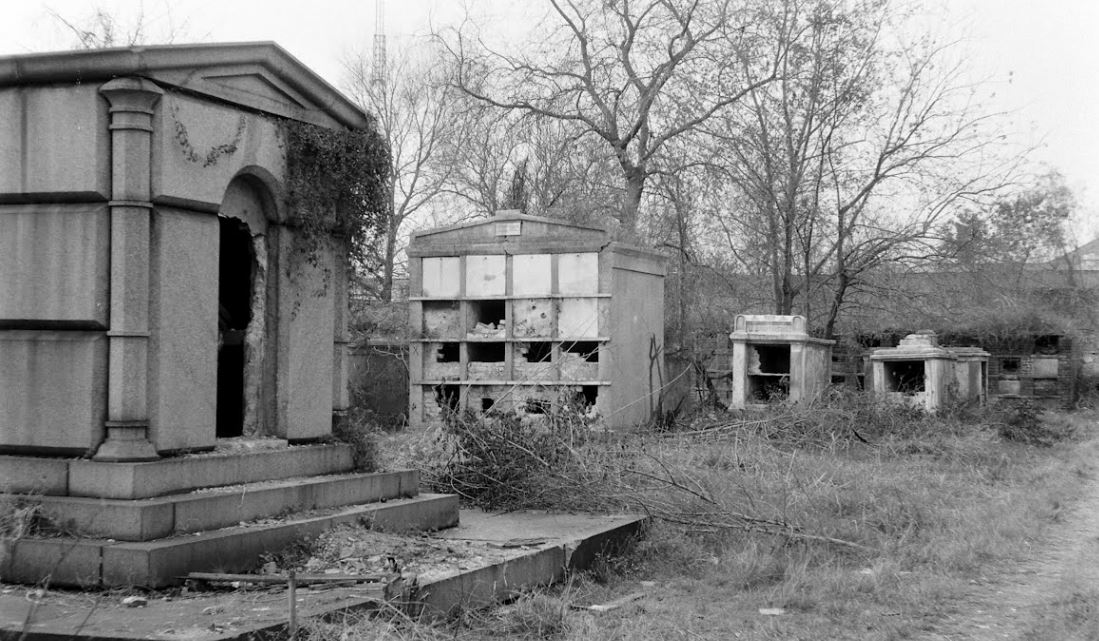
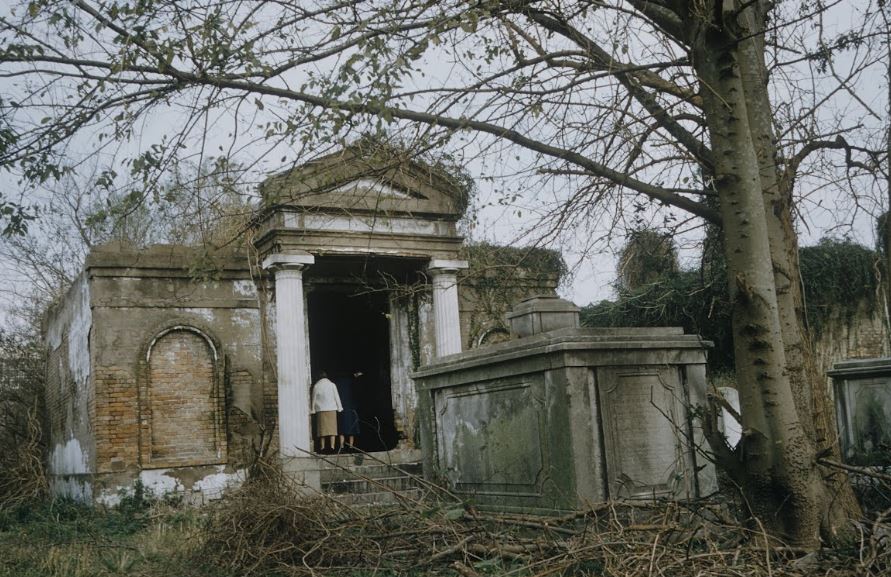
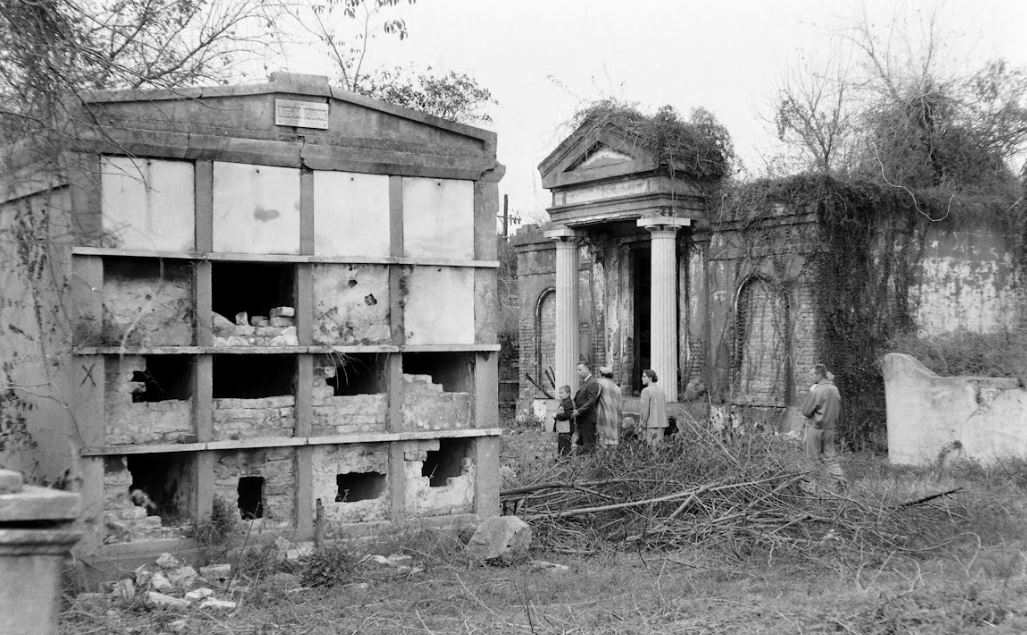
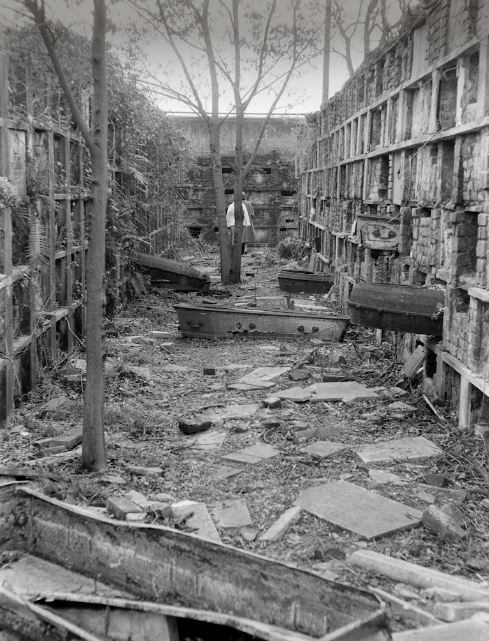
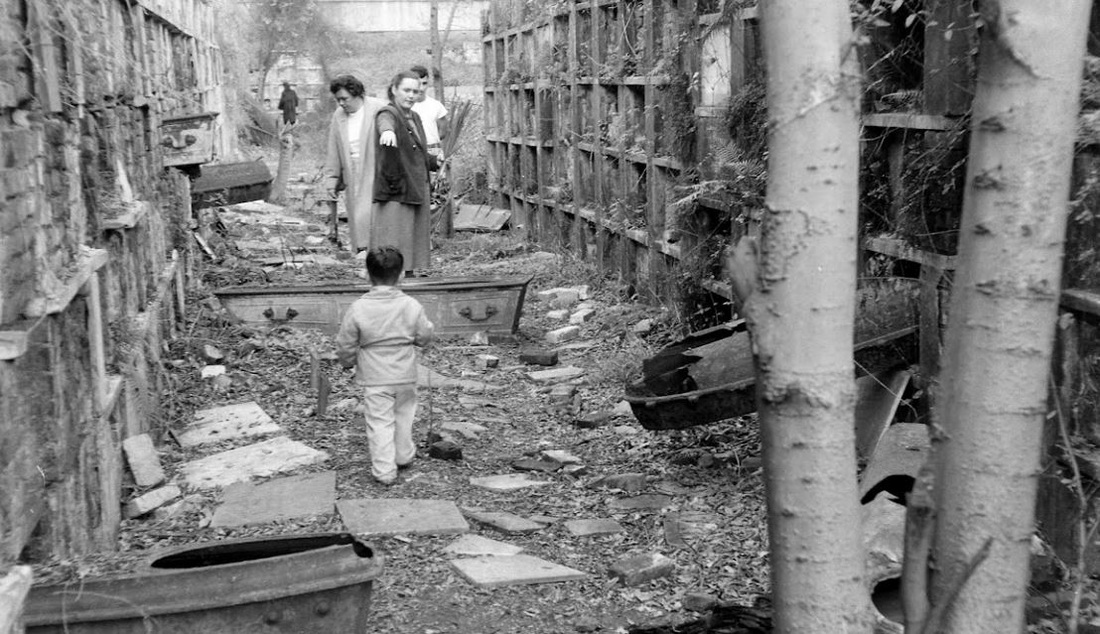
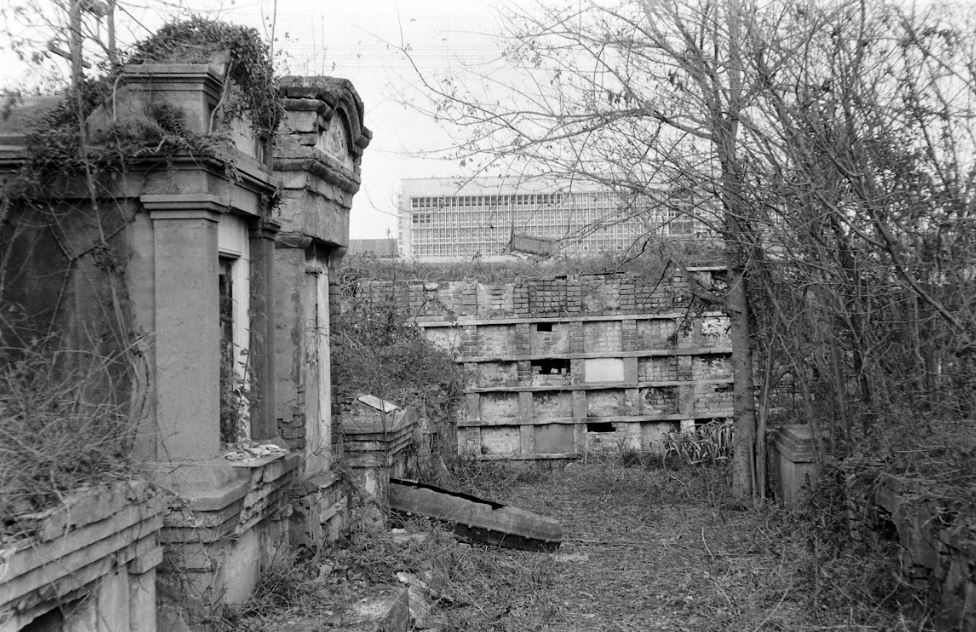
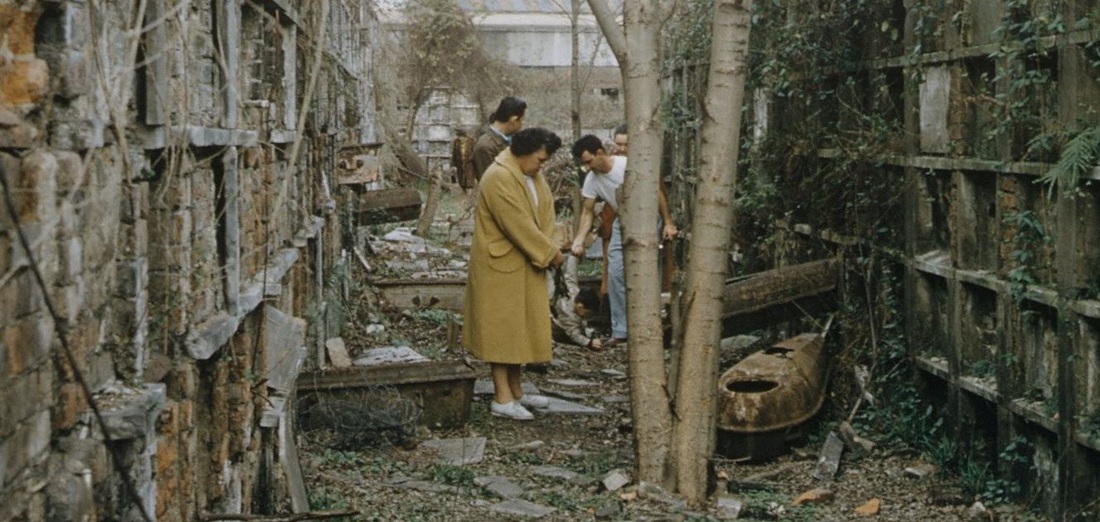
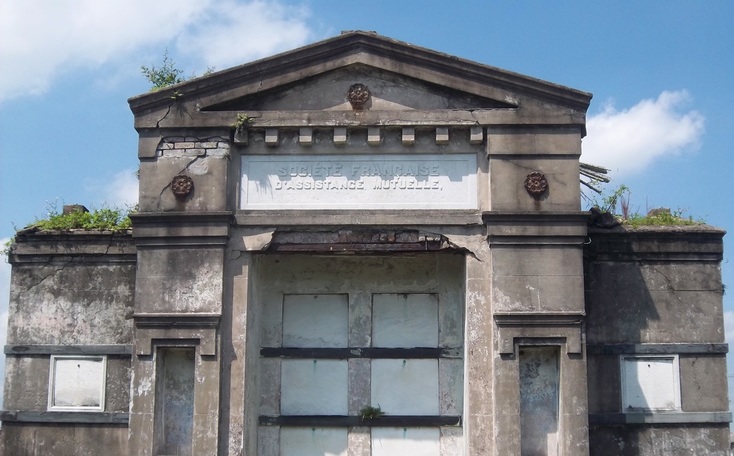
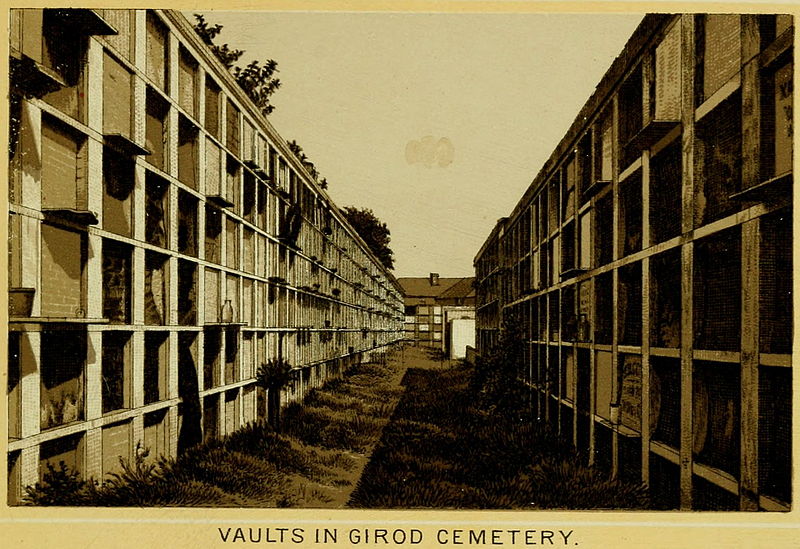
This blog post was inspired by the photos within, most of which were taken by Robert W. Kelley of LIFE Magazine in 1957. These images show Girod Street Cemetery in its final moments, as well-dressed adults and children mill around its collapsed tombs and open vaults, with newly-built New Orleans City Hall present in the background of many shots. Mis-labeled “Gerard” Street Cemetery, they offer a vignette of what has long since disappeared from the New Orleans landscape. The full album can be found via Google Cultural Commons here. The topic of Girod Street Cemetery is one that comes up in a few varieties of conversation among New Orleaneans, most often related to the charming notion that the Louisiana Superdome was built atop the burial ground (it wasn’t, per se). The relationship of the old cemetery, known also as the Protestant Cemetery, to the New Orleans Saints football team is one that has been described many times over, best by Richard Campanella and Doc Boudin of Canal Street Chronicles. Check them out to see why you can’t blame the vengeful dead for a losing season. The Protestant Cemetery, 1822 – 1940 The former footprint of the cemetery, however, was indeed quite close to the present-day Superdome. Originally bounded by Liberty, and the former Cypress and Perillat Streets, the cemetery once stood beneath where Superdome parking garages and the Champions Square complex now rise. Founded in 1822, this once-distinctive cemetery lay at the terminus of Girod Street. Previous to that date, non-Catholics were buried in the rear of St. Louis Cemetery No. 1. The narrow “Protestants Section” in St. Louis No. 1 was once much longer, but was truncated after construction to Treme Street in 1820. Shortly afterward, Episcopal Christ Church was awarded the land that became Girod Street Cemetery. Over the course of the nineteenth century, Girod Street Cemetery developed into a landscape distinct from its New Orleans cemetery sisters. As the second-oldest cemetery in the city, it amassed the vestiges of early cemetery architecture, from single-vault, stepped-roof structures to more ambitious marble-clad and Classically inspired sarcophagus tombs. The tomb of Angelica Monsanto Dow, who died in 1821, reflected this aesthetic well. Girod Street Cemetery furthermore was an “American” cemetery, in that it became the final resting place for many New Orleans residents who had travelled from elsewhere, particularly the Anglo-American north and Midwest. From these outsiders came tombs and materials inspired by northern cemetery designs – clean, wire-cut Philadelphia brick, liberal use of stone urns and many, many obelisks. Girod Street Cemetery kept within its walls a tableau of cemetery artisanship that stood out from the landscapes of its sister Catholic, municipal, and fraternal cemeteries. Through the nineteenth and into the twentieth century, Girod Street Cemetery would become the final resting place for many New Orleaneans of distinction. Heroes of the Mexican American War, civic leaders, and prominent families utilized the burial ground. One estimate suggested that the cemetery was once home to 100 society tombs. For comparison, Lafayette Cemetery No. 2, which is usually noted for its society tombs, has just twenty. In Girod Street Cemetery, the tomb of the New Lusitanos Benevolent Society was likely the most notable. Designed by J.N.B. de Pouilly and erected in 1869, the tomb had 100 vaults and a walk-in vestibule framed with a Classical portico. Being somewhat centrally located, Girod Street Cemetery was also heavily utilized as a public burying ground in times of epidemic. It seems as though nearly every major epidemic of the nineteenth century involved a terrible debacle at Girod Street Cemetery, in which bodies were stacked beyond capacity with no one to bury them. This may have also been due to the presence of a de facto Potter’s Field adjoining the cemetery, which was described as early as 1837: “This latter receptacle of the dead [the Protestant cemetery] has for many years been a disgrace to New Orleans. Once the Potters’ Field, it soon became the public burying ground, provided you were able to pay for a vault – otherwise you had to be sent further out into the swamp.”[1] The 1833 cholera epidemic in New Orleans proved especially tragic for Girod Street Cemetery, although it was not necessarily the last time the cemetery fell prey to insufficient manpower in the face of great loss of life: … the unshrouded dead dumped at the gateway of the Girod Street Cemetery accumulated in such numbers that the entrance to its precincts was so obstructed that arriving bodies had to be deposited on the outside; no graves at this time could be dug; no coffins were procurable, for there were neither grave diggers to be had nor undertakers to be found. The City Council was forced to order out the chain gang ‘prisoners’ from the city jails, to dig a trench the whole length of the lower side of the cemetery. It was dug some twelve or fifteen feet wide, and as deep as the filtering water soil would permit, into this receptacle the decomposing bodies were dragged by hooks from the fire companies, without the formality of precedence or order of any kind. As a part of the trench was filled, the earth taken from it was heaped upon the remains of the rich and the poor, the aged and the young.[2] This mass grave would eventually be erroneously referred to as the “yellow fever mound” in later years. In the late 1940s, historians would determine that this feature was in fact the burial of 1833 cholera victims.[3] The Back of the Swamp Girod Street Cemetery, for its stately obelisks and high society residents, would be plagued with issues surrounding its management and topography for most of its existence. In the 1830s, only years into its functional life as a cemetery, it would be noted that its vaults were built with only one brick thickness to their walls, which permitted the “escape of unhealthy odors.”[4] However this was not an issue exclusive to Girod Street – City ordinance did not regulate the quality of tomb construction until the 1850s. What did afflict Girod Street perhaps more than other cemeteries was its location in significantly low-lying land. Girod Street Cemetery swelled with feet of water in Sauve’s Cravasse of 1849, and frequently took on water in other instances, owing to its place on swampy land. In 1880, a special commission of Louisiana state representatives assessed the condition of New Orleans cemeteries and found them all to be in “proper” condition – with the exception of Girod Street Cemetery. Noting, “in the event of rain [Girod Street Cemetery] is always flooded to such an extent that it will affect the sanitary precautions necessary to prevent the contracting or spreading of any diseases,” the commission recommended the cemetery be closed. This recommendation was apparently declined.[5] Girod Street Cemetery’s troubles would not end there. The Fall of Girod Street Cemetery Through the course of its existence, Girod Street Cemetery was owned and operated by Christ Church Cathedral. Until the mid-twentieth century, most religiously-affiliated cemeteries were managed by the respective congregation that owned them. These congregations appointed a sexton or caretaker to manage them by performing burials, building tombs, and keeping records. Although city law required sextons to compile records to be submitted to the Board of Health, the interment records of each cemetery were kept by each sexton to varying degrees of organization. At the turn of the century, increasing industrialization of the monument trade shifted the role of sexton away from groundskeeper and toward that of a sales agent. In some cases, this meant a decline in peripheral duties. This shift is often credited for the lessening of care for the cemetery, as is the inclination of families to move their loved ones remains to newer cemeteries (namely Metairie Cemetery, established 1872). Lack of sellable space and changing racial demographics in the neighborhood of Girod Street Cemetery are also noted as causes for decline. For any combination of these reasons, or others, the administration of Christ Church found themselves in a difficult bind with their cemetery.[6] By the early 1940s, reports on the condition of Girod Street Cemetery appear to have drastically worsened. Wrote one reader in a 1943 letter to the Times-Picayune: … I was horrified to find many of the tombs broken open and others completely destroyed. There was a large fire burning at the top of one of the tombs. I saw what looked like wooden boxes burning. The cemetery looks more like a poultry farm. Atop the tombs are a number of chicken coops, and chickens wandering everywhere, and some of the lovely trees are completely or nearly burned down. Where are the owners of these tombs, that such desecration is allowed? And who cares for this unfortunate burying place?[7]
By the time of this announcement in 1947, Girod Street was merely joining in a much larger phenomenon in which cemetery management was drastically changing. In 1945, the City of New Orleans eliminated the position of sexton from the six municipal cemeteries. In the years following, former sextons and stonecutters would go into business for themselves as cemetery owners, profiting primarily from streamlined materials and low overhead costs. This process was best accomplished by Albert Weiblen, who eventually purchased Metairie Cemetery, and the Stewart family, who built Lake Lawn Park in the 1950s. However, this approach relied on the cemetery having lots available for sale. The last sexton of Girod Street Cemetery, Eugene Watson, died in 1950. In 1948, Christ Church ran multiple notices enjoining tomb owners to repair their property. However, as the cemetery owners pushed to bring the burial ground into the twentieth century, they would stumble over technicalities of property ownership, prohibitive costs, and a booming, modernizing world slowly encroaching on the Girod Street walls. “An Eyesore in the Midst of Progress” The Post-World War II era brought huge changes to nearly every facet of American life. In the cemeteries, everything from materials to business models to the funeral industry transformed. In the American city, revolutionary ideas of urban renewal swept through downtowns, destroying historic districts and erecting aggressively modern new landscapes. In New Orleans this urban renewal took place with mayor deLesseps “Chep” Morrison, and it took place along Loyola Avenue, where historic buildings were swept away for a new library, city hall, and train depot. The intersection of Liberty and Girod Street, at the boundary of the cemetery, was awkward and could not adequately accommodate recently increased truck traffic volumes. By the late 1940s, even the federal government eyed the Girod Street property as a potential site for a new post office and federal building. In the light of rapidly encroaching superhighways and new urban landscapes, Girod Street Cemetery became even more anachronistic. Perceived as an affront to the bright future of the city’s civic heart, plans to renovate the cemetery fizzled into outright demolition by neglect, aided by the agenda of modern city leaders. Lack of care led to vandalism, which led to inevitable decries that the cemetery was too broken to be fixed. In June 1948, city workers arrived at Girod Street Cemetery and knocked enormous holes in the perimeter wall, hauling away five truckloads of bricks. After protests from Christ Church, Mayor Morrison simply responded that he didn’t realize there would be an objection.[12] In 1954, the City of New Orleans successfully expropriated more than twenty thousand square feet of the cemetery for the purposes of widening Liberty Street. In addition to this seizure of land, city council furthermore requested the mass removal of all remains from the cemetery entirely, and that they be removed to newly-finished Lake Lawn Park, a for-profit venture of the Stewart family.[13] Girod Cemetery is Calling Days after the announcement of the expropriation, city attorneys placed ads in newspaper enjoining any person with family buried in Girod Street to contact the City. Attempt to salvage burials, tombs, sculpture, and any other remaining resource of the cemetery were launched. Many of these reburials had already taken place in years previous by families who suspected the cemetery’s demise. In 1955, the remains, tomb, and monument of Lt. Col. William Wallace Smith Bliss was removed to namesake Fort Bliss in Texas. The Louisiana Landmarks Society led this effort, as it did other efforts to locate families associated with the cemetery. In June of 1955, the city officially purchased the cemetery. In January 1957, it was deconsecrated. Only months later, Louisiana Landmarks member and remarkable cemetery historian Leonard Victor Huber decried the demolition process at the cemetery: “Another 60 days and there will be nothing left of Girod Street cemetery but a memory. Tombs are being broken up… I was in a garden recently with its walls built of marble slabs from the cemetery.[14]” Through the course of demolition, remains of white descent were reinterred at Hope Mausoleum, owned by Leonard V. Huber. African American burials were removed to Providence Memorial Park. In October 1958, Christ Church sold 96,000 remaining square feet of the cemetery to the federal government for nearly $300,000. This sale would transform sections of the cemetery into a parking garage for a planned post office and federal building on Loyola Avenue. Said Frank Schneider of the Times-Picayune, “Girod became an eye sore in the midst of progress but now it will contribute something to New Orleans’ changing skyline. The 14-level post office structure will be the largest federal building in the Deep South.”[15] Learning from Girod Street Although certainly accelerated by ambitions of new urbanism, the issues that led to the demolition of Girod Street Cemetery are the same issues that regularly appear in discussions of historic cemetery management today. The power of the cemetery authority to manage abandoned tombs and lots is a topic of constant contention. Cemetery owning bodies today can write off issues of abandonment by appealing to private property rights, and nearly in the same breath demolish lots that become hazardous or inconvenient to redevelopment. The ability to be conveniently selective regarding Louisiana cemetery law has, in many cases, enabled neglect. This neglect, of course, contributes to cyclical issues of cemetery vandalism, which often goes unabated until conditions are perceived as unsalvageable. The sweeping demolitions that took place across the United States during the 1940s through the 1960s spawned a revitalization of the American historic preservation movement. Iconized by the demolition of Pennsylvania Station in New York in 1963, fatigue over the loss of entire historic districts led to the passing of the National Historic Preservation Act of 1966 which, among other things, would have likely prevented the Federal government from purchasing portions of Girod Street Cemetery. The tale of Girod Street Cemetery is comprised of much more than a haunted sports arena. For cemetery preservationists in New Orleans, it is a cautionary tale that should never be too far from one’s mind. The stunted successes and disappointing failures could easily revisit any of our burial grounds. [1] “New Orleans Grave Yards,” The Picayune, September 19, 1837, 2.
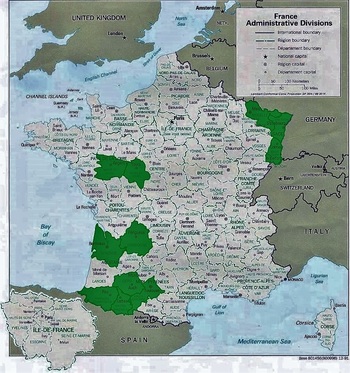
[2] Daily Picayune, August 21, 1885, 2. [3] Leonard Victor Huber and Guy F. Bernard, To Glorious Immortality: The Rise and Fall of Girod Street Cemetery, New Orleans’ First Protestant Cemetery, 1822-1957 (New Orleans: Ablen Books, 1961). [4] “New Orleans Grave Yards,” The Picayune, September 19, 1837, 2. [5] Louisiana State House of Representatives, Official Journal of the Proceedings of the House of Representatives of the State of Louisiana (New Orleans: The New Orleans Democrat Office, 1880), 285. [6] “The Crumbling World of Girod Cemetery,” Dixie: Times-Picayune States Roto Magazine, August 29, 1954, 6-7. [7] “Historic Cemetery Neglected,” Times-Picayune, June 23, 1945, 10. [8] “Old Cemetery to be Rebuilt,” Times-Picayune, December 21, 1947, 3. [9] “Threaten Razing of Vaults, Tombs, Fate of Old Cemetery to Rest with Lot Owners,” Times-Picayune, October 23, 1945; “Girod Cemetery Inspection Made,” Times-Picayune, October 30, 1945. [10] “Zulu Chief’s Wish to be Buried with Pomp and Ceremony Fulfilled,” Times-Picayune, August 23, 1948, 24. [11] “Old Cemetery to be Rebuilt,” Times-Picayune, December 21, 1947, 3. [12] “The Crumbling World of Girod Cemetery,” Dixie: Times-Picayune States Roto Magazine, August 29, 1954, 6-7. [13] “Girod Cemetery Strip is Sought,” Times-Picayune, November 12, 1954, 1. [14] “Up and Down the Street: Book on Girod Cemetery Needs Help,” Times-Picayune, August 15, 1957, 19. [15] “Old Burial Spot is Sold as Site for U.S. Garage,” Times Picayune, October 4, 1958, 11. This blog post is Part Two of a two-part piece on the tomb of the Sociètè Française de Bienfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Jefferson, located in Lafayette Cemetery No. 1. To learn about the history of this French Society, check out Part One here. Recently, Oak and Laurel Cemetery Preservation, LLC transcribed the burial records of the tomb of the Sociètè Française de Bienfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Jefferson, located in Lafayette Cemetery No. 2, thanks in part to a grant from genealogist Megan Smolenyak. The Society was absorbed by the Sociètè Française de Bienfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Nouvelle Orléans in 1900. About the Record Books The records of the Sociètè are housed at LSU Special Collections, Hill Memorial Library, in Baton Rouge. (MSS 318, 1012) The burial books appear to have been included with the larger collection of papers from the Sociètè Française de Bienfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Nouvelle Orléans (French Benevolent and Mutual Aid Society of New Orleans) which absorbed its Jefferson City counterpart in 1900. The collection is comprised of two books, dating from the tomb’s construction in 1872 through 1900. While later interments were certainly made in the Lafayette Cemetery No. 2 tomb, their record appears to have been incorporated into another, as-yet unstudied document. Within these two books are the burial documents for 186 individuals. Among these records, 142 people were buried in the society tomb in Lafayette Cemetery No. 2, 32 were provided formal burial aid by the society and were interred in family tombs throughout the city, and 12 were not specified as to burial location.[1] Each burial record documents the date and place of the individual’s birth, date and place of death, as well as cause of death and information regarding membership. These documents shed light on the lives of hundreds of people. They allude to intricate familial and professional relationships, personal tragedies, and public calamities. They offer a window into a rich community, the vestiges of which stand silent in this stately yet neglected tomb in Lafayette Cemetery No. 2. Today we share the stories of those buried within. The Foreign French: Founding Members and their Origins The Sociètè Française de Bienfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Jefferson was organized in 1868 by native-born French men – eight of whom are buried in the Lafayette No. 2 tomb. Much like the New Orleans French society, these immigrants sought fraternity among their countrymen. Incidentally (or perhaps not so much so), most of these men were born in the same French provinces (départments), and often in the same village. The majority of adults buried in the Sociètè tomb originated from two primary areas in continental France: the department now known as Midi-Pyrenees, including Gers, Haute-Pyrenees, Haute-Garonne, and Bass Pyrenees (now known as Pyrenees-Atlantiques), and the eastern departments of Alsace-Lorraine, specifically Haut-Rhin, Bas-Rhin, and Moselle. These two areas are nearly as geographically disparate as can be, with the former nestled along the Pyrenees mountains at the Spanish border, and the latter at the Rhine River beside present-day Germany.
In Alsace-Lorraine, a different climate motivated the eventual members of the Sociètè to emigrate from their homes. The Franco-Prussian War (1870-1871) forced many Alsatians from their homeland when the controls of the provinces shifted from France to newly-nationalized Germany. For French-speaking Alsatians, both Jewish and gentile, German citizenship was a less than desirable option. New Orleans was an attractive alternative due to its Francophone tradition. Among these Alsatian emigrants were sisters Catherine and Marie Sonntag, both in their early twenties from Altinstadt, Alsace. Nieces of Sociètè member O.M. Redon, they both died of yellow fever within weeks of each other in October 1872. They were buried in vaults 20 and 22 of the Lafayette No. 2 society tomb. While the people buried in this tomb overwhelmingly shared a linguistic and cultural bond, there is no shortage of strangers among the burials in Lafayette Cemetery No. 2. Although the tomb was built for French society members, those members were not always French. Strangers in a Strange Land: Non-French Buried in the French Tomb A handful of foreign-born non-French people were laid to rest in the Lafayette Cemetery No. 2 society tomb. Their stories contribute to the greater narrative of the society which at its heart was thoroughly New Orleanean in its cultural interactions. From Germany, Catherine Deffenback and brothers John and Jacob Schwenck were buried in this tomb at their time of death. The Schwenck brothers owned a saloon together on Magazine Street.[3] Leon Vignes, from Mont-de-Marrast, France, mourned the death of his Irish-born wife, Margaret, in 1884. She is buried in vault 35. Leon died fifteen years later and was buried in vault 38. He was not the only person to join the matrimonial melting pot: The wife of J.M. Gelé was born in England and died in 1872, buried in vault 26. Perhaps the most interesting foreign-born member of the society is not buried in the Lafayette No. 2 tomb but instead only blocks away in Lafayette Cemetery No. 1, although no tablet remains to mark his name. Louis Savini was born in 1830 in Mortara, Italy. By the time he was eleven years old, he and his family had taken residence in New Orleans. From the very scant documentation remaining, Savini appears to have led a colorful life. He owned a saloon in what is now the Central Business District on Common Street, near the Mississippi River.[4] For reasons unclear from available records, Savini joined the Sociètè Française de Bienfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Jefferson in 1874. Only months after joining the group, however, Savini was struck down by a “cerebral fever,” which could indicate encephalitis, meningitis, or scarlet fever. He died on June 1, 1874 in his home on Poydras Street. The Sociètè not only furnished his burial in Lafayette Cemetery No. 1, but also provided a procession befitting a French society member. Savini was buried in the tomb of his brother, Paul Savini, in Quadrant 2 of Lafayette Cemetery No. 1. Today, the tomb is in a state of dangerous neglect and has lost the closure tablet bearing Louis Savini’s name. As the Sociètè aged, its members increasingly were New Orleans natives. Over time, both the children of members and other Francophone Louisianans joined, advancing the process of assimilation in a new country. The Family Tomb At least one hundred and forty-two individuals are buried in the Sociètè Française de Bienfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Jefferson tomb in Lafayette Cemetery No. 2. Some were recent immigrants with little or no family left behind. For a striking number of society members, however, the tomb was the final resting place for multiple generations. It has already been noted that Leon and Margaret Vignes rest near each other in this tomb. They are also interred with their son, Joseph, who drowned at the age of 14 in 1891. He is interred in the same vault as his mother. The Fortassin family likely also utilized the society tomb for the interment of multiple generations. In 1870, twenty year-old Gabriel Fortassin, Jr., arrived in New Orleans from Trie, France. His parents joined him as well. In 1882, he married Alexandrine Claverotte.[5] The two would briefly move to San Antonio, Texas before returning to New Orleans. In his lifetime, Gabriel would bury his parents in the society tomb, as well as five of his infant children. When he died in 1927, he was given a French Society burial in Lafayette Cemetery No. 2.[6] One of Gabriel’s adult sons, Baptiste Fortassin was also buried in Lafayette Cemetery No. 2, in 1929. Two years later, Baptiste’s widow Marie Maille joined him. With no Fortassin tomb in Lafayette Cemetery No. 2, it is very likely they joined their relatives in this tomb, making it the last resting place of three generations of one family, with at least nine burials.[7] Other families utilized the society tomb similarly. Surnames such as Tujague[8], Abadie, Mouledous[9], Vignes, and Carrare appear multiple times through the burial books, representing multiple generations. These records also show combinations of the above-mentioned names, linked by intermarriage. Eleanor Vignes Tujague and Pauline Mouledous Tujague are both buried in the Lafayette Cemetery No. 2 society tomb. Society members formed a strong, interdependent community. They even stood at each other’s deathbeds to witness a last will and testament.[10] Death and burial were only the final threads that tied these French-speaking New Orleaneans together. In life, they lived and worked beside one another. As the French Society of Jefferson, members lived predominately within the boundaries of the former Jefferson suburb (portions of present-day Garden District, Irish Channel, Central City, and Uptown neighborhoods). Burial records note the residences of a multitude of members as near the St. Mary’s Market and along Tchoupitoulas Street. Even more records note residence as simply “aux abbatoirs,” or “near the slaughterhouses.” Which is no surprise: the majorit of members were butchers. A Workingman’s Society The Sociètè Française de Bienfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Jefferson shared members and celebrated social events with the Sociètè de Bienfaisance des Bouchers, or the French Butchers Society. Their enormous, eighty-vault society tomb remains also in Lafayette Cemetery No. 2. Members of each society lived near the Mississippi River, where cattle were unloaded at river docks. Until the late 1860s, the City of New Orleans had little regulation regarding the slaughter of livestock. Butchers were free to practice their trade where they pleased, usually near a market where they could sell their wares. This changed with a municipal law that required butchers slaughter livestock exclusively in a city-owned slaughterhouse, the goal of which was to prevent public health hazards.[11] Opposition to this law among butchers of both French societies led to civil unrest and years of legal battles. The case finally reached the Supreme Court in a landmark ruling known as the Slaughterhouse Case. Among the French and Butchers societies, the butcher’s trade was passed through generations and within a tight-knit community. Members lived in close proximity to each other, with addresses at Louisiana, Camp, Chippewa, Annunciation, Constance, Josephine, St. Mary, Tchoupitoulas, St. Andrew, Washington, Magazine, and Rousseau Streets. The propensity to take on the butcher’s trade among these society members is truly overwhelming. One casual cross reference of members’ names with an 1878 directory revealed nine butcher/members alive and working at the time: Gabriel Fortassin, Jr., Jean Abadie, Joseph Barrere, Pierre Lacaze, Bernard Lacoste, John William Lannes (Lannis), Pierre Sabatte, and Leon Vignes. The other three members searched, Victor Brisbois, Ulysses Mailhes, and Jacob Schwenck, were all listed as saloon owners or bartenders. Causes of Death If cursory research is to be trusted, the Sociètè Française de Bienfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Jefferson was populated by close friends who slaughtered animals and served alcohol for a living. When this living ended for each individual, however, the causes varied. It should be noted that 65 of the 142 burials (45%) in the Lafayette Cemetery No. 2 tomb were for children under six years of age. The Fortassin family, who buried five children in this tomb, were by no means unusual in their parental grief. Joseph Bararre and his wife Amanda Mailhes buried four children as well, all of whom were interred in vault 8. The high concentration of child burials in this tomb has a dual explanation. In addition to the well-understood status of childhood illness and mortality in the late nineteenth century, it was also much more likely for a family to bury a child in a society tomb than one built for a family. Married couples without their own family tomb were unlikely to purchase a lot for the burial of a child or stillborn infant. Instead, it was much more affordable to inter the child in a wall vault or society tomb, if available. Furthermore, the spiritual and emotional benefits of society-supported burial of a child were likely comforting. A significant percentage of the 65 infant/child burials were the stillborn or nonviable infants of society members. The other children of the Sociètè died of many common childhood maladies, including lockjaw (tetanus), cholera, croup, seizures, and whooping cough. Six children were listed as having died either of “bad teething” or a jaw ailment. In the nineteenth century, a range of many ailments was attributed to the process of teething in toddlers, including intestinal disease, seizures, meningitis, or even crib death. About half of the burial records in the Sociètè burial book list a cause of death. Among the adult members, most causes of death of typical of the time period: apoplexy, Bright’s disease, consumption (tuberculosis), and yellow fever. Surprisingly, only four burial certificates mark yellow fever as cause of death. This statistical anomaly may be explained by society members being buried hastily during times of epidemic, either in other tombs or too quickly to fill the burial form completely. “A Mort et Sans Espoir de Guerison” A few members, however, appear to have died in a slightly more unusual manner. Among them are:
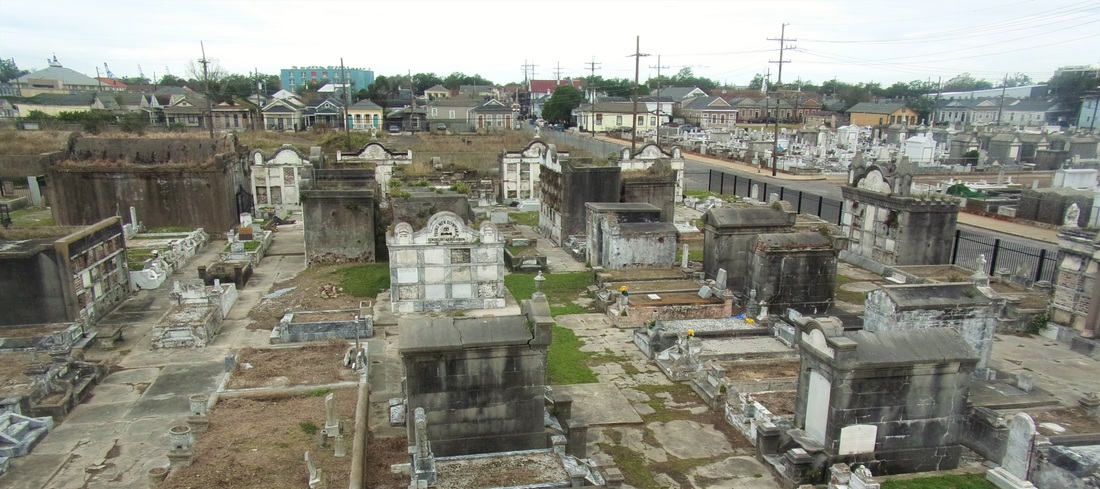
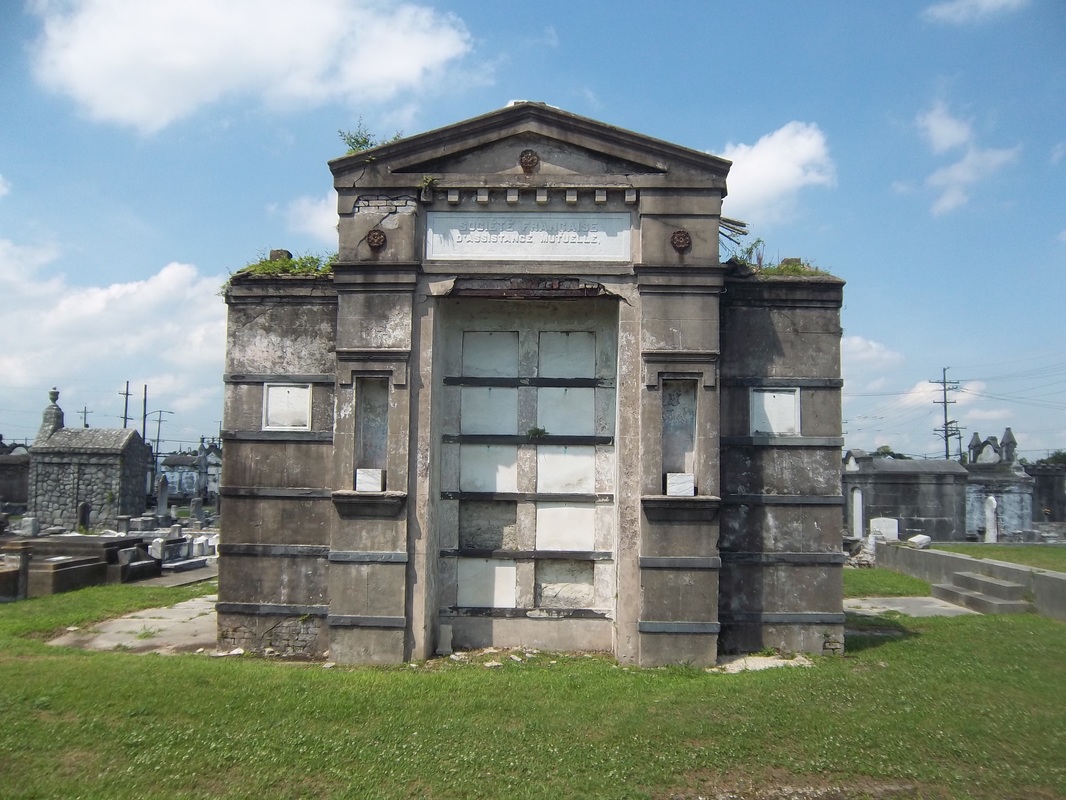
All of the above-listed men were members of the Sociètè who were buried in the Lafayette Cemetery No. 2 tomb alongside lost children, fellow butchers, and more than a few bartenders, as well as many wives, nieces, and grandchildren. A Community Buried Together Nearly all vestiges of Sociètè Française de Bienfaisance et d’Assistance Mutuelle de Jefferson have faded from popular memory. The tomb itself does not have a single carved name on any of its forty marble vault tablets. Yet within the decaying stucco vaults of this tomb in Lafayette Cemetery No. 2 are the relics of a great communal history that remains vitally significant to New Orleans cultural heritage. It is the hope that this research might connect the descendants of those buried in this tomb with their ancestors. The full burial rolls of interments into this tomb from 1872 to 1900 (up to the society’s merger with Sociètè Française d’Assistance Mutuelle de Nouvelle Orléans) have been uploaded to FindaGrave, in hopes their descendants may find them. The burial books are also available as an Excel Spreadsheet , MS Access Database, or PDF Document. Click here for burials listed by vault number. [1] Unless otherwise noted, all content is referenced directly from the original burial books as transcribed and documented by Oak and Laurel Cemetery Preservation, LLC. Links to these materials can be found at the end of this blog post.
[2] Arnold R. Hirsch and Joseph Logsdon, editors. Creole New Orleans: Race and Americanization (Baton Rouge: LSU Press, 1992), 112. [3] Edwards’ Annual Directory…in the City of New Orleans, for 1872 (New Orleans: Southern Publishing Company 1872), 366. [4] New Orleans City Directory 1870, 531. [5] State of Louisiana, Secretary of State, Division of Archives, Records Management, and History. Vital Records Indices. Baton Rouge, LA, USA. [6] Times-Picayune, August 28, 1927, 2. [7] Times-Picayune, January 18, 1929, 2; [8] To our knowledge, if this family is related to Guillaume Tujague, restauranteur, it is only distantly. [9] Alternately spelled Moledous, Mouledoux, etc. [10] Pierre Lacaze, also from Trie, witnessed Sylvain Tujague’s final will in 1882. Louisiana Will Book, Vol. 21 (1880-1883). [11] “City Litigation,” Morning Star and Catholic Messenger, May 30, 1869, 5. In this article regarding the Butchers’ filed injunction against the City, the author notes their injunction as “a string of reasons as clear and cutting as the keenest cleaver could demonstrate.” |
About the Author:Emily Ford owns and operates Oak and Laurel Cemetery Preservation, LLC. Archives
November 2019
Categories
All
|
- About
-
Restoration
- Services
-
Portfolio
>
- Turning Angel Statue, Natchez, MS
- Ledger Monument, Baton Rouge, LA
- Pyramid Statuary, New Orleans, LA
- Bronze and Granite Monument, Carville, LA
- Box Tomb, New Orleans, LA
- Vernacular Concrete Monument, Pensacola, FL
- 1830s Family Tomb, Covington, LA
- 1850s Family Tomb, New Orleans, LA
- 1880s Family Tomb, New Orleans, LA
- Headstone and Monument Restorations, Pensacola, FL
- Society Tomb, New Orleans, LA
- Education
- Blog
- Contact
|
Oak and Laurel Cemetery Preservation, LLC is a preservation contractor in New Orleans, Louisiana, specializing in historic cemeteries, stone conservation, educational workshops and lectures. Oak and Laurel serves the region of the Southeastern US.
|
QUICK LINKS |
CONNECT |
Proudly powered by Weebly